|
Manjhitar
Manjhitar is a small town in the Indian states and union territories of India, state of Sikkim. It is under the jurisdiction of the administrative divisions of India, district of South Sikkim. The Sikkim Manipal University is situated here. Geography It is located at at an elevation of 278 m above MSL. References External links Satellite image of Manjhitar Cities and towns in Namchi district {{Sikkim-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Towns In India By Population
The entire work of this article is based on the 2011 Census of India, conducted by the Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, under Ministry of Home Affairs (India), Government of India. Categorization Census of India (2011) states the following criteria in defining towns. They are: * Statutory Town (ST): All places with a municipality, corporation, cantonment board or notified town area committee etc. * Census Town (CT): Those which have a population greater than 5000. Other definitions include percentage of non-agriculture working population and population density. Abbreviations Sources: * Abbreviation reference List See also * List of cities in India by population * Place names in India Place names in India are usually in Indian languages. Other languages include Portuguese, Dutch, English and Arabic. Since Indian Independence, several Indian cities have adopted pre-English names, most notably Chennai (formerly Madras), Mumbai ... * Tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
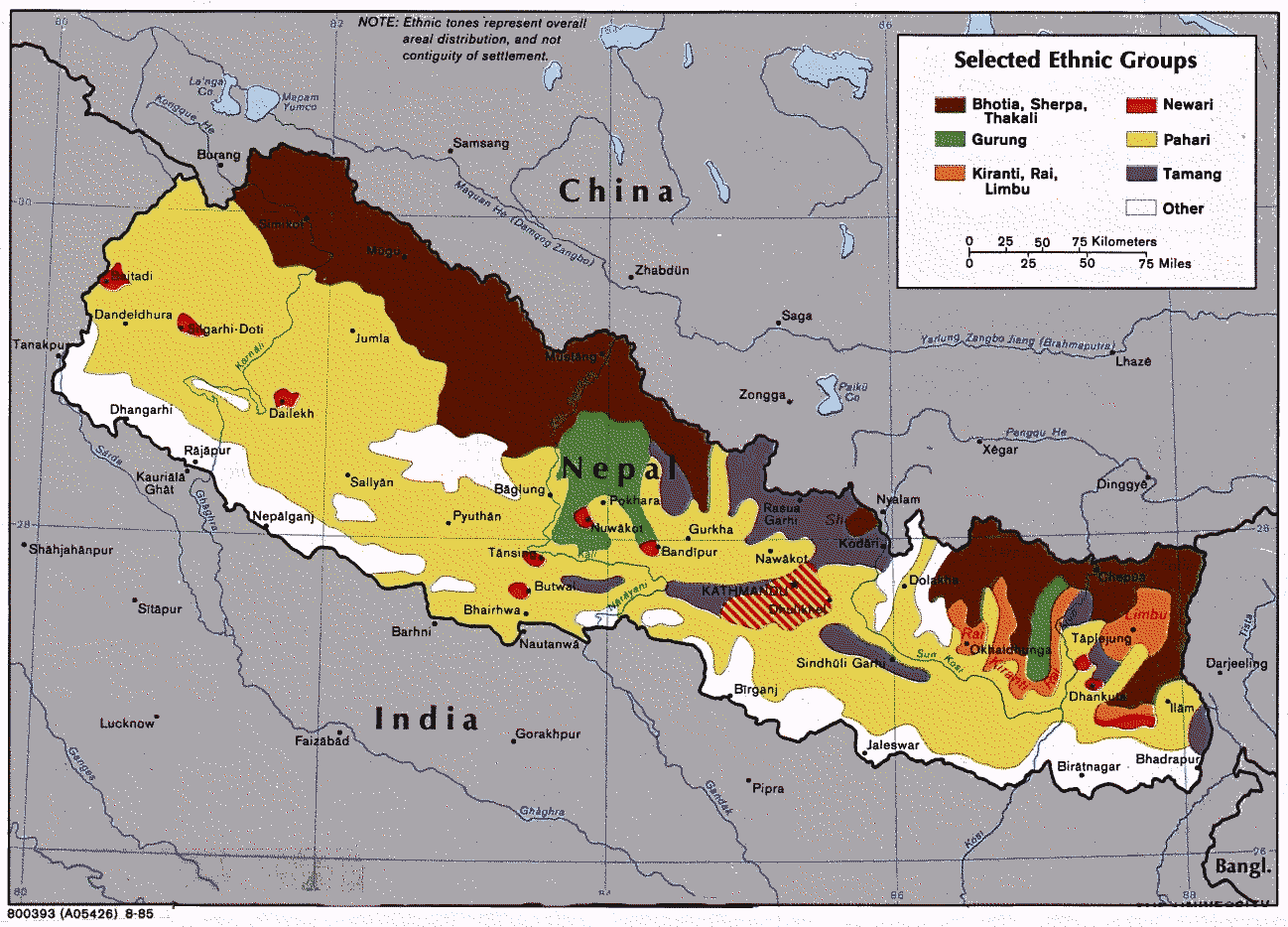
Sherpa Language
Sherpa (also Sharpa, Xiaerba, or Sherwa) is a Tibetic language spoken in Nepal and the Indian state of Sikkim, mainly by the Sherpa. The majority speakers of the Sherpa language live in the Khumbu region of Nepal, spanning from the Chinese (Tibetan) border in the east to the Bhotekosi River in the west. About 200,000 speakers live in Nepal (2001 census), some 20,000 in Sikkim (1997) and some 800 in Tibetan Autonomous Region (1994). Sherpa is a subject-object-verb (SOV) language. Sherpa is predominantly a spoken language, although it is occasionally written using either the Devanagari or Tibetan script. Phonology Sherpa is a tonal language. Sherpa has the following consonants: Consonants * Stop sounds can be unreleased in word-final position. * Palatal sounds can neutralize to velar sounds when preceding . * can become a retroflex nasal when preceding a retroflex stop. * can have an allophone of when occurring in fast speech. Vowels * Vowel sounds have the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Divisions Of India
The administrative divisions of India are subnational administrative units of India; they are composed of a nested hierarchy of administrative divisions. Indian states and territories frequently use different local titles for the same level of subdivision (e.g., the ''mandals'' of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana correspond to ''tehsils'' of Uttar Pradesh and other Hindi-speaking states but to ''talukas'' of Gujarat, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu). The smaller subdivisions (villages and blocks) exist only in rural areas. In urban areas, urban local bodies exist instead of these rural subdivisions. Tiers of India The diagram below outlines the six tiers of government: Zones and regions Zones The states of India have been grouped into six zones having an Advisory Council "to develop the habit of cooperative working" among these States. Zonal Councils were set up vide Part-III of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956. The North Eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurisdiction
Jurisdiction (from Latin 'law' + 'declaration') is the legal term for the legal authority granted to a legal entity to enact justice. In federations like the United States, areas of jurisdiction apply to local, state, and federal levels. Jurisdiction draws its substance from international law, conflict of laws, constitutional law, and the powers of the executive and legislative branches of government to allocate resources to best serve the needs of society. International dimension Generally, international laws and treaties provide agreements which nations agree to be bound to. Such agreements are not always established or maintained. The exercise of extraterritorial jurisdiction by three principles outlined in the UN charter. These are equality of states, territorial sovereignty and non-intervention. This raises the question of when can many states prescribe or enforce jurisdiction. The ''Lotus'' case establishes two key rules to the prescription and enforcement of jurisdi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Union Territories Of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions. History Pre-independence The Indian subcontinent has been ruled by many different ethnic groups throughout its history, each instituting their own policies of administrative division in the region. The British Raj mostly retained the administrative structure of the preceding Mughal Empire. India was divided into provinces (also called Presidencies), directly governed by the British, and princely states, which were nominally controlled by a local prince or raja loyal to the British Empire, which held ''de facto'' sovereignty ( suzerainty) over the princely states. 1947–1950 Between 1947 and 1950 the territories of the princely states were politically integrated into the Indian union. Most were merged into existing provinces; others were organised into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world. Origin and use The word "town" shares an origin with the German word , the Dutch word , and the Old Norse . The original Proto-Germanic word, *''tūnan'', is thought to be an early borrowing from Proto-Celtic *''dūnom'' (cf. Old Irish , Welsh ). The original sense of the word in both Germanic and Celtic was that of a fortress or an enclosure. Cognates of ''town'' in many modern Germanic languages designate a fence or a hedge. In English and Dutch, the meaning of the word took on the sense of the space which these fences enclosed, and through which a track must run. In England, a town was a small community that could not afford or was not allowed to build walls or other larger fortifications, and built a palisade or stockade instead. In the Netherlands, this space was a garden, mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postal Index Number
A Postal Index Number (PIN; sometimes redundantly a PIN code) refers to a six-digit code in the Indian postal code system used by India Post. On 15 August 2022, the PIN system celebrated its 50th anniversary. History The PIN system was introduced on 15 August 1972 by Shriram Bhikaji Velankar, an additional secretary in the Government of India's Ministry of Communications. The system was introduced to simplify the manual sorting and delivery of mail by eliminating confusion over incorrect addresses, similar place names, and different languages used by the public. PIN structure The first digit of a PIN indicates the zone, the second indicates the sub-zone, and the third, combined with the first two, indicates the sorting district within that zone. The final three digits are assigned to individual post offices within the sorting district. Postal zones There are nine postal zones in India, including eight regional zones and one functional zone (for the Indian Army). The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Standard Time
Indian Standard Time (IST), sometimes also called India Standard Time, is the time zone observed throughout India, with a time offset of UTC+05:30. India does not observe daylight saving time or other seasonal adjustments. In military and aviation time, IST is designated E* ("Echo-Star"). It is indicated as Asia/Kolkata in the IANA time zone database. History After Independence in 1947, the Union government established IST as the official time for the whole country, although Kolkata and Mumbai retained their own local time (known as Calcutta Time and Bombay Time) until 1948 and 1955, respectively. The Central observatory was moved from Chennai to a location at Shankargarh Fort in Allahabad district, so that it would be as close to UTC+05:30 as possible. Daylight Saving Time (DST) was used briefly during the China–India War of 1962 and the Indo-Pakistani Wars of 1965 and 1971. Calculation Indian Standard Time is calculated from the clock tower in Mirzapur nearly exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunwar Language
Sunuwar, Sunuwar, or Kõinch (; ; other spellings are Koinch and Koincha), is a Kiranti language spoken in Nepal and India by the Sunuwar people. It was first comprehensively attested by the Himalayan Languages Project. It is also known as Kõits Lo ( ; ), Kiranti-Kõits ( ; ), Mukhiya ( ; ). The Sunwar language is one of the smaller members of the Tibeto-Burman language family. About 40,000 speakers are residing in eastern Nepal. Names The language is commonly known as ''Koic,'' for many ethnic Sunwar and Sunwar speakers also refer to the language as “''Sunuwar, Kõinch'' '', Koinch'' or ''Koincha'' (कोँइच); ''Kõits Lo'' (कोँइच लो), ''Kiranti-Kõits'' (किराँती-कोँइच) or ''Mukhiya'' (मुखिया).” Moreover, most Sunwar speakers have the surname (सुनुवार), ''Sunuvār'' in Latin script. Many affiliated Sunwar with Sunar; they share the initial syllable, ''sun'', “gold,” in Nepali, similar to the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamang Language
Tamang (Devanagari: तामाङ; ''tāmāng'') is a term used to collectively refer to a dialect cluster spoken mainly in Nepal, Sikkim, West Bengal (Darjeeling) and North-Eastern India. It comprises Eastern Tamang, Northwestern Tamang, Southwestern Tamang, Eastern Gorkha Tamang, and Western Tamang. Lexical similarity between Eastern Tamang (which is regarded as the most prominent) and other Tamang languages varies between 81% to 63%. For comparison, lexical similarity between Spanish and Portuguese, is estimated at 89%. Ethnologue report for Spanish Dialects ''Ethnologue'' divides Tamang into the following varieties due to mutual unintelligibility. *Eastern Tamang: 759,000 in Nepal (2000 WCD). Population total all countries: 773,000. Sub-dialects are as follows. **Outer-Eastern Tamang (Sailung Tamang) **Central-Eastern Tamang (Temal Tamang) **Southwestern Tamang (Kath-Bhotiya, Lama Bhote, Murmi, Rongba, Sain, Tamang Gyoi, Tamang Gyot, Tamang Lengmo, Tamang Tam) *Western T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurung Language
Gurung (Devanagari: ), also known as Tamu Kyi (, ; Tibetan: ) or Tamu Bhaasaa (, ), is a language spoken by the Gurung people of Nepal. The total number of all Gurung speakers in Nepal was 227,918 in 1991 and 325,622 in 2011. The official language of Nepal, Nepali, is an Indo-European language, whereas Gurung is a Sino-Tibetan language. Gurung is one of the major languages of Nepal, and is also spoken in India, Bhutan, and by diaspora communities in countries such as Singapore and Hong Kong. Geographical distribution Gurung is spoken in the following districts of Nepal and India (''Ethnologue''): *Gandaki Province: Kaski District, Syangja District, Lamjung District, Tanahu District, Gorkha District, Manang District and Mustang *Dhawalagiri Zone: Parbat district *Sikkim: South Sikkim, West Sikkim, East Sikkim Classification At higher levels, Gurung is a member of the Tibeto-Burman (or Trans-Himalayan) family. Robert Shafer classified Gurung within the Bodic division, sub-gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)