|
Manutūkē
Manutūkē is a settlement in the Gisborne District of New Zealand's North Island. It is located to the west of the city of Gisborne on State Highway 2, close to the mouth of the Waipaoa River. The name was officially modified to include macrons in 2021. Demographics Statistics New Zealand describes Manutūkē as a rural settlement, which covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. It is part of the larger Te Arai statistical area. Manutūkē had a population of 399 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 15 people (3.9%) since the 2013 census, and a decrease of 21 people (−5.0%) since the 2006 census. There were 147 households, comprising 198 males and 207 females, giving a sex ratio of 0.96 males per female, with 69 people (17.3%) aged under 15 years, 57 (14.3%) aged 15 to 29, 201 (50.4%) aged 30 to 64, and 72 (18.0%) aged 65 or older. Ethnicities were 41.4% European/ Pākehā, 71.4% Māori, 3.8% Pacific pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pātūtahi
Pātūtahi is a small settlement 15 kilometres from Gisborne, in the northeast of New Zealand's North Island. It is located in the valley of the Waipaoa River. From 1915 to 1931 Pātūtahi had a railway station on the Ngātapa Branch. The name was officially modified to include macrons in 2021. Demographics Statistics New Zealand describes Pātūtahi as a rural settlement, which covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. It is part of the larger Te Arai statistical area. Pātūtahi had a population of 330 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 12 people (3.8%) since the 2013 census, and a decrease of 9 people (−2.7%) since the 2006 census. There were 108 households, comprising 162 males and 168 females, giving a sex ratio of 0.96 males per female, with 84 people (25.5%) aged under 15 years, 66 (20.0%) aged 15 to 29, 129 (39.1%) aged 30 to 64, and 48 (14.5%) aged 65 or older. Ethnicities were 50.9% European/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of New Zealand
New Zealand is divided into sixteen regions () for local government in New Zealand, local government purposes. Eleven are administered by regional councils (the top tier of local government), and five are administered by Unitary authority#New Zealand, unitary authorities, which are territorial authorities of New Zealand, territorial authorities (the second tier of local government) that also perform the functions of regional councils. The Chatham Islands#Government, Chatham Islands Council is not a region but is similar to a unitary authority, authorised under its own legislation. Current regions History and statutory basis The regional councils are listed in Part 1 of Schedule 2 of the Local Government Act 2002 (New Zealand), Local Government Act 2002, along with reference to the ''New Zealand Gazette, Gazette'' notices that established them in 1989. The Act requires regional councils to promote sustainable developmentthe social, economic, environmental and cultural well-bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
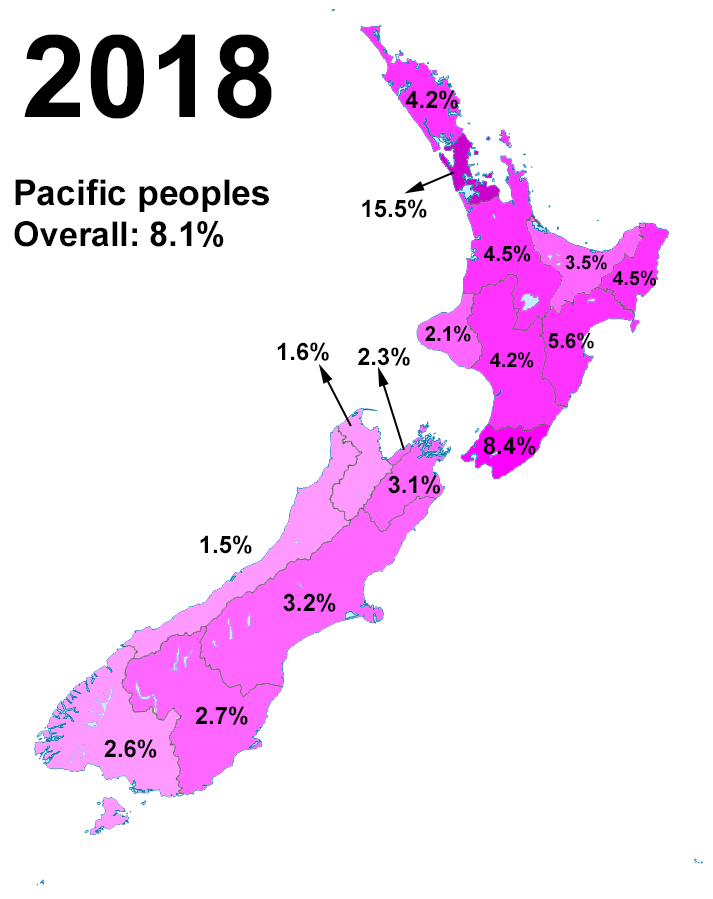
Pasifika New Zealanders
Pasifika New Zealanders are a pan-ethnic group of New Zealanders associated with, and descended from, the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands outside of New Zealand itself (also known as Pacific Islanders). They form the fourth-largest ethnic grouping in the country, after European-descended Pākehā, indigenous Māori, and Asian New Zealanders. There are over 380,000 Pasifika people in New Zealand, with the majority living in Auckland. 8% of the population of New Zealand identifies as being of Pacific origin. History Prior to the Second World War Pasifika in New Zealand numbered only a few hundred. Wide-scale Pasifika migration to New Zealand began in the 1950s and 1960s, typically from countries associated with the Commonwealth and the Realm of New Zealand, including Western Samoa (modern-day Samoa), the Cook Islands and Niue. In the 1970s, governments (both Labour and National), migration officials, and special police squads targeted Pasifika illegal overstayers. Paci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngāti Maru (Rongowhakaata)
Rongowhakaata is a Māori ''iwi'' of the Gisborne region of New Zealand. Hapū and marae There are three primary ''hapū'' (subtribes) of Rongowhakaata today: Ngati Kaipoho, Ngai Tawhiri and Ngati Maru. Ngāti Kaipoho Ngāti Kaipoho descend from Kaipoho, the son of Whare (also known as Whare-rau-o-te-tahinga) and great-grandson of Rongomairatahi. Kaipoho built Tapui pa on the west bank of Te Arai River, he also had a fishing settlement at Te Kowhai, near pakirikiri (what is now known as "Browns Beach"). Kaipoho was killed in battle and later avenged by his son Te Aweawe, who took over Tapui Pa. Ngati Kaipoho at one time fought against Ngati Maru and caused Ngati Maru's exodus from Waiapu, where they had lived for a time. The Marae of Ngati Kaipoho And Ngati Aweawe today is called Manutuke marae which is situated on the Manutuke 1, C, E4 blocks. There are two meeting houses situated on Manutuke Marae Te Poho o Rukupo, and Te Poho o Epeha The marae received a makeover in a 2006 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruapani (Rongowhakaata)
Rongowhakaata is a Māori ''iwi'' of the Gisborne region of New Zealand. Hapū and marae There are three primary ''hapū'' (subtribes) of Rongowhakaata today: Ngati Kaipoho, Ngai Tawhiri and Ngati Maru. Ngāti Kaipoho Ngāti Kaipoho descend from Kaipoho, the son of Whare (also known as Whare-rau-o-te-tahinga) and great-grandson of Rongomairatahi. Kaipoho built Tapui pa on the west bank of Te Arai River, he also had a fishing settlement at Te Kowhai, near pakirikiri (what is now known as "Browns Beach"). Kaipoho was killed in battle and later avenged by his son Te Aweawe, who took over Tapui Pa. Ngati Kaipoho at one time fought against Ngati Maru and caused Ngati Maru's exodus from Waiapu, where they had lived for a time. The Marae of Ngati Kaipoho And Ngati Aweawe today is called Manutuke marae which is situated on the Manutuke 1, C, E4 blocks. There are two meeting houses situated on Manutuke Marae Te Poho o Rukupo, and Te Poho o Epeha The marae received a makeover in a 2006 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngāi Tāwhiri
Rongowhakaata is a Māori ''iwi'' of the Gisborne region of New Zealand. Hapū and marae There are three primary ''hapū'' (subtribes) of Rongowhakaata today: Ngati Kaipoho, Ngai Tawhiri and Ngati Maru. Ngāti Kaipoho Ngāti Kaipoho descend from Kaipoho, the son of Whare (also known as Whare-rau-o-te-tahinga) and great-grandson of Rongomairatahi. Kaipoho built Tapui pa on the west bank of Te Arai River, he also had a fishing settlement at Te Kowhai, near pakirikiri (what is now known as "Browns Beach"). Kaipoho was killed in battle and later avenged by his son Te Aweawe, who took over Tapui Pa. Ngati Kaipoho at one time fought against Ngati Maru and caused Ngati Maru's exodus from Waiapu, where they had lived for a time. The Marae of Ngati Kaipoho And Ngati Aweawe today is called Manutuke marae which is situated on the Manutuke 1, C, E4 blocks. There are two meeting houses situated on Manutuke Marae Te Poho o Rukupo, and Te Poho o Epeha The marae received a makeover in a 2006 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngāti Kaipoho
Rongowhakaata is a Māori ''iwi'' of the Gisborne region of New Zealand. Hapū and marae There are three primary ''hapū'' (subtribes) of Rongowhakaata today: Ngati Kaipoho, Ngai Tawhiri and Ngati Maru. Ngāti Kaipoho Ngāti Kaipoho descend from Kaipoho, the son of Whare (also known as Whare-rau-o-te-tahinga) and great-grandson of Rongomairatahi. Kaipoho built Tapui pa on the west bank of Te Arai River, he also had a fishing settlement at Te Kowhai, near pakirikiri (what is now known as "Browns Beach"). Kaipoho was killed in battle and later avenged by his son Te Aweawe, who took over Tapui Pa. Ngati Kaipoho at one time fought against Ngati Maru and caused Ngati Maru's exodus from Waiapu, where they had lived for a time. The Marae of Ngati Kaipoho And Ngati Aweawe today is called Manutuke marae which is situated on the Manutuke 1, C, E4 blocks. There are two meeting houses situated on Manutuke Marae Te Poho o Rukupo, and Te Poho o Epeha The marae received a makeover in a 2006 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rongowhakaata
Rongowhakaata is a Māori ''iwi'' of the Gisborne region of New Zealand. Hapū and marae There are three primary ''hapū'' (subtribes) of Rongowhakaata today: Ngati Kaipoho, Ngai Tawhiri and Ngati Maru. Ngāti Kaipoho Ngāti Kaipoho descend from Kaipoho, the son of Whare (also known as Whare-rau-o-te-tahinga) and great-grandson of Rongomairatahi. Kaipoho built Tapui pa on the west bank of Te Arai River, he also had a fishing settlement at Te Kowhai, near pakirikiri (what is now known as "Browns Beach"). Kaipoho was killed in battle and later avenged by his son Te Aweawe, who took over Tapui Pa. Ngati Kaipoho at one time fought against Ngati Maru and caused Ngati Maru's exodus from Waiapu, where they had lived for a time. The Marae of Ngati Kaipoho And Ngati Aweawe today is called Manutuke marae which is situated on the Manutuke 1, C, E4 blocks. There are two meeting houses situated on Manutuke Marae Te Poho o Rukupo, and Te Poho o Epeha The marae received a makeover in a 2006 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hapū
In Māori and New Zealand English, a ' ("subtribe", or "clan") functions as "the basic political unit within Māori society". A Māori person can belong to or have links to many hapū. Historically, each hapū had its own chief and normally operated independently of its iwi (tribe). Etymology The word literally means "pregnant", and its usage in a socio-political context is a metaphor for the genealogical connection that unites hapū members. Similarly, the Māori word for land, whenua, can also mean "placenta", metaphorically indicating the connection between people and land, and the Māori word for tribe, iwi, can also mean "bones", indicating a link to ancestors. Definition As named divisions of (tribes), hapū membership is determined by genealogical descent; a hapū consists of a number of (extended family) groups. The Māori scholar Hirini Moko Mead states the double meanings of the word hapū emphasise the importance of being born into a hapū group. As a metaphor t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marae
A ' (in New Zealand Māori, Cook Islands Māori, Tahitian), ' (in Tongan), ' (in Marquesan) or ' (in Samoan) is a communal or sacred place that serves religious and social purposes in Polynesian societies. In all these languages, the term also means cleared and free of weeds or trees. generally consist of an area of cleared land roughly rectangular (the itself), bordered with stones or wooden posts (called ' in Tahitian and Cook Islands Māori) perhaps with ' (terraces) which were traditionally used for ceremonial purposes; and in some cases, a central stone ' or ''a'u''. In the Rapa Nui culture of Easter Island, the term ' has become a synonym for the whole marae complex. In some modern Polynesian societies, notably that of the Māori of New Zealand, the marae is still a vital part of everyday life. In tropical Polynesia, most marae were destroyed or abandoned with the arrival of Christianity in the 19th century, and some have become an attraction for tourists or archaeol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gisborne District Council
Gisborne District Council ( mi, Te Kaunihera o Te Tairāwhiti) is the unitary authority for the Gisborne District of New Zealand. The council consists of a mayor and 13 ward councillors. The district consists of the city of Gisborne and a largely rural region on the east coast of the North Island. Structure Gisborne District Council is a unitary territorial authority, which means that it performs the functions of a regional council as well as those of a territorial authority (a district or city). The area it governs is constituted as both the ''Gisborne District'' and the ''Gisborne Region''. The council consists of a mayor and 13 elected councillors. Nine councillors are elected from the Gisborne Ward, and one each from the four wards of Matakaoa-Waiapu, Taruheru-Patutahi, Tawhiti-Uawa and Waipaoa. Under the elected members, there is an appointed chief executive officer, 4 department managers and approximately 250 staff. The district council and main administration centre is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism In New Zealand
Buddhism is New Zealand's third-largest Religion in New Zealand, religion after Christianity in New Zealand, Christianity and Hinduism in New Zealand, Hinduism standing at 1.5% of the population of New Zealand. Buddhism originates in Asia and was introduced to New Zealand by immigrants from East Asia. History The first Buddhists in New Zealand were Chinese diggers in the Otago goldfields in the 1860s. Their numbers were small, and the 1926 census, the first to include Buddhism, recorded only 169. In the 1970s travel to Asian countries and visits by Buddhist teachers sparked an interest in the religious traditions of Asia, and significant numbers of New Zealanders adopted Buddhist practices and teachings. Since the 1980s Asian migrants and refugees have established their varied forms of Buddhism in New Zealand. In the 2010s more than 50 groups, mostly in the Auckland region, offered different Buddhist traditions at temples, centres, monasteries and retreat centres. Many migrant c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |