|
Marcus Caelius Rufus
Marcus Caelius Rufus (28 May 82 BC – after 48 BC) was an orator and politician in the late Roman Republic. He was born into a wealthy equestrian family from Interamnia Praetuttiorum (Teramo), on the central east coast of Italy. He is best known for his prosecution of Gaius Antonius Hybrida in 59 BC. He was also known for his trial for public violence (''de vi publica'') in March 56 BC, when Cicero defended him in the extant speech ''Pro Caelio'', and as both recipient and author of some of the best-written letters in the ''ad Familiares'' corpus of Cicero's extant correspondence (Book 8). He may be the Rufus named in the poems of Catullus. Life and career In his twenties Caelius became associated with Crassus and Cicero, while he was also briefly connected to Catiline and his conspiracy. Caelius first achieved fame through his successful prosecution in 59 BC of Gaius Antonius Hybrida for corruption. Antonius Hybrida had served as consul with Cicero for the year 63 BC, and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orator
An orator, or oratist, is a public speaker, especially one who is eloquent or skilled. Etymology Recorded in English c. 1374, with a meaning of "one who pleads or argues for a cause", from Anglo-French ''oratour'', Old French ''orateur'' (14th century), Latin ''orator'' ("speaker"), from ''orare'' ("speak before a court or assembly; plead"), derived from a Proto-Indo-European base *''or-'' ("to pronounce a ritual formula"). The modern meaning of the word, "public speaker", is attested from c. 1430. History In ancient Rome, the art of speaking in public (''Ars Oratoria'') was a professional competence especially cultivated by politicians and lawyers. As the Greeks were still seen as the masters in this field, as in philosophy and most sciences, the leading Roman families often either sent their sons to study these things under a famous master in Greece (as was the case with the young Julius Caesar), or engaged a Greek teacher (under pay or as a slave). In the young revolutionar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribune Of The Plebs
Tribune of the plebs, tribune of the people or plebeian tribune ( la, tribunus plebis) was the first office of the Roman Republic, Roman state that was open to the plebs, plebeians, and was, throughout the history of the Republic, the most important check on the power of the Roman Senate and Roman magistrate, magistrates. These tribunes had the power to convene and preside over the ''Plebeian Council, Concilium Plebis'' (people's assembly); to summon the senate; to propose legislation; and to intervene on behalf of plebeians in legal matters; but the most significant power was to veto the actions of the Roman consul, consuls and other magistrates, thus protecting the interests of the plebeians as a class. The tribunes of the plebs were sacrosanct, meaning that any assault on their person was punishable by death. In Roman Empire, imperial times, the powers of the tribunate were granted to the Roman emperor, emperor as a matter of course, and the office itself lost its independence a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigram
An epigram is a brief, interesting, memorable, and sometimes surprising or satirical statement. The word is derived from the Greek "inscription" from "to write on, to inscribe", and the literary device has been employed for over two millennia. The presence of wit or sarcasm tends to distinguish non-poetic epigrams from aphorisms and adages, which tend to lack those qualities. Ancient Greek The Greek tradition of epigrams began as poems inscribed on votive offerings at sanctuariesincluding statues of athletesand on funerary monuments, for example "Go tell it to the Spartans, passersby...". These original epigrams did the same job as a short prose text might have done, but in verse. Epigram became a literary genre in the Hellenistic period, probably developing out of scholarly collections of inscriptional epigrams. Though modern epigrams are usually thought of as very short, Greek literary epigram was not always as short as later examples, and the divide between "ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pro Caelio
''Pro Caelio'' is a speech given on 4 April 56 BC, by the famed Roman orator Marcus Tullius Cicero in defence of Marcus Caelius Rufus, who had once been Cicero's student but more recently was a political rival. Cicero's reasons for defending Caelius are uncertain, but various theories have been postulated. The speech is regarded as one of the best examples of Roman oratory known and has been so regarded throughout history. It is noteworthy as a prime example of Ciceronian oratorical technique. Caelius was charged with ''vis'' (political violence), one of the most serious crimes in Republican Rome. Caelius' prosecutors, Lucius Sempronius Atratinus, Publius Clodius (it has been suggested to be Publius Clodius Pulcher, but it was more likely a freedman or relative), and Lucius Herennius Balbus, charged him with the following crimes: # Inciting civil disturbances at Naples; # Assault on the Alexandrians at Puteoli; # Damage to the property of Palla (about which we know little to noth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robinson Ellis
Robinson Ellis, FBA (5 September 1834 – 9 October 1913) was an English classical scholar. Ellis was born at Barming, near Maidstone, and was educated at Elizabeth College, Guernsey, Rugby School, and Balliol College, Oxford. He took a First in Classical Moderations in 1854 and a First in Literae Humaniores ('Greats') in 1856. In 1858 he became fellow of Trinity College, Oxford, and in 1870 professor of Latin at University College, London. In 1876 he returned to Oxford, where from 1883 to 1893 he held the university readership in Latin. In 1893 he succeeded Henry Nettleship as Corpus Professor of Latin.''Who Was Who, 1897-1916'', London : A. & C. Black, 1920, p. 226. His chief work was on Catullus, whom he began to study in 1859. In the course of his research he used an important early manuscript of Catullus, named the ''Codex Oxoniensis'' (many sources credit him with a discovery here, but that exact codex is already mentioned in an edition of Catullus made by Friedrich Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognomen
A ''cognomen'' (; plural ''cognomina''; from ''con-'' "together with" and ''(g)nomen'' "name") was the third name of a citizen of ancient Rome, under Roman naming conventions. Initially, it was a nickname, but lost that purpose when it became hereditary. Hereditary ''cognomina'' were used to augment the second name, the ''nomen gentilicium'' (the family name, or clan name), in order to identify a particular branch within a family or family within a clan. The term has also taken on other contemporary meanings. Roman names Because of the limited nature of the Latin '' praenomen'', the ''cognomen'' developed to distinguish branches of the family from one another, and occasionally, to highlight an individual's achievement, typically in warfare. One example of this is Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, whose cognomen ''Magnus'' was earned after his military victories under Sulla's dictatorship. The ''cognomen'' was a form of distinguishing people who accomplished important feats, and those who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate ( la, Senātus Rōmānus) was a governing and advisory assembly in ancient Rome. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being established in the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC). It survived the overthrow of the Roman monarchy in 509 BC; the fall of the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC; the division of the Roman Empire in AD 395; and the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476; Justinian's attempted reconquest of the west in the 6th century, and lasted well into the Eastern Roman Empire's history. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, most of the time the Senate was little more than an advisory council to the king, but it also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive magistr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debt Relief
Debt relief or debt cancellation is the partial or total forgiveness of debt, or the slowing or stopping of debt growth, owed by individuals, corporations, or nations. From antiquity through the 19th century, it refers to domestic debts, in particular agricultural debts and freeing of debt slaves. In World War I the United States Treasury made large loans to the allies that were postponed, reduced and finally paid off in 1953. In the late 20th century, it came to refer primarily to Third World debt, which started exploding with the Latin American debt crisis (Mexico 1983, etc.). In the early 21st century, it is of increased applicability to individuals in developed countries, due to credit bubbles and housing bubbles. International debt relief First World War reparations War debt payments by World War I Allies to the U.S. had been suspended in 1931—only Finland paid in full—and American public opinion demanded repayments resume as a condition of U.S. postwar aid. Germany had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetor Peregrinus
Praetor ( , ), also pretor, was the title granted by the government of Ancient Rome to a man acting in one of two official capacities: (i) the commander of an army, and (ii) as an elected '' magistratus'' (magistrate), assigned to discharge various duties. The functions of the magistracy, the ''praetura'' (praetorship), are described by the adjective: the ''praetoria potestas'' (praetorian power), the ''praetorium imperium'' (praetorian authority), and the ''praetorium ius'' (praetorian law), the legal precedents established by the ''praetores'' (praetors). ''Praetorium'', as a substantive, denoted the location from which the praetor exercised his authority, either the headquarters of his ''castra'', the courthouse (tribunal) of his judiciary, or the city hall of his provincial governorship. History of the title The status of the ''praetor'' in the early republic is unclear. The traditional account from Livy claims that the praetorship was created by the Sextian-Licinian Rogation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
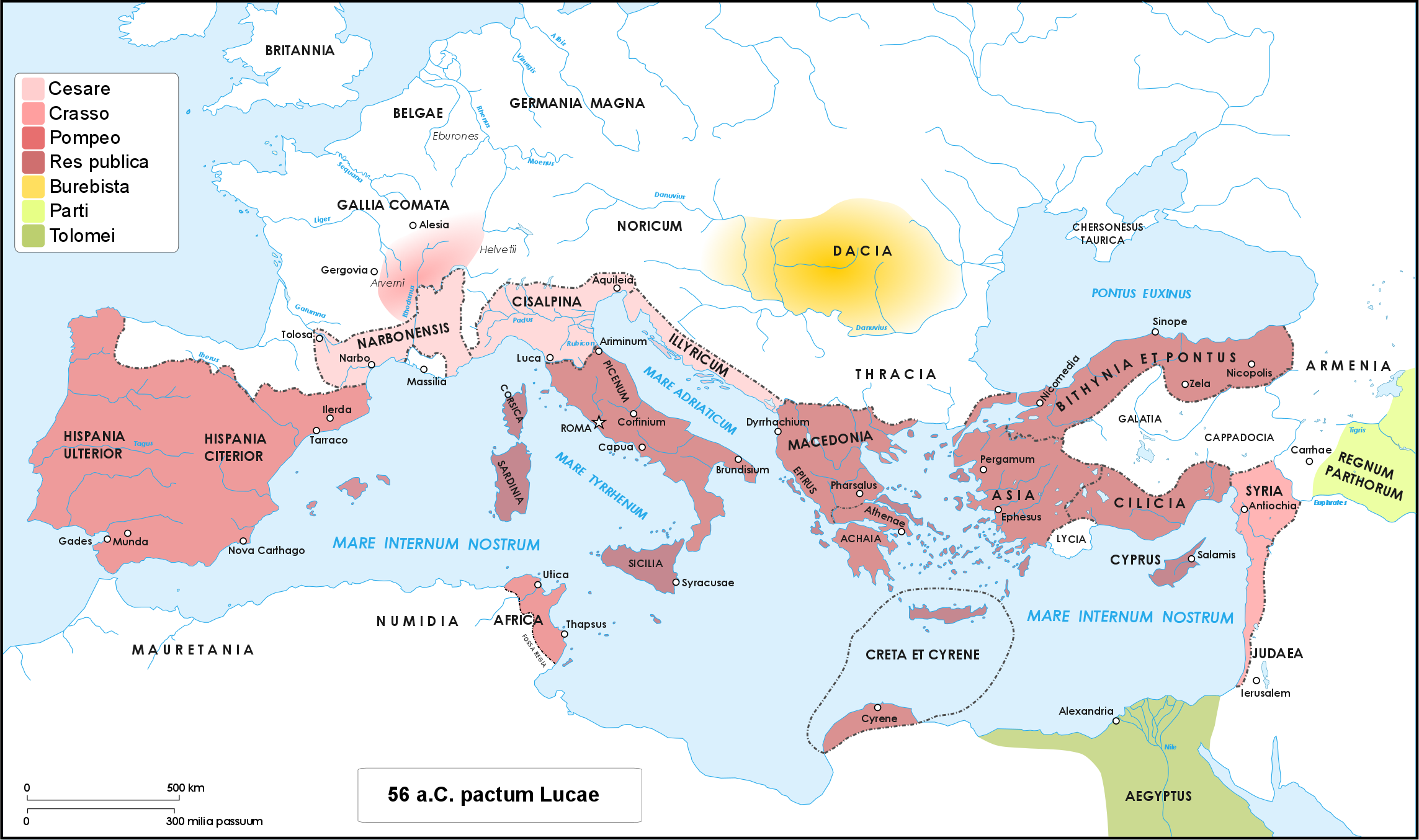
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus. Before the war, Caesar had led an invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 49 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down led, however, to the outbreak of civil war. Eventually, Pompey and his allies induced the Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies. Caesar refused and instead marched on Rome. The war was a four-year-long politico-military struggle, fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece, Egypt, Africa, and Hispania. Pompey defeated Caesar in 48 BC at the Battle of Dyrrhachium, but was himself defeated decisively at the Battle of Pharsalus. Many former Pompeians, including Marcus Junius Brutus and Cicero, surrendered after the battle, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of Rome from republic to empire. He was (for a time) a student of Roman general Sulla as well as the political ally, and later enemy, of Julius Caesar. A member of the senatorial nobility, Pompey entered into a military career while still young. He rose to prominence serving the dictator Sulla as a commander in the civil war of 83–82 BC. Pompey's success as a general while young enabled him to advance directly to his first Roman consulship without following the traditional '' cursus honorum'' (the required steps to advance in a political career). He was elected as Roman consul on three occasions. He celebrated three Roman triumphs, served as a commander in the Sertorian War, the Third Servile War, the Third Mithridatic War, and in va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and subsequently became dictator from 49 BC until his assassination in 44 BC. He played a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Crassus and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass power as were opposed by the within the Roman Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the frequent support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the Gallic Wars, completed by 51 BC, which greatly extended Roman territory. During this time he both invaded Britain and built a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |