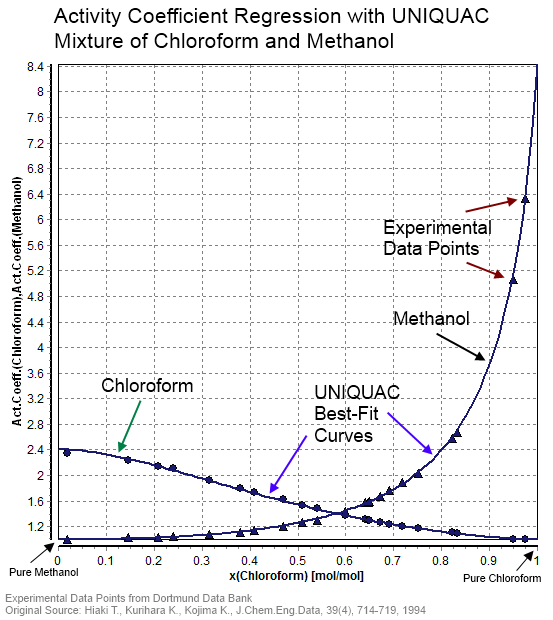
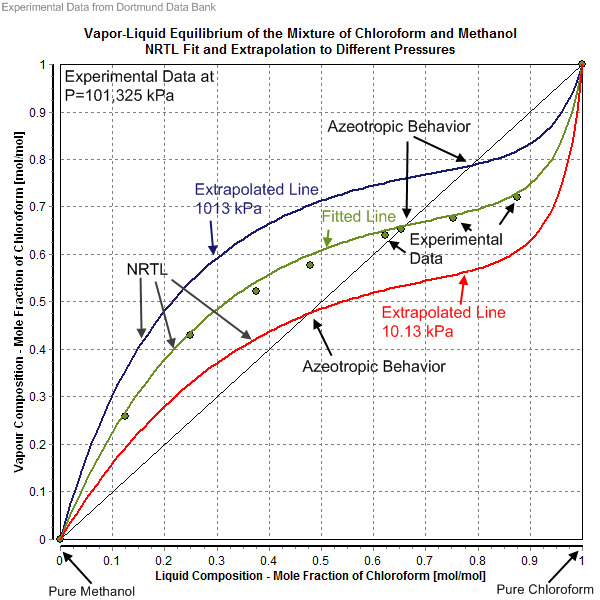
|
Margules Function
The Margules activity model is a simple thermodynamic model for the excess Gibbs free energy of a liquid mixture introduced in 1895 by Max Margules. After Lewis had introduced the concept of the activity coefficient, the model could be used to derive an expression for the activity coefficients \gamma_i of a compound i in a liquid, a measure for the deviation from ideal solubility, also known as Raoult's law. In chemical engineering the Margules Gibbs free energy model for liquid mixtures is better known as the Margules activity or activity coefficient model. Although the model is old it has the characteristic feature to describe extrema in the activity coefficient, which modern models like NRTL and Wilson cannot. Equations Excess Gibbs free energy Margules expressed the intensive excess Gibbs free energy of a binary liquid mixture as a power series of the mole fractions xi: : \frac=X_1 X_2 (A_ X_1 +A_ X_2) + X_1^2 X_2^2 (B_X_1+ B_ X_2) + ... + X_1^m X_2^m (M_X_1+ M_ X_2) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibbs Free Energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy (or Gibbs energy; symbol G) is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum amount of work (physics), work that may be performed by a closed system, thermodynamically closed system at constant temperature and pressure. It also provides a necessary condition for processes such as Chemical reaction, chemical reactions that may occur under these conditions. The Gibbs free energy change , measured in joules in International System of Units, SI) is the ''maximum'' amount of non-expansion work that can be extracted from a closed system (one that can exchange heat and work with its surroundings, but not matter) at fixed temperature and pressure. This maximum can be attained only in a completely reversible process (thermodynamics), reversible process. When a system transforms reversibly from an initial state to a final state under these conditions, the decrease in Gibbs free energy equals the work done by the system to its s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Margules
Max Margules (1856-1920) was a mathematician, physicist, and chemist. In 1877 he joined the Central Institute of Meteorology and Geodynamics (ZAMG) in Vienna as a volunteer. After two years he left Vienna to study in Berlin for a year. He returned to Vienna and received his PhD in Electrodynamics. During his doctoral studies he was a : an unpaid position, but one which allowed him to lecture students. Students' fees gave him some income. Later, administration offered this teaching job to someone else after he refused to convert from Judaism to acquire the position, which ended his academic career. In 1882 he returned to ZAMG. Durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activity Coefficient
In thermodynamics, an activity coefficient is a factor used to account for deviation of a mixture of chemical substances from ideal behaviour. In an ideal mixture, the microscopic interactions between each pair of chemical species are the same (or macroscopically equivalent, the enthalpy change of solution and volume variation in mixing is zero) and, as a result, properties of the mixtures can be expressed directly in terms of simple concentrations or partial pressures of the substances present e.g. Raoult's law. Deviations from ideality are accommodated by modifying the concentration by an ''activity coefficient''. Analogously, expressions involving gases can be adjusted for non-ideality by scaling partial pressures by a fugacity coefficient. The concept of activity coefficient is closely linked to that of activity in chemistry. Thermodynamic definition The chemical potential, \mu_\mathrm, of a substance B in an ideal mixture of liquids or an ideal solution is given by :\mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-Random Two Liquid Model
The non-random two-liquid model (abbreviated NRTL model) is an activity coefficient model that correlates the activity coefficients \gamma_i of a compound with its mole fractions x_i in the liquid phase concerned. It is frequently applied in the field of chemical engineering to calculate phase equilibria. The concept of NRTL is based on the hypothesis of Wilson that the local concentration around a molecule is different from the bulk concentration. This difference is due to a difference between the interaction energy of the central molecule with the molecules of its own kind U_ and that with the molecules of the other kind U_. The energy difference also introduces a non-randomness at the local molecular level. The NRTL model belongs to the so-called local-composition models. Other models of this type are the Wilson model, the UNIQUAC model, and the group contribution model UNIFAC. These local-composition models are not thermodynamically consistent for a one-fluid model for a real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grant M
Grant or Grants may refer to: Places *Grant County (other) Australia * Grant, Queensland, a locality in the Barcaldine Region, Queensland, Australia United Kingdom *Castle Grant United States * Grant, Alabama *Grant, Inyo County, California * Grant, Colorado *Grant-Valkaria, Florida *Grant, Iowa *Grant, Michigan * Grant, Minnesota *Grant, Nebraska * Grant, Ohio, an unincorporated community *Grant, Washington *Grant, Wisconsin (other) (six towns) * Grant City, Indiana *Grant City, Missouri *Grant City, Staten Island *Grant Lake (other), several lakes * Grant Park, Illinois *Grant Park (Chicago) *Grant Town, West Virginia *Grant Township (other) (100 townships in 12 states) *Grant Village in Yellowstone National Park *Grants, New Mexico *Grants Pass, Oregon * U.S. Grant Bridge over Ohio River and Scioto River *General Grant National Memorial aka Grant's Tomb India *Jolly Grant Airport Dehradun, Uttarakhand Canada *Rural Municipality of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibbs–Duhem Equation
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs–Duhem equation describes the relationship between changes in chemical potential for components in a thermodynamic system: :\sum_^I N_i \mathrm\mu_i = - S \mathrmT + V \mathrmp where N_i is the number of moles of component i, \mathrm\mu_i the infinitesimal increase in chemical potential for this component, S the entropy, T the absolute temperature, V volume and p the pressure. I is the number of different components in the system. This equation shows that in thermodynamics intensive properties are not independent but related, making it a mathematical statement of the state postulate. When pressure and temperature are variable, only I-1 of I components have independent values for chemical potential and Gibbs' phase rule follows. The Gibbs−Duhem equation cannot be used for small thermodynamic systems due to the influence of surface effects and other microscopic phenomena. The equation is named after Josiah Willard Gibbs and Pierre Duhem. Derivatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chem Eng Sci
''Chemical Engineering Science'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of chemical engineering. It is published by Elsevier and was established in 1951. The editor-in-chief is A.P.J. Middelberg (University of Queensland). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2019 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 3.871. References External links * Chemical engineering journals Elsevier academic journals Publications established in 1951 Semi-monthly journals English-language journals {{engineering-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Laar Equation
The Van Laar equation is a thermodynamic activity model, which was developed by Johannes van Laar in 1910-1913, to describe phase equilibria of liquid mixtures. The equation was derived from the Van der Waals equation. The original van der Waals parameters didn't give good description of vapor-liquid equilibria of phases, which forced the user to fit the parameters to experimental results. Because of this, the model lost the connection to molecular properties, and therefore it has to be regarded as an empirical model to correlate experimental results. Equations Van Laar derived the excess enthalpy from the van der Waals equation: : H^= \frac \left( \frac- \frac \right)^2 In here ''a''i and ''b''i are the van der Waals parameters for attraction and excluded volume of component i. He used the conventional quadratic mixing rule for the energy parameter ''a'' and the linear mixing rule for the size parameter ''b.'' Since these parameters didn't lead to good phase equilibrium de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Chemistry
Physical chemistry is the study of macroscopic and microscopic phenomena in chemical systems in terms of the principles, practices, and concepts of physics such as motion, energy, force, time, thermodynamics, quantum chemistry, statistical mechanics, analytical dynamics and chemical equilibria. Physical chemistry, in contrast to chemical physics, is predominantly (but not always) a supra-molecular science, as the majority of the principles on which it was founded relate to the bulk rather than the molecular or atomic structure alone (for example, chemical equilibrium and colloids). Some of the relationships that physical chemistry strives to resolve include the effects of: # Intermolecular forces that act upon the physical properties of materials ( plasticity, tensile strength, surface tension in liquids). # Reaction kinetics on the rate of a reaction. # The identity of ions and the electrical conductivity of materials. # Surface science and electrochemistry of cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |