|
Marat Gimaev
{{disambiguation, ...
Marat may refer to: People *Marat (given name) *Marat (surname) **Jean-Paul Marat (1743-1793), French political theorist, physician and scientist Arts, entertainment, and media *''Marat/Sade'', a 1963 play by Peter Weiss * ''Marat/Sade'' (film), a 1967 adaptation by Adrian Mitchell *''The Death of Marat'', a 1793 painting *''Il piccolo Marat'', an opera Places * Marat (Phoenicia), a former Phoenician town now known as Amrit, Syria * Marat, Puy-de-Dôme, a commune in France * Marat Fjord, Severnaya Zemlya * Marat Shahr, a village in Mazandaran Province, Iran Ships * ''Marat'' (ex- ''Petropavlovsk''), a Soviet battleship * ''Marat'', the French name of HMS ''Belleisle'' See also *Murat (other) Murat may refer to: Places Australia * Murat Bay, a bay in South Australia * Murat Marine Park, a marine protected area France * Murat, Allier, a commune in the department of Allier * Murat, Cantal, a commune in the department of Cantal Elsewhe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marat (given Name)
Marat is a common given name for males from the former Soviet republics. Marat's language of origin is the Tatar language. Its meaning can be translated into desire (desired), wish. It derives from the Turkish name Murat, itself derived from the Arabic Murad. People named Marat * Marat Akbarov, former Soviet pairs figure skater *Marat Balagula * Marat Basharov, actor * Marat Bikmoev, football striker (soccer forward) * Marat Bisengaliev *Marat Ganeyev, Russian track cyclist *Marat Gelman * Marat Grigorian, Armenian professional kickboxer * Marat Izmailov, Russian football player * Marat Khusnullin, Russian Tatar politician * Marat Ksanayev * Marat Magkeyev, football (soccer) player *Marat Safin Marat Mubinovich Safin ( rus, Мара́т Муби́нович Са́фин, , mɐˈrat ˈsafʲɪn, Ru-Marat-Safin.ogg; tt-Cyrl, Марат Мөбин улы Сафин; born 27 January 1980) is a Russian retired world No. 1 tennis player an ..., Russian professional tennis pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marat (surname) , Gabonese politician
{{surname, Marat ...
Marat is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Jean-Paul Marat (1743–1793), French revolutionary journalist, physician, and scientist * Allan Marat (born 1954), Papua New Guinean politician *Luc Marat Abyla Luc Marat Abyla is a Gabonese politician. He is a member of the Gabonese Democratic Party (''Parti démocratique gabonais'', PDG), and is a Deputy in the National Assembly of Gabon The National Assembly (french: Assemblée Nationale) is the lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Paul Marat
Jean-Paul Marat (; born Mara; 24 May 1743 – 13 July 1793) was a French political theorist, physician, and scientist. A journalist and politician during the French Revolution, he was a vigorous defender of the ''sans-culottes'', a radical voice, and published his views in pamphlets, placards and newspapers. His periodical ''L'Ami du peuple'' (''Friend of the People'') made him an unofficial link with the radical Jacobin group that came to power after June 1793. His journalism was known for its fierce tone and uncompromising stance toward the new leaders and institutions of the revolution. Responsibility for the September massacres has been attributed to him, given his position of renown at the time, and an alleged paper trail of decisions leading up to the massacres. Others posit the collective mentality that made them possible resulted from circumstances and not from the will of any particular individual.Lefebvre, p. 236 Marat was assassinated by Charlotte Corday, a Giro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marat/Sade
''The Persecution and Assassination of Jean-Paul Marat as Performed by the Inmates of the Asylum of Charenton Under the Direction of the Marquis de Sade'' (german: Die Verfolgung und Ermordung Jean Paul Marats dargestellt durch die Schauspielgruppe des Hospizes zu Charenton unter Anleitung des Herrn de Sade), usually shortened to ''Marat/Sade'' (), is a 1963 play by Peter Weiss. The work was first published in German. Incorporating dramatic elements characteristic of both Antonin Artaud and Bertolt Brecht, it is a depiction of class struggle and human suffering that asks whether true revolution comes from changing society or changing oneself. Plot Set in the historical Charenton Asylum, ''Marat/Sade'' is almost entirely a "play within a play". The main story takes place on 13 July 1808; the play directed by the Marquis de Sade within the story takes place fifteen years earlier, during the French Revolution, culminating in the assassination (13 July 1793) of Jean-Paul Marat, then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marat/Sade (film)
''The Persecution and Assassination of Jean-Paul Marat as Performed by the Inmates of the Asylum of Charenton Under the Direction of the Marquis de Sade'', usually shortened to ''Marat/Sade'' (), is a 1967 British film adaptation of Peter Weiss' play ''Marat/Sade''. The screen adaptation is directed by Peter Brook, and originated in his theatre production for the Royal Shakespeare Company. The English version was written by Adrian Mitchell from a translation by Geoffrey Skelton. The cast included Ian Richardson, Patrick Magee, Glenda Jackson, Clifford Rose, and Freddie Jones. It was filmed at Pinewood Studios in Buckinghamshire and released by United Artists on 22 February 1967 in the United States, and 8 March 1967 in the United Kingdom. The film's score comprised Richard Peaslee's compositions. David Watkin was the cinematographer. The film uses the full title in the opening credits, though most of the publicity materials use the shortened form. Plot In the Charenton Asyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
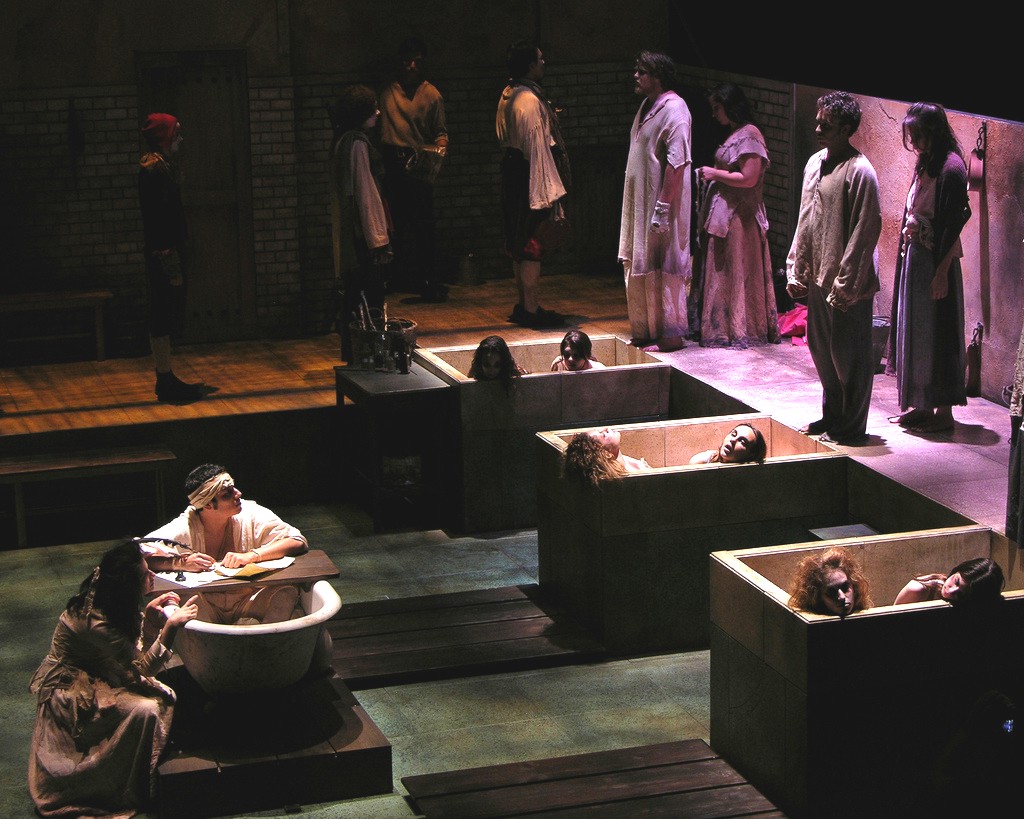
The Death Of Marat
''The Death of Marat'' (french: La Mort de Marat or ''Marat Assassiné'') is a 1793 painting by Jacques-Louis David depicting the artist's friend and murdered French revolutionary leader, Jean-Paul Marat. One of the most famous images from the era of the French Revolution, David painted it when he was the leading French Neoclassical painter, a Montagnard, and a member of the revolutionary Committee of General Security. Created in the months after Marat's death, the painting shows Marat lying dead in his bath after his murder by Charlotte Corday on 13 July 1793. Art historian T. J. Clark called David's painting the first modernist work for "the way it took the stuff of politics as its material, and did not transmute it". The painting is in the collection of the Royal Museum of Fine Arts of Belgium. A replica, created by the artist's studio, is on display at the Louvre. The assassination of Marat Jean-Paul Marat (24 May 1743 – 13 July 1793) was one of the leaders of the Monta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Il Piccolo Marat
''Il piccolo Marat'' is a ''dramma lirico'' or opera in three acts by the Italian composer Pietro Mascagni from a libretto by Giovacchino Forzano. Performance history The opera was first performed on 2 May 1921 at the Teatro Costanzi, Rome and then many times in Italy and South America, with at least 450 individual performances documented. Though Mascagni was slated to perform the opera in the United States in 1926, logistics proved too difficult for rehearsal, and the North American premiere waited until 13 April 2009, when Teatro Grattacielo performed the opera at Avery Fisher Hall in New York. Roles Synopsis Source: Time of the Reign of Terror in France. Act One Scene: A small town square. On the left a building with a gallery and stairs, door beneath the gallery - The Committee Building. In the distance a bridge spanning a river. On the right a convent converted to a prison. All is deserted save "an American hussar" who stands guard at the prison. An autumn evening ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marat (Phoenicia)
Amrit ( ar, عمريت), the classical Marathus ( grc-gre, Μάραθος, ''Marathos''), was a Phoenician port located near present-day Tartus in Syria. Founded in the third millenniumBC, Marat ( phn, 𐤌𐤓𐤕, ) was the northernmost important city of ancient Phoenicia and a rival of nearby Arwad. During the 2ndcenturyBC, Amrit was defeated and its site largely abandoned, leaving its ruins well preserved and without extensive remodeling by later generations. History The city lies on the Mediterranean coast around south of modern-day Tartus. Two rivers cross the city: Nahr Amrit, near the main temple, and Nahr al-Kuble near the secondary temple, a fact that might be linked to the importance of water in the religious traditions in Amrit. The city was probably founded by the Arvadites, and served as their continental base. It grew to be one of the wealthiest towns in the dominion of Arwad. The city surrendered, along with Arwad, to Alexander the Great in 333 BC. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marat, Puy-de-Dôme
Marat () is a commune in the Puy-de-Dôme department in Auvergne in central France. See also *Communes of the Puy-de-Dôme department The following is a list of the 464 communes of the Puy-de-Dôme department of France. Intercommunalities The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Puy-de-Dôme {{PuyDôme-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marat Fjord
Marat Fjord (russian: Фьорд Марата, ''Fiord Marata''), is a fjord in Severnaya Zemlya, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia.GoogleEarth It is blocked by ice most of the year. History Although the shore of the island further north had been visited by Boris Vilkitsky's Arctic Ocean Hydrographic Expedition in 1913, Vilkitsky surveyed the eastern shores of what is now known as Severnaya Zemlya in a fragmentary way —he did not explore the Shokalsky Strait and assumed that the whole of Severnaya Zemlya was one single landmass. This fjord was first surveyed and put in the map at the time of the 1931 expedition led by Soviet researchers Georgy Ushakov and Nikolay Urvantsev that explored for the first time Severnaya Zemlya. The fjord was named after prominent revolutionary figure Jean-Paul Marat (1743–1793). As in Matusevich Fjord further north, more accurate cartographic work of the fjord area was carried out by the 1950 expedition led by B.V. Zubov and A.I. Stepanov AI using aerial p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marat Shahr
Marat Shahr ( fa, مرتع شهر, also Romanized as Maratʿ Shahr) is a village in Deraz Kola Rural District, Babol Kenar District, Babol County, Mazandaran Province, Iran Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni .... At the 2006 census, its population was 20, in 4 families. References Populated places in Babol County {{Babol-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
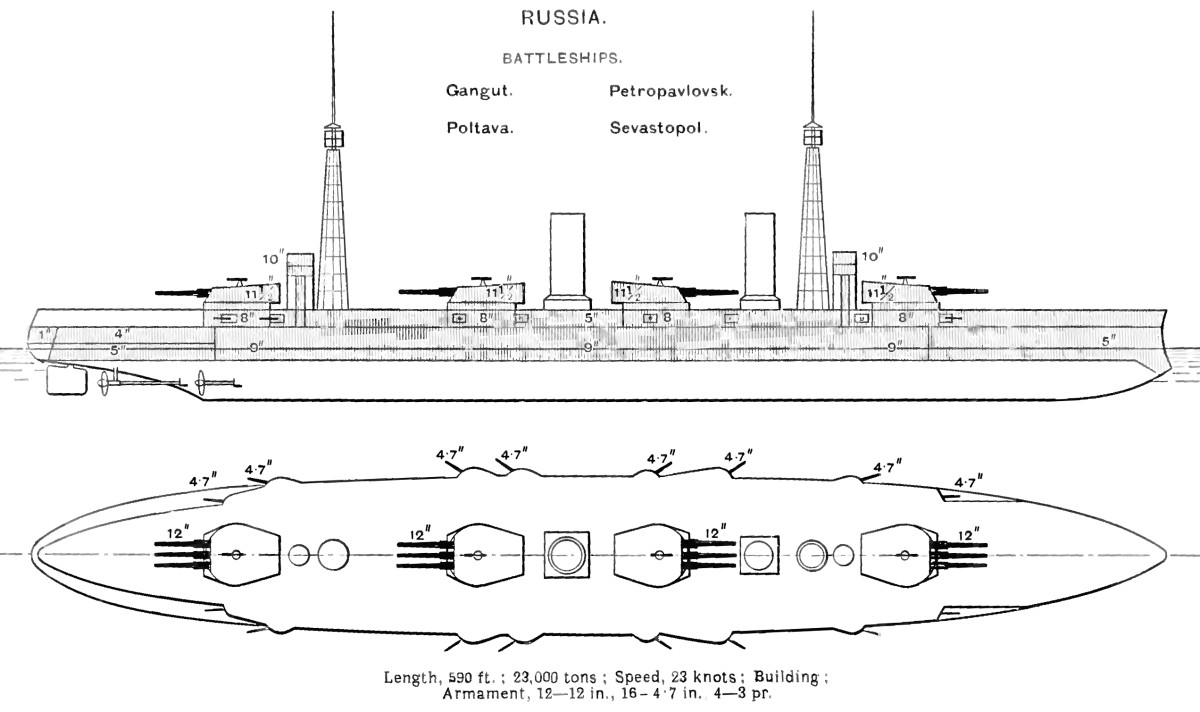
Russian Battleship Petropavlovsk (1911)
''Petropavlovsk'' (russian: Петропавловск) was the third of the four dreadnoughts built before World War I for the Imperial Russian Navy, the first Russian class of dreadnoughts. She was named after the Russian victory in the siege of Petropavlovsk during the Crimean War. The ship was completed during the winter of 1914–1915, but was not ready for combat until mid-1915. Her role was to defend the mouth of the Gulf of Finland against the Germans, who never tried to enter, so she spent her time training and providing cover for minelaying operations. Her crew joined the general mutiny of the Baltic Fleet after the February Revolution of 1917 and she was the only dreadnought available to the Bolsheviks for several years after the October Revolution of 1917. She bombarded the mutinous garrison of Fort Krasnaya Gorka and supported Bolshevik light forces operating against British ships supporting the White Russians in the Gulf of Finland in 1918–1919. Later, her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |