|
Manouria Impressa
The impressed tortoise (''Manouria impressa'') occurs in mountainous forest areas in Southeast Asia, mainly in Myanmar Burma, southern China, Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, Cambodia, Malaysia and Northeast India. The species has a golden brown shell and skin. Adults are much smaller than their relatives the Asian forest tortoise ('' Manouria emys''), with a maximum carapace A carapace is a Dorsum (biology), dorsal (upper) section of the exoskeleton or shell in a number of animal groups, including arthropods, such as crustaceans and arachnids, as well as vertebrates, such as turtles and tortoises. In turtles and tor ... length of . The impressed tortoise lives at high elevations, up to . Its behavior is little known due to the small known population; diet in the wild may consist largely of mushrooms, although bamboo shoots are also eaten. The species is known for being difficult to keep alive in captivity because not much is known about it; although its status in the wild is uncertai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalyar Platt
Kalyar Platt is a Burmese herpetologist and turtle conservationist. She is the director of the Myanmar Program of the Turtle Survival Alliance and oversees conservation, breeding and reintroduction projects for some of Southeast Asia's rarest turtle species. She formerly worked for Wildlife Conservation Society and earned her PhD from Bangkok's Chulalongkorn University in 2007. Early life and education Kalyar was born in 1972 in Yangon, Myanmar, to U Nyunt Thein and Daw San San. Her father was a government engineer involved in the construction of hydroelectric dams. She accompanied him to work sites where she witnessed construction workers collecting turtles in pits. She was fascinated by the variety of species but recoiled in horror when the turtles were pulled from the pit, butchered and cooked by the camp chef. She earned her B.Sc. with honours from Yangon University in 1995. She earned her M.Sc. from the same university in 2000. Fearing that the Burmese military junta would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
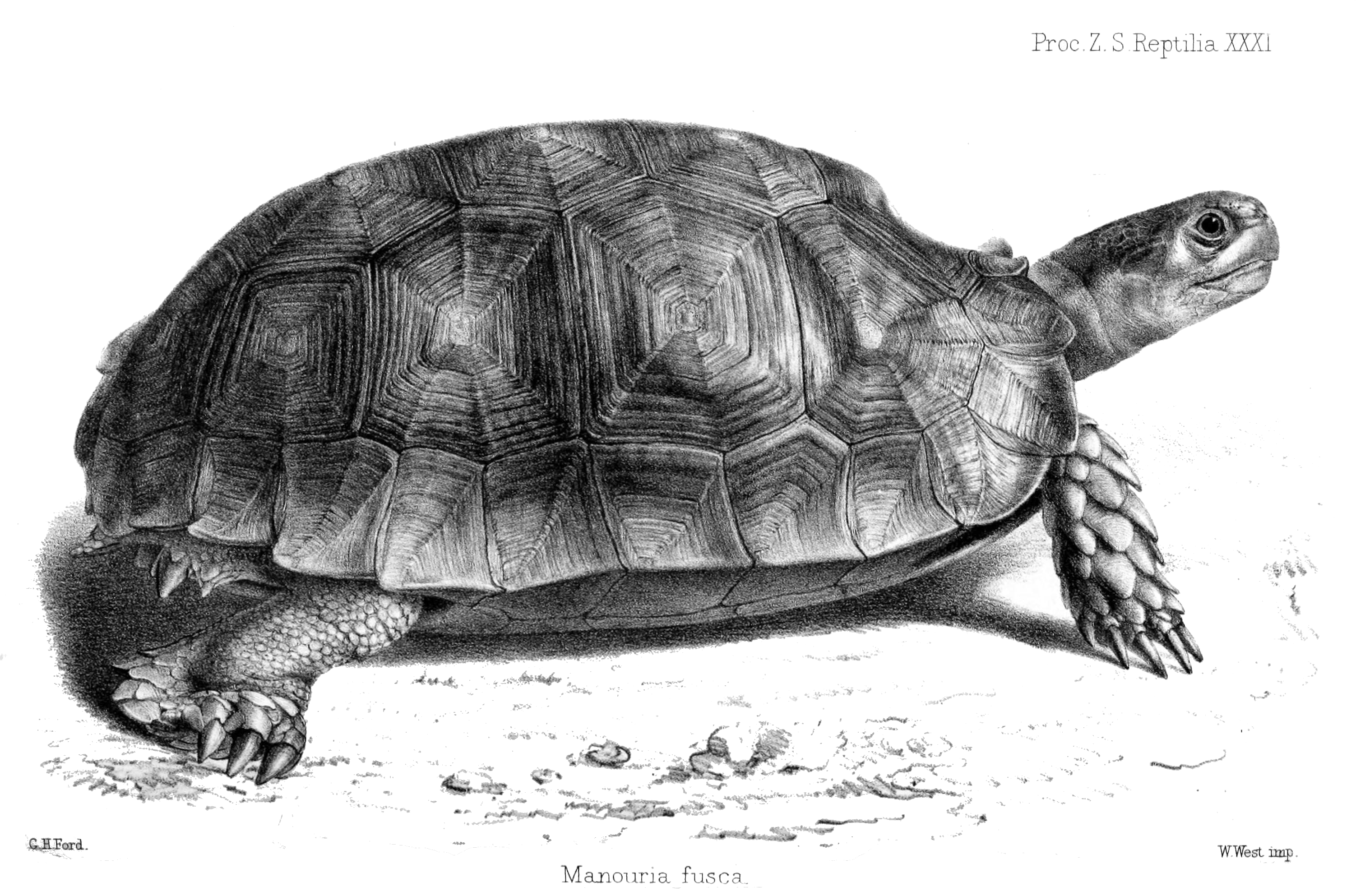
Manouria Emys
The Asian forest tortoise (''Manouria emys''), also known commonly as the Mountain tortoise, is a species of tortoise in the family Testudinidae. The species is endemic to Southeast Asia. It is believed to be among the most primitive of living tortoises, based on molecular and morphological studies. Taxonomy There are two recognized subspecies: ''M. e. emys'' occurring in southern Thailand, Malaysia, Sumatra, Borneo; and ''M. e. phayrei'', occurring from northwestern Thailand to northeastern India. The latter was named after Sir Arthur Purves Phayre (1812–1885), British Army officer in India who became Commissioner of British Burma. Based on a variety of phylogenetic characteristics, the genus ''Manouria'' is regarded as comparatively primitive and basal to other Testudinidae. Description The Asian forest tortoise is the largest tortoise in mainland Asia. The largest adults of the northern subspecies, ''Manouria emys phayrei'', can reach in the wild and much more than t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of Vietnam
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of Malaysia
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around 31 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of Cambodia
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates ( lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of Laos
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates ( lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of Thailand
The following is a list of reptiles of Thailand. There are more than 400 species recorded. Order Crocodylia (crocodilians) Order Testudines (turtles) Order Squamata, Suborder Lacertilia (lizards) Order Squamata, Suborder Serpentes (snakes) Common species Reptile species commonly found in anthropogenically modified environments (i.e., near human settlements) include:http://www.ahr-journal.com/OA/pdfdow.aspx?Sid=210130105 *''Calotes versicolor'' (oriental garden lizard) *''Eutropis macularia'' (bronze grass skink) *'' Eutropis multifasciata'' (common sun skink) *''Gekko gecko'' (tokay gecko) *''Gehyra mutilata'' (stump-toed gecko) *''Hemidactylus frenatus'' (common house gecko) *'' Hemidactylus platyurus'' (flat-tailed house gecko) *''Ramphotyphlops braminus'' (common blind snake) *''Python reticulatus'' (reticulated python) *''Dendrelaphis pictus'' (painted bronzeback) *'' Enhydris plumbea'' (rice paddy snake) *''Ptyas mucosa'' (oriental ratsnake) *''Rhabdophis subminiatus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of Myanmar
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around 31 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of China
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manouria
''Manouria'' is a genus of tortoises in the family Testudinidae. The genus was erected by John Edward Gray in 1854. Species The following five species are recognized as being valid, two of which are extant, and three of which are extinct: *''Manouria emys'' – Asian forest tortoise *''Manouria impressa'' – impressed tortoise *†''Manouria sondaari'' – a giant land tortoise from Luzon Island, PhilippinesStaesche, Ulrich (coordinator) (2007). ''Fossile Schildkröten aus vier Ländern in drei Kontinenten: Deutschland, Türkei, Niger, Philippen'' Fossil Turtles from Four Countries on Three Continents: Germany, Turkey, Niger, and the Philippines ''Geologisches Jahrbuch, Reihe B, Heft 98'' Series B, Issue 98 197 pp. . http://www.schweizerbart.de/publications/detail/artno/186029800 (in German). however, Rhodin et al. (2015) transferred this species to the genus ''Megalochelys''. *†''Manouria punjabiensis'' – a fossil tortoise from Siwaliks, India *†''Manouria oyamai' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carapace
A carapace is a Dorsum (biology), dorsal (upper) section of the exoskeleton or shell in a number of animal groups, including arthropods, such as crustaceans and arachnids, as well as vertebrates, such as turtles and tortoises. In turtles and tortoises, the underside is called the plastron. Crustaceans In crustaceans, the carapace functions as a protective cover over the cephalothorax (i.e., the fused head and thorax, as distinct from the abdomen behind). Where it projects forward beyond the eyes, this projection is called a rostrum (anatomy), rostrum. The carapace is Calcification, calcified to varying degrees in different crustaceans. Zooplankton within the phylum Crustacea also have a carapace. These include Cladocera, ostracods, and Isopoda, isopods, but isopods only have a developed "cephalic shield" carapace covering the head. Arachnids In arachnids, the carapace is formed by the fusion of prosomal tergites into a single Plate (animal anatomy), plate which carries the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast India
, native_name_lang = mni , settlement_type = , image_skyline = , image_alt = , image_caption = , motto = , image_map = Northeast india.png , map_alt = Northeast india map.png , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = States , subdivision_name1 = , subdivision_type2 = Largest city , subdivision_name2 = Guwahati , subdivision_type3 = Major cities (2011 Census of India) , subdivision_name3 = [Baidu] |




.png)

