|
Maringá
Maringá () is a municipality in southern Brazil founded on 10 May 1947 as a planned urban area. It is the third largest city in the state of Paraná, with 385,753 inhabitants in the city proper, and 764,906 in the metropolitan area ( IBGE 2013). Located in northwestern Paraná, and crossed by the Tropic of Capricorn, it is a regional centre for commerce, services, agro-industries, and universities, including the State University of Maringá. History Toponymy Maringá takes its name from a song by Joubert de Carvalho in honour of his great love, Maria do Ingá, later shortened to Maringá. As a result, the city is nicknamed "Song City". At the time the settlement was established, the song was very popular in the media. Settlement In 1925, the Northern Paraná Land Company was established in London, England and was responsible for the management of more than in the northern part of the State, which today contains some of the largest cities in Paraná. The region's fertile land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maringá Regional Airport
Sílvio Name Júnior Regional Airport , is the airport serving Maringá, Brazil. It is named after Sílvio Name Júnior (1967-2000), a local businessman and politician who died in a plane crash. It is operated by Terminais Aéreos de Maringá – SBMG, a semi-independent Transportation Authority of Maringá, indirectly related to the Municipality of Maringá, and under the supervision of Aeroportos do Paraná (SEIL). History The airport serves an area composed of the city of Maringá and neighboring communities, with a total number of 2 million inhabitants. The new terminal was built between October, 1994 and September 16, 2000. It began operating on April 25, 2001. The airport is very modern and the runway of the airport is capable to handle major regional and domestic flights. Its terminal is designed to handle more than 430,000 passengers per year. The airport has service with over 120 parking places. Airlines and destinations Access The airport is located from downtown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State University Of Maringá
The State University of Maringá ( pt, Universidade Estadual de Maringá, UEM) is a public university whose main campus is in Maringá, Paraná, Brazil. It was founded in 1970 and recognized in 1976 by the Federal Government of Brazil. Its academic population is estimated in 18,000 people among professors, undergraduates, graduate students and manager technicals. UEM has 48 undergraduate courses and about 25 graduate programs. The university has 5 campuses in Maringá, Goioere, Cianorte, Cidade Gaúcha and Umuarama, all cities located in Paraná state. See also *Brazil University Rankings *Universities and Higher Education in Brazil Brazil adopts a mixed system of public and privately funded universities. Public universities can be federally funded or financed by State governments (such as USP, Unicamp and Unesp in the State of São Paulo). Private schools can be for-profit ... References External links Official website(in Portuguese) Maringá Educational instit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathedral Of Maringá
Catedral Basílica Menor Nossa Senhora da Glória (or simply Catedral de Maringá ''Cathedral of Maringá'') is a Roman Catholic cathedral located in downtown Maringá, Paraná, Brazil, reaching 124 m in height. It was completed in 1972 and is the tallest church building in the Americas and the 18th tallest in the world. Architect José Augusto Bellucci was inspired by the Soviet Sputnik satellites when he designed the cathedral's modernist, conical shape. The design was idealized by the archbishop Dom Jaime Luiz Coelho. The foundation stone, a piece of marble from St. Peter's Basilica in Rome , established_title = Founded , established_date = 753 BC , founder = King Romulus ( legendary) , image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg , map_caption ... blessed by Pope Pius XII, was laid on August 15, 1958. The church was built between July 1959 and May 10, 1972, the 25th anniversary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maringa 02 2016 1512 , known as "Maringa" in Sierra Leone
{{disambiguation ...
Maringa may refer to: * Maringa people, a sub-group of the Burarra Aboriginal Australian people * Maringá, a city in the state of Paraná in southern Brazil * Maringa River in the Democratic Republic of the Congo * Maringa-Lopori-Wamba Landscape, an ecologically sensitive area in the Democratic Republic of the Congo * Nova Maringá, a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso in the Central-West Region of Brazil * Grêmio de Esportes Maringá, a Brazilian soccer club from the city of Maringá * Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Maringá, an archdiocese located in the city of Maringá * Maringá Regional Airport, the airport serving Maringá, Brazil * Palm-wine music Palm-wine music (known as maringa in Sierra Leone) is a West African musical genre. It evolved among the Kru people of Liberia and Sierra Leone, who used Portuguese guitars brought by sailors, combining local melodies and rhythms with Trinidadia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraná (state)
Paraná () is one of the 26 states of Brazil, in the south of the country, bordered on the north by São Paulo state, on the east by the Atlantic Ocean, on the south by Santa Catarina state and the province of Misiones, Argentina, and on the west by Mato Grosso do Sul and Paraguay, with the Paraná River as its western boundary line. It is subdivided into 399 municipalities, and its capital is the city of Curitiba. Other major cities are Londrina, Maringá, Ponta Grossa, Cascavel, São José dos Pinhais and Foz do Iguaçu. The state is home to 5.4% of the Brazilian population and has 6.2% of the Brazilian GDP. Crossed by the Tropic of Capricorn, Paraná has what is left of the araucaria forest, one of the most important subtropical forests in the world. At the border with Argentina is the National Park of Iguaçu, considered by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. At only from there, at the border with Paraguay, the largest dam in the world was built, the Hidroelétri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropic Of Capricorn
The Tropic of Capricorn (or the Southern Tropic) is the circle of latitude that contains the subsolar point at the December (or southern) solstice. It is thus the southernmost latitude where the Sun can be seen directly overhead. It also reaches 90 degrees below the horizon at solar midnight on the June Solstice. Its northern equivalent is the Tropic of Cancer. The Tropic of Capricorn is one of the five major circles of latitude marked on maps of Earth. Its latitude is currently south of the Equator, but it is very gradually moving northward, currently at the rate of 0.47 arcseconds, or 15 metres, per year. Less than 3% of the world's population lives south of it; this is equivalent to about 30% of the population of the Southern Hemisphere. Name When this line of latitude was named in the last centuries BC, the Sun was in the constellation Capricornus at the December solstice. This is the date each year when the Sun reaches zenith at this latitude, the southernmost lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Region, Brazil
The South Region of Brazil (; ) is one of the five regions of Brazil. It includes the states of Paraná, Rio Grande do Sul, and Santa Catarina, and covers , being the smallest region of the country, occupying only about 6.76% of the territory of Brazil. Its whole area is smaller than that of the state of Minas Gerais, in Southeast Brazil, for example. It is a tourist, economic and cultural pole. It borders Uruguay, Argentina, and Paraguay, as well as the Centre-West and Southeast regions, and the Atlantic Ocean. The region is considered the safest in Brazil to visit, having a lower crime rate than other regions in the country. History Pre-Columbian history By the time the first European explorers arrived, all parts of the territory were inhabited by semi- nomadic hunter-gatherer native tribes. They subsisted on a combination of hunting, fishing, and gathering. Portuguese colonization European colonization in Southern Brazil started with the arrival of Portuguese an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
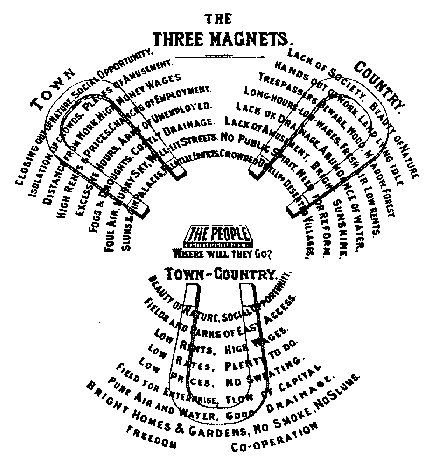
Garden City Movement
The garden city movement was a 20th century urban planning movement promoting satellite communities surrounding the central city and separated with greenbelts. These Garden Cities would contain proportionate areas of residences, industry, and agriculture. Ebenezer Howard first posited the idea in 1898 as a way to capture the primary benefits of the countryside and the city while avoiding the disadvantages presented by both. In the early 20th century, Letchworth, Brentham Garden Suburb and Welwyn Garden City were built in or near London according to Howard's concept and many other garden cities inspired by his model have since been built all over the world. History Conception Inspired by the utopian novel '' Looking Backward'' and Henry George's work '' Progress and Poverty'', Howard published the book '': a Peaceful Path to Real Reform'' in 1898 (which was reissued in 1902 as '' Garden Cities of To-morrow''). His idealised garden city would house 32,000 people on a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Brazil
Brazil is geopolitics, geopolitically divided into five regions (also called macroregions), by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, which are formed by the federative units of Brazil. Although officially recognized, the division is merely academic, considering geographic, social and economic factors, among others, and has no political effects other than orientating Federal-level government programs. Under the state level, there are also mesoregions of Brazil, mesoregions and microregions of Brazil, microregions. The five regions North Region *Area: 3,689,637.9 km2 (45.27%) *Population: 17,707,783 (4,6 people/km2; 6.2%; 2016) *Gross domestic product, GDP: Brazilian real, R$ 308 billion / United States dollar, US$94,8 billion (2016; 4.7%) (Economy of Brazil, 5th) *Climate: Equatorial *States: Acre (state), Acre, Amapá, Amazonas (Brazilian state), Amazonas, Pará, Rondônia, Roraima, Tocantins (state), Tocantins *Largest Cities: Manaus (2,094,391); Bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capela Madre Paulina - IMG 0630
Capela may refer to: Places *Capela (Penafiel), a parish in Penafiel Municipality, Portugal * Capela, Sergipe, a municipality in the Brazilian state of Sergipe * Capela, Alagoas, a municipality in the Brazilian state of Alagoas * Capela, Râmnicu Vâlcea, a neighborhood in Râmnicu Vâlcea * Capela Hill, a hill in the western part of the Romanian town of Râmnicu Vâlcea *A Capela, a place in Galicia, Spain *Capelas, a civil parish on the island of São Miguel in the Portuguese Azores. People *Aníbal Capela, a Portuguese professional footballer *Clint Capela, Swiss professional basketball player (NBA, Europe) *Manuel Capela, a Portuguese footballer who played as goalkeeper *Capela (footballer) (Fernando Jorge Barbosa Martins, born 1986), Portuguese football midfielder Music *Mestre de capela *Capela Real, Lisbon *Capela Real do Rio de Janeiro, 1808 See also *Kapela (other) *Cappella (other) *Capella (other) Capella is a bright star in the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipe Amarelo Uem
Ipe or IPE can refer to: * Isopropyl ether, a chemical solvent, usually in the form of DIPE (diisopropyl ether) * Icosapent ethyl, that is, ethyl eicosapentaenoic acid, an omega-3 lipid formulation * ''L’Institut pour I’Expertise'' (IPE), that is, IPE Management School Paris, a private higher education institution in Paris, France * International political economy, an academic discipline * Ipê, trees in the genus ''Handroanthus'' and their wood * Ipe (software), an extensible drawing editor * Innotech Performance Exhaust (iPE), a manufacturer of exhaust system and wheels in Taiwan. * Institute of Public Enterprise in India * Integrity Policy Enforcement, a Linux Security Module (LSM) that enables additional security features * International Petroleum Exchange (old name), that is, Intercontinental Exchange Futures (ICE Futures), a futures and options exchange * International Petroleum Exposition, a former trade fair held periodically in Oklahoma from 1923 to 1979 * Interprof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
By Robertoserviço - Panoramio - Robertografiteiro (4)
{{disambiguation, geo ...
By or BY may refer to: Places * By, Doubs, France, a commune * By, Norway, a village Codes * Belarus ISO country code ** .by, country-code top-level domain for Belarus * Burundi FIPS Pub 10-4 and obsolete NATO digram country code * TUI Airways IATA airline code, formerly Thomson Airways, Thomsonfly and Britannia Airways Other uses * John By (1779–1836), British military engineer famous for his work in Canada * CC-BY, a Creative Commons attribution license * Budget year, a synonym for fiscal year See also * -by, a common suffix for settlements in northern England *Bye (other) Bye may refer to: * BYE, UNDP county code for Belarus *Bye (cricket), a special type of run scored in the game of cricket * Bye (sports), when a player or team is allowed to advance to the next round of a playoff tournament without playing * Bye ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |