|
Mardonius (nephew Of Darius I)
Mardonius ( peo, 𐎶𐎼𐎯𐎢𐎴𐎡𐎹 ; grc-gre, Μαρδόνιος ; died 479 BC) was a leading Persian military commander during the Persian Wars with Greece in the early 5th century BC who died at the Battle of Plataea. Early years Mardonius was the son of Gobryas, a Persian nobleman who had assisted the Achaemenid prince Darius when he claimed the throne. The alliance between the new king and his friend was cemented by diplomatic marriages: Darius married Gobryas' daughter, and Gobryas married Darius' sister. Furthermore, Mardonius married Darius' daughter Artozostra. Thus, Darius the Great was simultaneously Mardonius' uncle, father-in-law, and half-brother-in-law. Persian Wars with the Greeks First Persian invasion of Greece Darius appointed Mardonius as one of his generals and, after the Ionian Revolt, sent him in 492 BC to punish the Greek city-state of Athens for assisting the Ionians. On his way to Athens, he used his army in the Ionian cities to depose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Navy
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages across its t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires. The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with considerable autonomy. The word came to suggest tyranny or ostentatious splendour, and in modern usage refers to any subordinate or local ruler, usually with unfavourable connotations of corruption. A satrapy is the territory governed by a satrap. Etymology The word is derived via Latin from Greek ''satrápes'' (), itself borrowed from an Old Iranian ''*khshathra-pa''. In Old Persian, which was the native language of the Achaemenids, it is recorded as ''khshathapavan'' (, literally "protector of the province"). The Median form is reconstructed as ''*khshathrapavan-''. It is cognate with Sanskrit ''kshetrapal'' (). The Biblical Hebrew form is ''aḥashdarpan'' , as found in . In the Parthian (language of the Arsacid Empire) and Middle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artabanus (son Of Hystaspes)
Artabanus was a son of Hystaspes, and therefore brother of Darius I as well as uncle of Xerxes I. Artabanus had a reputation for great wisdom. Artabanus is known to have advised his brother Darius I against the Achaemenid campaign against the Scythians, saying that the Scythians were "impossible to deal with", but he wasn't heard, and the invasion proceeded, but was ultimately unsuccessful as Artabanus had predicted. According to Herodotus, Artabanus saw a ghost enjoining him to allow the invasion of Greece, which decided both him and Xerxes to launch the invasion without delay. According to Herodotus, Artabanus had a son named Artyphius, who became a general of Xerxes I in the Second Persian invasion of Greece (480-479 BC). Artyphius was in charge of the Gandharian Paropamisadae or Parapamisadae ( Greek: Παροπαμισάδαι) was a satrapy of the Alexandrian Empire in modern Afghanistan and Pakistan, which largely coincided with the Achaemenid province of Parup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ξέρξης ; – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, ruling from 486 to 465 BC. He was the son and successor of Darius the Great () and his mother was Atossa, a daughter of Cyrus the Great (), the founder of the Achaemenid empire. Like his father, he ruled the empire at its territorial peak. He ruled from 486 BC until his assassination in 465 BC at the hands of Artabanus, the commander of the royal bodyguard. Xerxes I is notable in Western history for his invasion of Greece in 480 BC. His forces temporarily overran mainland Greece north of the Isthmus of Corinth until losses at Salamis and Plataea a year later reversed these gains and ended the second invasion decisively. However, Xerxes successfully crushed revolts in Egypt and Babylon. Xerxes also oversaw the completion of various construction projects at Susa and Persepolis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Marathon
The Battle of Marathon took place in 490 BC during the first Persian invasion of Greece. It was fought between the citizens of Athens, aided by Plataea, and a Persian force commanded by Datis and Artaphernes. The battle was the culmination of the first attempt by Persia, under King Darius I, to subjugate Greece. The Greek army inflicted a crushing defeat on the more numerous Persians, marking a turning point in the Greco-Persian Wars. The first Persian invasion was a response to Athenian involvement in the Ionian Revolt, when Athens and Eretria sent a force to support the cities of Ionia in their attempt to overthrow Persian rule. The Athenians and Eretrians had succeeded in capturing and burning Sardis, but they were then forced to retreat with heavy losses. In response to this raid, Darius swore to burn down Athens and Eretria. According to Herodotus, Darius had his bow brought to him and then shot an arrow "upwards towards heaven", saying as he did so: "Zeus, that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
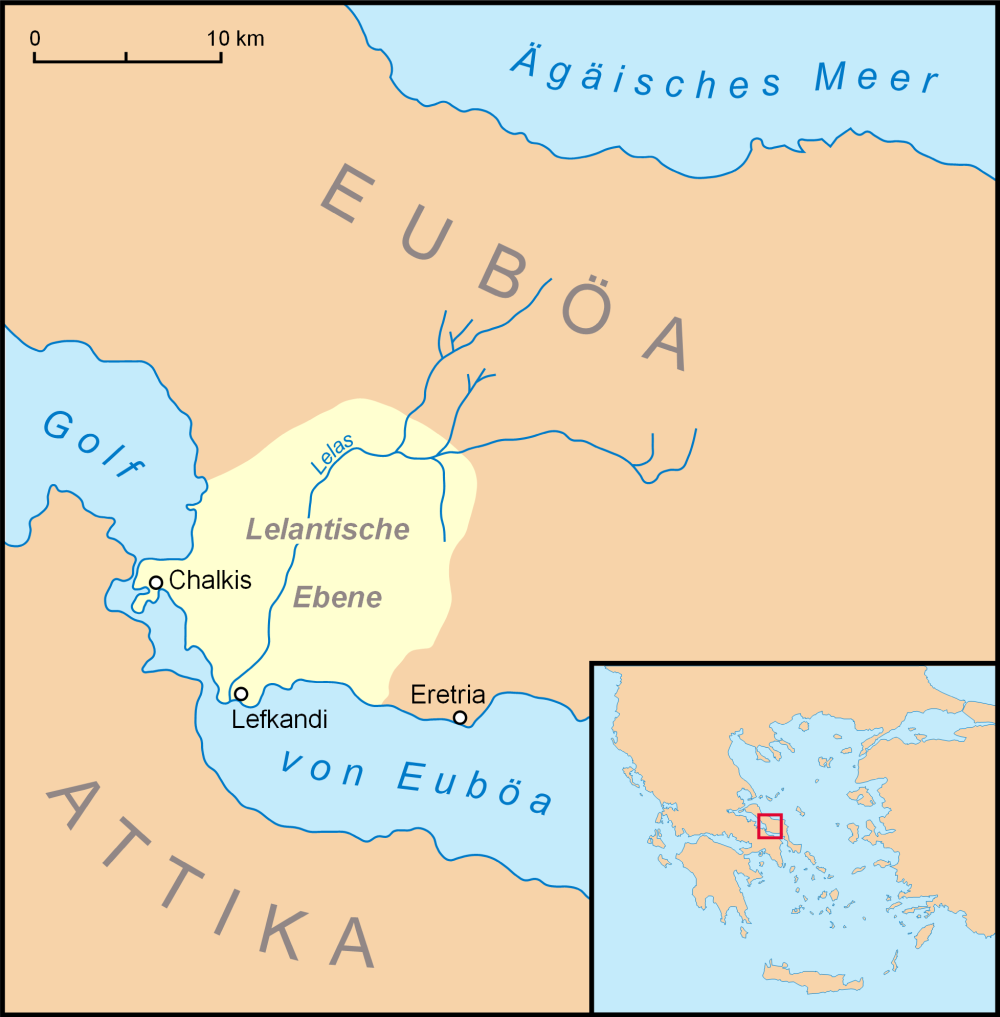
Eretria
Eretria (; el, Ερέτρια, , grc, Ἐρέτρια, , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events. Excavations of the ancient city began in the 1890s and have been conducted since 1964 by the Greek Archaeological Service (11th Ephorate of Antiquities) and the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. History of Eretria Prehistory The first evidence for human activity in the area of Eretria are pottery shards and stone artifacts from the late Neolithic period (3500–3000 BC) found on the Acropolis as well as in the plain. No permanent structures have yet been found. It is therefore unclear whether a permanent settlement existed at that time. The first known settlement from the Early Helladic period (3000–2000 BC) was located on the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naxos
Naxos (; el, Νάξος, ) is a Greek island and the largest of the Cyclades. It was the centre of archaic Cycladic culture. The island is famous as a source of emery, a rock rich in corundum, which until modern times was one of the best abrasives available. The largest town and capital of the island is Chora or Naxos City, with 7,374 inhabitants (2011 census). The main villages are Filoti, Apiranthos, Vivlos, Agios Arsenios, Koronos and Glynado. Geography Climate Naxos experiences a Mediterranean climate, with relatively mild winters and warm summers. The Köppen Climate Classification subtype for this climate is "Csa". (Mediterranean Climate). Inland areas of the island are much wetter and cooler in winter. Mythic Naxos According to Greek mythology, the young Zeus was raised in a cave on Mt. Zas ("''Zas''" meaning "''Zeus''"). Homer mentions " Dia"; literally the sacred island "of the Goddess". Károly Kerényi explains: One legend has it that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artaphernes (son Of Artaphernes)
Artaphernes ( el, Ἀρταφέρνης, Old Persian: Artafarna, from Median ''Rtafarnah''), son of Artaphernes, was the nephew of Darius the Great, and a general of the Achaemenid Empire. He was a Satrap of Lydia from 492 to after 480. He was appointed, together with Datis, to take command of the expedition sent by Darius to punish Athens and Eretria for their support for the Ionian Revolt. Artaphernes and Datis besieged and destroyed Eretria, Athenians fled so Persians burnt their city. Finally when most of the Persian fleet had gone back to Persia were beaten by the Athenians at the Battle of Marathon in 490 BC.Persian Fire. Holland, T. Ten years later, Artaphernes is recorded as being in command of the Lydians and Mysians in the Second Persian invasion of Greece.Herodotus, ''Histories'' VII 74; Aeschylus ''The Persians'' 21 See also *Artaphernes *Greco-Persian Wars *Battle of Marathon *Darius I of Persia Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Datis
Datis or Datus ( el, Δάτης, Old Iranian: *Dātiya-, Achaemenid Elamite: Da-ti-ya), was a Median noble and admiral who served the Persian Empire during the reign of Darius the Great. He was familiar with Greek affairs and maintained connections with Greek leaders. He is noted for his joint leadership with the younger Artaphernes of the Persian forces in the first campaign of the Persian Wars against the Greeks. Biography Before the Persian Wars Datis was a Persian commander during the Ionian Revolt. Datis led the counter-offensive against the Ionians in 494 BCE. Datis and another officer named Artaphernes replaced a commander named Mardonius. Datis was ordered to reduce Athens and Eretria to slavery, and bring the Greek slaves before the Achaemenid king. To achieve this, Datis sought to establish a bridgehead on the eastern coast of Greece. In 490 BCE, Datis sailed from the Ionian shoreline to Samos, and then he travelled through the Icarian sea to the islands of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. It comprises southeastern Bulgaria ( Northern Thrace), northeastern Greece (Western Thrace), and the European part of Turkey (East Thrace). The region's boundaries are based on that of the Roman Province of Thrace; the lands inhabited by the ancient Thracians extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania and to the west into the region of Macedonia. Etymology The word ''Thrace'' was first used by the Greeks when referring to the Thracian tribes, from ancient Greek Thrake (Θρᾴκη), descending from ''Thrāix'' (Θρᾷξ). It referred originally to the Thracians, an ancient people inhabiting Southeast Europe. The name ''Europe'' first referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)