|
Mansur Al-Atrash
Mansur al-Atrash ( ar, منصور الأطرش; 3 February 1925 – 14 November 2006) was a Syrian politician and journalist. Together with fellow university students, Atrash became a founding member of the Ba'ath Party and its Syrian regional branch in 1947. During the presidency of Adib Shishakli (1951–54), he became an anti-government activist and was imprisoned twice, only to be released in an unsuccessful attempt by Shishakli to gain the support of Atrash's father, Sultan. In the year Shishakli was overthrown, Atrash was elected to parliament and turned down an offer to serve in Said al-Ghazzi's government. During the period of the United Arab Republic (1958–61), Atrash became a strong supporter of Egyptian president and pan-Arab leader Gamal Abdel Nasser. He opposed Syria's secession from the UAR and turned down offers to serve in successive separatist governments in protest. When the Ba'ath Party gained power in the 1963 coup, Atrash became Minister of Social Aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speaker Of Parliament (Syria)
The Speaker of the People's Assembly of Syria (Arabic: رئيس مجلس الشعب السوري rayiys majlis alshaeb alsuwrii) represents the People's Assembly, Syria's legislature, signs documents and speaks on its behalf. Throughout its history, the Speaker has been responsible for representing the Assembly. As of 2017, 30 different people have served as speakers. Election A People's Assembly is elected every fourth calendar year. The first meeting of a newly elected People's Assembly is responsible for electing its Speaker. Powers The People's Assembly should meet at least three times a year, the Speaker has the power to convene an extraordinary meeting of the Assembly. The guards of the People's Assembly are under the authority of the Speaker. Presidential elections 60 days before the term of the President expires, the Speaker calls for new elections. All presidential candidates have to be approved personally by the Speaker. If only one candidate is acceptable, the Speake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adib Shishakli
Adib al-Shishakli (1909 – 27 September 1964 ar, أديب الشيشكلي, ʾAdīb aš-Šīšaklī) was a Syrian military leader and President of Syria from 1953 to 1954. Early life Adib Shishakli was born (1909) in the Hama Sanjak of Ottoman Syria to a Syrian family. His mother was of Kurds, Kurdish origin. His family name, Shishakli, is a common surname derived from Turkish word "wikt:çiçek, çiçek" which means flower and çiçekli (Shishakli) means someone or some place with flowers in Turkish language, Turkish. Political/military career Shishakli was commissioned during the Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon, French Mandate as an officer in the Syrian military in 1930. He studied at the Military Academy of Damascus (which later was relocated to Homs) and became an early member of the Syrian Social Nationalist Party (SSNP), founded by Antun Saadeh, promoting the concept of a Greater Syria. His brother Salah was also a prominent member of the SSNP. Following Syria's S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansur Al-Atrash1
Mansour ( ar, منصور, Manṣūr); also spelled Mounsor, Monsur (Bengali), Mansoor, Manser, Mansur, Mansyur (Indonesian) or Mensur (Turkish), is a male Arabic name that means "He who is victorious", from the Arabic root '' naṣr'' (نصر), meaning "victory." The first known bearer of the name was Al-Mansur, second Abbasid caliph and the founder of Baghdad. Other people called Mansour during the golden Age of Islam include: * Ismail al-Mansur, third ruler of the Fatimid dynasty ruled from 946 to 953. * Mansur Al-Hallaj, Persian mystic, writer, and teacher of Sufism * Almanzor, 10th-century ruler of al-Andalus * Mansur ibn Ilyas, Timurid physician * Mansur Khan (Moghul Khan), a khan of Moghulistan * Mansur Shah of Malacca, a sultan of Malacca * Mansur I of Samanid and Mansur II of Samanid, amirs of the Samanids * Mansur ad-Din of Adal, 15th-century sultan of Adal. Imams of Yemen * Al-Mansur Yahya (d. 976) * Al-Mansur Abdallah (1166-1217) * Al-Mansur al-Hasan (1199–1271) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lies to its west across the Mediterranean Sea; its location at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian hinterland has contributed to its rich history and shaped a cultural identity of religious diversity. It is part of the Levant region of the Middle East. Lebanon is home to roughly six million people and covers an area of , making it the second smallest country in continental Asia. The official language of the state is Arabic, while French is also formally recognized; the Lebanese dialect of Arabic is used alongside Modern Standard Arabic throughout the country. The earliest evidence of civilization in Lebanon dates back over 7000 years, predating recorded history. Modern-day Lebanon was home to the Phoenicians, a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occupations outside Africa and was among the earliest known sites of agriculture. It was inhabited by the Canaanites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
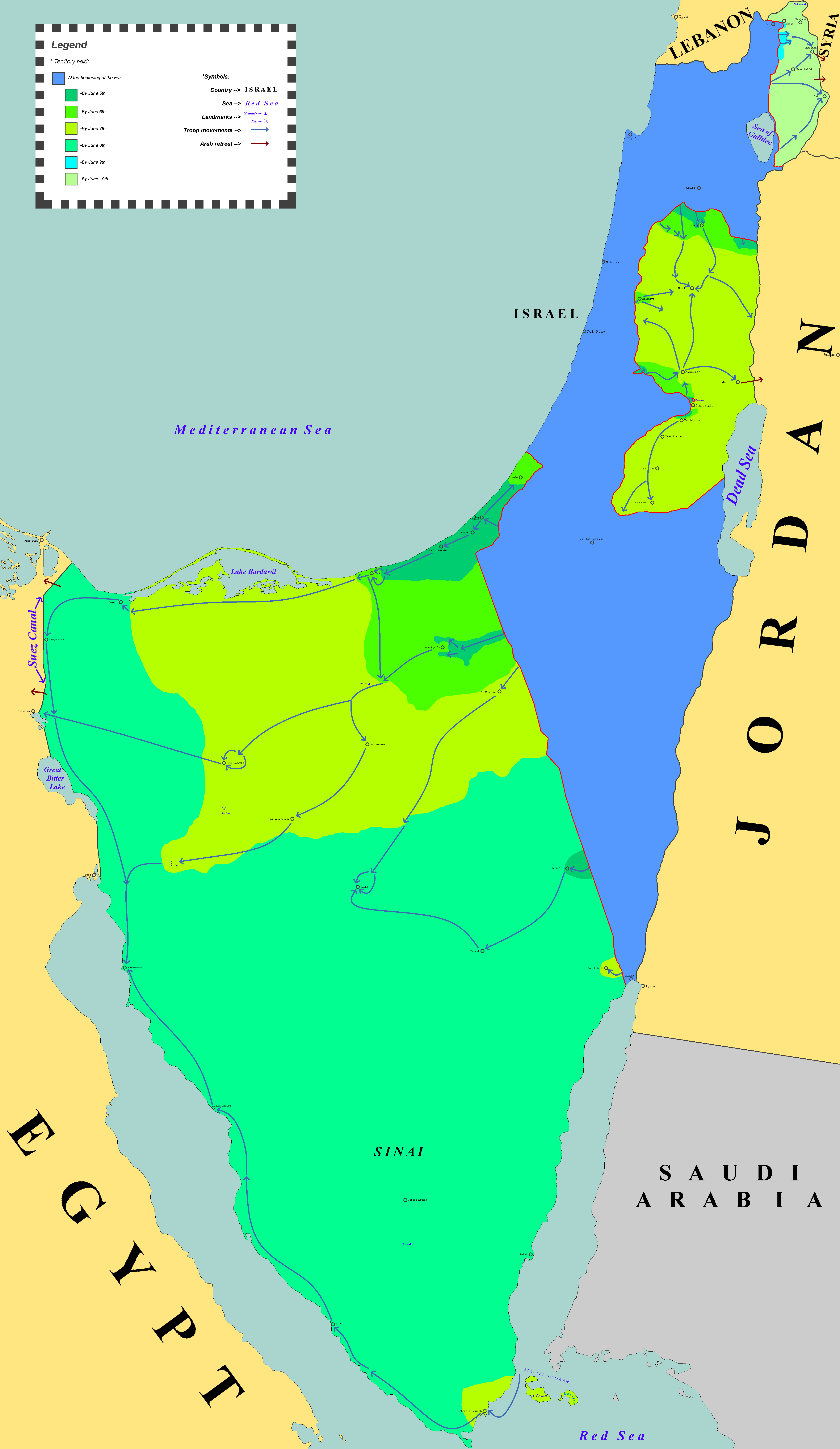
Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 June 1967. Escalated hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbours following the 1949 Armistice Agreements, which were signed at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, First Arab–Israeli War. Earlier, in 1956, regional tensions over the Straits of Tiran escalated in what became known as the Suez Crisis, when Israel invaded Egypt over the Israeli passage through the Suez Canal and Straits of Tiran, Egyptian closure of maritime passageways to Israeli shipping, ultimately resulting in the re-opening of the Straits of Tiran to Israel as well as the deployment of the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) along the Borders of Israel#Border with Egypt, Egypt–Israel border. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michel Aflaq
Michel Aflaq ( ar, ميشيل عفلق, Mīšīl ʿAflaq, , 9 January 1910 – 23 June 1989) was a Syrian philosopher, sociologist and Arab nationalist. His ideas played a significant role in the development of Ba'athism and its political movement; he is considered by several Ba'athists to be the principal founder of Ba'athist thought. He published various books during his lifetime, the most notable being '' The Battle for One Destiny'' (1958) and ''The Struggle Against Distorting the Movement of Arab Revolution'' (1975). Born into a middle-class family in Damascus, Syria, Aflaq studied at the Sorbonne, where he met his future political companion Salah al-Din al-Bitar. He returned to Syria in 1932, and began his political career in communist politics. Aflaq became a communist activist, but broke his ties with the communist movement when the Syrian–Lebanese Communist Party supported colonial policies through the Popular Front under the French Mandate of Syria. Later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Committee (Syria)
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1966 Syrian Coup D'état
The 1966 Syrian coup d'état refers to events between 21 and 23 February during which the government of the Syrian Arab Republic was overthrown and replaced. The ruling National Command of the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party were removed from power by a union of the party's Military Committee and the Regional Command, under the leadership of Salah Jadid. The coup was precipitated by a heightening in the power struggle between the party's old guard, represented by Michel Aflaq, Salah al-Din al-Bitar, and Munif al-Razzaz, and the younger factions adhering to a Neo-Ba'athist position. On 21 February, supporters of the old guard in the army ordered the transfer of their rivals. Two days later, the Military Committee, backing the younger factions, launched a coup that involved violent fighting in Aleppo, Damascus, Deir ez-Zor, and Latakia. As a result of the coup, the party's historical founders fled the country and spent the rest of their lives in exile. Jadid's government was the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Council Of The Revolutionary Command
The National Council for the Revolutionary Command (NCRC) is the twenty-man council set up to rule Syria after the 1963 Syrian coup d'état The 1963 Syrian coup d'état, referred to by the Syrian government as the 8 March Revolution ( ar, ثورة الثامن من آذار), was the successful seizure of power in Syrian Republic (1946-63), Syria by the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party .... The NCRC was composed of 12 Ba'athists and eight Nasserists and independents. Its exact membership was kept secret for the first few months. Though some civilians were admitted, it was dominated by military officers. Within the NCRC, the military officers created a committee to hold the real power described as a "Junta with in a Junta." References Ba'athism 1963 establishments in Syria History of the Ba'ath Party Military dictatorships Political history of Syria Provisional governments Government of Syria {{Syria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1963 Syrian Coup D'état
The 1963 Syrian coup d'état, referred to by the Syrian government as the 8 March Revolution ( ar, ثورة الثامن من آذار), was the successful seizure of power in Syrian Republic (1946-63), Syria by the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party – Syria Region#Military Bureau, military committee of the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party – Syria Region, Syrian Regional Branch of the Ba'ath Party, Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party. The planning and the unfolding conspiracy was inspired by the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party – Iraq Region, Iraqi Regional Branch's Ramadan Revolution, successful military coup. The coup was planned by the military committee, rather than the Ba'ath Party's civilian leadership, but Michel Aflaq, the leader of the party, consented to the conspiracy. The leading members of the military committee throughout the planning process and in the immediate aftermath of taking power were Muhammad Umran, Salah Jadid and Hafez al-Assad. The committee enlisted the support of two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamal Abdel Nasser
Gamal Abdel Nasser Hussein, . (15 January 1918 – 28 September 1970) was an Egyptian politician who served as the second president of Egypt from 1954 until his death in 1970. Nasser led the Egyptian revolution of 1952 and introduced far-reaching land reforms the following year. Following a 1954 attempt on his life by a Muslim Brotherhood member, he cracked down on the organization, put President Mohamed Naguib under house arrest and assumed executive office. He was formally elected president in June 1956. Nasser's popularity in Egypt and the Arab world skyrocketed after his nationalization of the Suez Canal Company and his political victory in the subsequent Suez Crisis, known in Egypt as the ''Tripartite Aggression''. Calls for pan-Arab unity under his leadership increased, culminating with the formation of the United Arab Republic with Syria from 1958 to 1961. In 1962, Nasser began a series of major socialist measures and modernization reforms in Egypt. Despite setba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)
