|
Maria (Ukrainian Novel)
''Maria'' is a 1934 historical novel by the Ukrainian author Ulas Samchuk. The novel, dedicated "to the mothers who died of hunger in Ukraine in 1932-33", follows the life of a village woman, Maria, between the 1861 emancipation of serfs to the 1932-33 Holodomor. ''Maria'', the first work of fiction to treat the Ukrainian famine, has been included in post-1991 Ukrainian school curricula. The book is organised into three parts: A Book about the Birth of Maria, A Book of Maria's Days, and A Book about Bread. Orphaned at the age of six, Maria is illiterate and forced into work when young. Her first three children die of infectious disease. Her son Maksym, before his murder by his father, is a poor farmer who evicts his parents, denounces his brother, and watches his sister starve. Maksym "combines many features of the Holodomor perpetrator: a quisling, communist, profiteer, sadist and Russian-speaking". Behind Maksym, as the 'Other' bearing ultimate responsibility for the famine, lies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulas Samchuk
Ulas Oleksiiovych Samchuk (; 20 February 1905, Derman – 9 July 1987 Toronto) was a Ukrainian writer, propagandist, publicist, journalist, and a member of the Government of the Ukrainian People's Republic in exile. He was a member of the nationalistic Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists, a Nazi collaborator, and noted antisemite. Biography Samchuk was born on 20 February 1905, in the village of . From 1917 to 1920 he studied at a four-grade elementary school in Derman. In 1921–1925 he studied at the Kremenets Ukrainian private gymnasium. Before he finished his secondary education, he was called up for service in the Polish Army in 1927, and later deserted in August of that year, escaping to Germany. In Germany he worked delivering coal, and with the help of a supportive German family, Samchuk continued his studies at the University of Breslau. In 1929, Samchuk moved to Prague, Czechoslovakia. He was attracted by the city's vibrant Ukrainian community and the Ukraini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emancipation Reform Of 1861
The emancipation reform of 1861 in Russia, also known as the Edict of Emancipation of Russia, (russian: Крестьянская реформа 1861 года, translit=Krestyanskaya reforma 1861 goda – "peasants' reform of 1861") was the first and most important of the liberal reforms enacted during the reign (1855–1881) of Emperor Alexander II of Russia. The reform effectively abolished serfdom throughout the Russian Empire. The 1861 Emancipation Manifesto proclaimed the emancipation of the serfs on private estates and of the domestic (household) serfs. By this edict more than 23 million people received their liberty.Mee, Arthur; Hammerton, J.A.; Innes, Arthur D.; Harmsworth History of the World: Volume 7', 1907, Carmelite House, London; p. 5193. Serfs gained the full rights of free citizens, including rights to marry without having to gain consent, to own property and to own a business. The Manifesto prescribed that peasants would be able to buy the land from the landlords ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
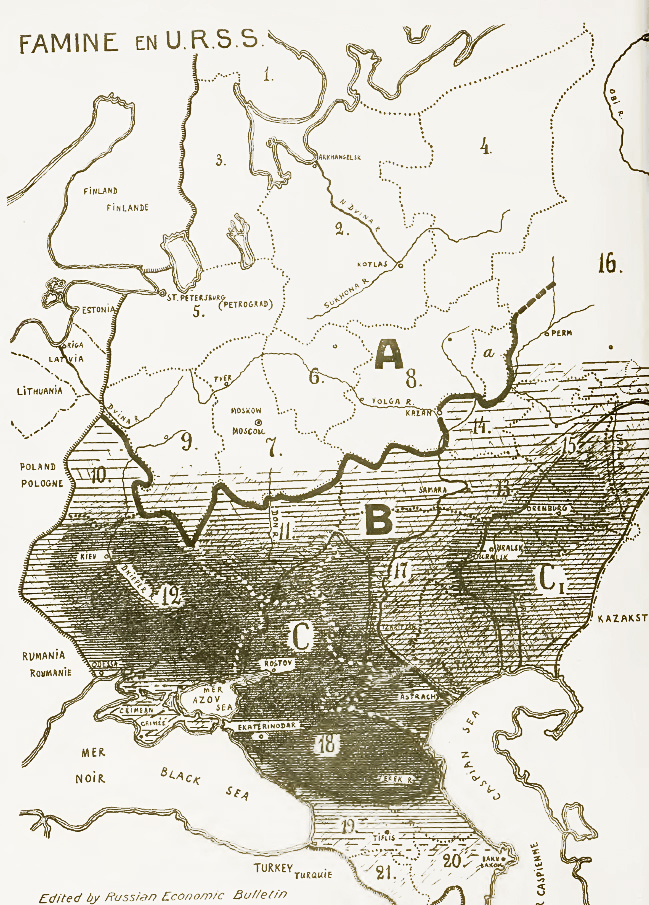
Holodomor
The Holodomor ( uk, Голодомо́р, Holodomor, ; derived from uk, морити голодом, lit=to kill by starvation, translit=moryty holodom, label=none), also known as the Terror-Famine or the Great Famine, was a man-made famine in Soviet Ukraine from 1932 to 1933 that killed millions of Ukrainians. The Holodomor was part of the wider Soviet famine of 1932–1933 which affected the major grain-producing areas of the Soviet Union. While scholars universally agree that the cause of the famine was man-made, whether the Holodomor constitutes a genocide remains in dispute. Some historians conclude that the famine was planned and exacerbated by Joseph Stalin in order to eliminate a Ukrainian independence movement. This conclusion is supported by Raphael Lemkin. Others suggest that the famine arose because of rapid Soviet industrialisation and collectivization of agriculture. Ukraine was one of the largest grain-producing states in the USSR and was subject to unre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Other (philosophy)
In phenomenology, the terms the Other and the Constitutive Other identify the other human being, in their differences from the Self, as being a cumulative, constituting factor in the self-image of a person; as acknowledgement of being real; hence, the Other is dissimilar to and the opposite of the Self, of Us, and of the Same.''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'' (1995) p. 637. The Constitutive Other is the relation between the personality (essential nature) and the person (body) of a human being; the relation of essential and superficial characteristics of personal identity that corresponds to the relationship between opposite, but correlative, characteristics of the Self, because the difference is inner-difference, within the Self. The condition and quality of Otherness (the characteristics of the Other) is the state of being different from and alien to the social identity of a person and to the identity of the Self. In the discourse of philosophy, the term Otherness iden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev ( Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow grew to become a prosperous and powerful city that served as the capital of the Grand Duchy that bears its name. When the Grand Duchy of Moscow evolved into the Tsardom of Russia, Moscow remained the political and economic center for most of the Tsardom's history. When th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1934 Novels
Events January–February * January 1 – The International Telecommunication Union, a specialist agency of the League of Nations, is established. * January 15 – The 8.0 Nepal–Bihar earthquake strikes Nepal and Bihar with a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''), killing an estimated 6,000–10,700 people. * January 26 – A 10-year German–Polish declaration of non-aggression is signed by Nazi Germany and the Second Polish Republic. * January 30 ** In Nazi Germany, the political power of federal states such as Prussia is substantially abolished, by the "Law on the Reconstruction of the Reich" (''Gesetz über den Neuaufbau des Reiches''). ** Franklin D. Roosevelt, President of the United States, signs the Gold Reserve Act: all gold held in the Federal Reserve is to be surrendered to the United States Department of the Treasury; immediately following, the President raises the statutory gold price from US$20.67 per ounce to $35. * February 6 – French pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Novels
Ukrainian may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to Ukraine * Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe * Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine * Something relating to Ukrainian culture * Ukrainian language, an East Slavic language, the native language of Ukrainians and the official state language of Ukraine * Ukrainian alphabet, a Ukrainian form of Cyrillic alphabet * Ukrainian cuisine See also * Languages of Ukraine * Name of Ukraine * Ukrainian Orthodox Church (other) * Ukrainians (other) * Ukraine (other) * Ukraina (other) * Ukrainia (other) Ukrainia may refer to: * The land of Ukraine, the land of the Kievan Rus * The land of the Ukrainians, an ethnic territory * Montreal ''Ukrainia'', a sports team in Canada * Toronto ''Ukrainia'', a sports team in Canada See also * * Ukraina ... * {{disambiguation Language and nationality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |