|
Margaret Nicholson
Margaret Nicholson (c. 1750 – 14 May 1828) was an Englishwoman who assaulted King George III in 1786. Her futile and somewhat half-hearted attempt on the King's life became famous and was featured in one of Shelley's first works: '' Posthumous Fragments of Margaret Nicholson'', published in 1810. Life Nicholson was born in Stockton-on-Tees in County Durham to a barber called George Nicholson. At the age of 12, she was found a place as a maid, and from then worked as a servant in various notable households, including those of Sir John Sebright and Lord Coventry. She showed no sign of mental illness. Before 1783, she was dismissed from her employment after a love affair with a fellow servant, and she seemed to fall on hard times. Her lover left her, and she supported herself through needlework, lodging in a house in Wigmore Street.''The Times'', Friday, 11 August 1786, p. 3, col. A She was described as "below the middle size, and of a very swarthy complexion".''The Times'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret Nicholson Attempting To Assassinate His Majesty King George III' (Margaret Nicholson; King George III) By Carington Bowles
Margaret is a female first name, derived via French () and Latin () from grc, μαργαρίτης () meaning "pearl". The Greek is borrowed from Persian. Margaret has been an English name since the 11th century, and remained popular throughout the Middle Ages. It became less popular between the 16th century and 18th century, but became more common again after this period, becoming the second-most popular female name in the United States in 1903. Since this time, it has become less common, but was still the ninth-most common name for women of all ages in the United States as of the 1990 census. Margaret has many diminutive forms in many different languages, including Maggie, Madge, Daisy, Margarete, Marge, Margo, Margie, Marjorie, Meg, Megan, Rita, Greta, Gretchen, and Peggy. Name variants Full name * (Irish) * (Irish) * (Dutch), (German), (Swedish) * (English) Diminutives * (English) * (English) First half * ( French) * (Welsh) Second half * (English), (Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Townshend, 1st Viscount Sydney
Thomas Townshend, 1st Viscount Sydney (24 February 1733 – 30 June 1800) was a British politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1754 to 1783 when he was raised to the peerage as Baron Sydney. He held several important Cabinet posts in the second half of the 18th century. The cities of Sydney in Nova Scotia, Canada, and Sydney in New South Wales, Australia were named in his honour, in 1785 and 1788, respectively. Background and education Townshend was born at Raynham, Norfolk, the son of the Hon. Thomas Townshend, who was the second son of Charles Townshend, 2nd Viscount Townshend, also known as "Turnip" Townshend for his agricultural innovations. Thomas Townshend the younger's mother was Albinia, daughter of John Selwyn. He was educated at Clare College, Cambridge. Political career Townshend was elected to the House of Commons in 1754 as Whig member for Whitchurch in Hampshire, and held that seat till his elevation to the peerage in 1783. He initially aligned himsel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Jefferson Hogg
Thomas Jefferson Hogg (24 May 1792 – 27 August 1862) was a British barrister and writer best known for his friendship with the Romantic poetry, Romantic poet Percy Bysshe Shelley. Hogg was raised in County Durham, but spent most of his life in London. He and Shelley became friends while studying at University College, Oxford, and remained close until Shelley's death. During their time at Oxford they collaborated on several literary projects, culminating in their joint expulsion following the publication of an essay titled "The Necessity of Atheism". They remained good friends, but their relationship was sometimes strained because of Hogg's attraction to the women who were romantically involved with Shelley. Hogg became a barristers in England and Wales, barrister and met Jane Williams, who had become a close friend of Percy Shelley's shortly before the poet's death. Jane became Hogg's Common-law marriage, common-law wife and they had two children together. The family s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JAMA (journal)
''The Journal of the American Medical Association'' (''JAMA'') is a peer-reviewed medical journal published 48 times a year by the American Medical Association. It publishes original research, reviews, and editorials covering all aspects of biomedicine. The journal was established in 1883 with Nathan Smith Davis as the founding editor. Kirsten Bibbins-Domingo of the University of California San Francisco became the journal editor-in-chief on July 1, 2022, succeeding Howard Bauchner of Boston University. History The journal was established in 1883 by the American Medical Association and superseded the ''Transactions of the American Medical Association''. ''Councilor's Bulletin'' was renamed the ''Bulletin of the American Medical Association'', which later was absorbed by the ''Journal of the American Medical Association''. In 1960, the journal obtained its current title, ''JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association''. The journal is commonly referred to as ''JAMA''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bethlem Royal Hospital
Bethlem Royal Hospital, also known as St Mary Bethlehem, Bethlehem Hospital and Bedlam, is a psychiatric hospital in London. Its famous history has inspired several horror books, films and TV series, most notably '' Bedlam'', a 1946 film with Boris Karloff. The hospital is closely associated with King's College London and, in partnership with the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neuroscience, is a major centre for psychiatric research. It is part of the King's Health Partners academic health science centre and the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre for Mental Health. Founded in 1247, the hospital was originally near Bishopsgate just outside the walls of the City of London. It moved a short distance to Moorfields in 1676, and then to St George's Fields in Southwark in 1815, before moving to its current location in Monks Orchard in 1930. The word " bedlam", meaning uproar and confusion, is derived from the hospital's nickn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
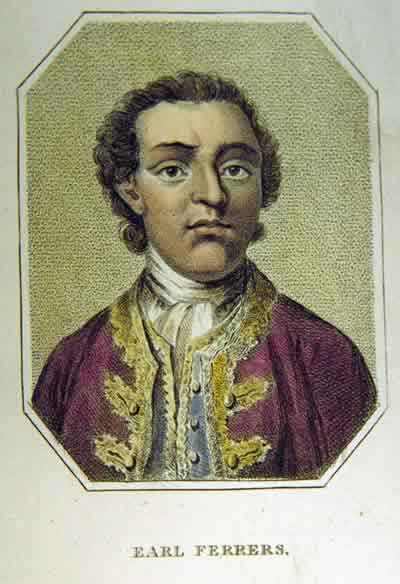
Laurence Shirley, 4th Earl Ferrers
Laurence Shirley, 4th Earl Ferrers (18 August 1720 – 5 May 1760) was an English nobleman, notable for being the last peer to be hanged, following his conviction for murdering his steward. Biography Shirley was the eldest son of Laurence Ferrers, himself the third son of the first Earl Ferrers. At the age of twenty, he quit his estates and Oxford University education, and began living a debauched life in France in Paris. At the age of 25 he inherited his title from his insane uncle the 3rd Earl Ferrers, and with it estates in Leicestershire, Derbyshire and Northamptonshire. He lived at Staunton Harold Hall in northwest Leicestershire. In 1752, he married Mary, the youngest sister of Sir William Meredith, 3rd Baronet. Ferrers was also a cousin to Selina, Countess of Huntingdon, the prominent Methodist lady and supporter of George Whitefield, though he was not involved in the Methodist revival. Marriage troubles Ferrers had a family history of insanity, and from an ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monro Family (physicians)
The Monro of Fyrish family were a Scottish family and branch of the ancient highland Clan Munro. The family produced a notable dynasty of doctors to London in the 18th and 19th century where they were involved in early work on curing 'insanity'. Four generations occupied successively the position of (Principal) Physician of the notorious Bethlem Hospital (Bedlam). They were also leading members of a variety of important medical associations. Other members were painters, priests and philanthropists of note and one was an important early patron to J. M. W. Turner. Early family history Hector Munro, 1st of Fyrish was the second son of Robert Munro, 14th Baron of Foulis (d.1547), chief of the Scottish clan, Clan Munro. Hector Munro received as his patrimony the lands of Fyrish, Contullich and Kildermorie in the parish of Alness. He had four sons and one daughter: # William Munro, 2nd of Fyrish. #John Munro, 3rd of Fyrish. #George Munro, who fought in the Thirty Years' War on the Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantua (clothing)
A mantua (from the French or "mantle") is an article of women's clothing worn in the late 17th century and 18th century. Originally a loose gown, the later mantua was an overgown or robe typically worn over stays, stomacher and a co-ordinating petticoat. The mantua or was a new fashion that arose in the 1670s. Instead of a bodice and skirt cut separately, the mantua hung from the shoulders to the floor (in the manner of dresses of earlier periods) started off as the female version of the men's banyan, worn for 'undress' wear. Gradually it developed into a draped and pleated dress and eventually evolved into a dress worn looped and draped up over a contrasting petticoat and a stomacher. The mantua-and-stomacher resulted in a high, square neckline in contrast to the broad, off-the-shoulder neckline previously in fashion. The new look was both more modest and covered-up than previous fashions and decidedly fussy, with bows, frills, ribbons, and other trim, but the short string of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stationer
Stationery refers to commercially manufactured writing materials, including cut paper, envelopes, writing implements, continuous form paper, and other office supplies. Stationery includes materials to be written on by hand (e.g., letter paper) or by equipment such as computer printers. History of stationery Originally, the term 'stationery' referred to all products sold by a stationer, whose name indicated that his book shop was on a fixed spot. This was usually somewhere near a university, and permanent, while medieval trading was mainly carried on by itinerant peddlers (including chapmen, who sold books) and others (such as farmers and craftsmen) at markets and fairs. It was a unique term used between the 13th and 15th centuries in the manuscript culture. Stationers' shops were places where books were bound, copied, and published. These shops often loaned books to nearby university students for a fee. The books were loaned out in sections, allowing students to study or copy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Wedderburn, 1st Earl Of Rosslyn
Alexander Wedderburn, 1st Earl of Rosslyn, PC, KC (3 February 1733 – 2 January 1805) was a Scottish lawyer and politician who sat in the House of Commons between 1761 and 1780 when he was raised to the peerage as Baron Loughborough. He served as Lord High Chancellor of Great Britain from 1793 to 1801. Life Wedderburn was the eldest son of Peter Wedderburn, Lord Chesterhall (a lord of session), and was born in East Lothian. He received his basic education at Dalkeith and at the Royal High School, Edinburgh, and matriculated at the University of Edinburgh aged 14. Though he wanted to practise at the English bar, in deference to his father's wishes he qualified as an advocate at Edinburgh, in 1754. His father was called to the bench in 1755, and for the next three years Wedderburn stuck to his practice in Edinburgh, when he employed his oratorical powers in the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland, and passed his evenings in social and argumentative clubs. In 1755 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Murray, 1st Earl Of Mansfield
William Murray, 1st Earl of Mansfield, PC, SL (2 March 170520 March 1793) was a British barrister, politician and judge noted for his reform of English law. Born to Scottish nobility, he was educated in Perth, Scotland, before moving to London at the age of 13 to take up a place at Westminster School. He was accepted into Christ Church, Oxford, in May 1723, and graduated four years later. Returning to London from Oxford, he was called to the Bar by Lincoln's Inn on 23 November 1730, and quickly gained a reputation as an excellent barrister. He became involved in politics in 1742, beginning with his election as a Member of Parliament for Boroughbridge, now in North Yorkshire, and appointment as Solicitor General. In the absence of a strong Attorney General, he became the main spokesman for the government in the House of Commons, and was noted for his "great powers of eloquence" and described as "beyond comparison the best speaker" in the House of Commons. With the promotion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Addington (judge)
{{hndis, Addington, William ...
William Addington may refer to: * William Addington, 3rd Viscount Sidmouth (1824–1913) * William Addington (judge), see Margaret Nicholson *William Leonard Addington, 2nd Viscount Sidmouth (1794–1864) See also *Addington (surname) Addington is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Anthony Addington (1713–1790), English physician and writer * Crandell Addington (born 1938), American poker player, one of the founders of the World Series of Poker * David Addi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |