|
Maniot Dialect
The Maniots or Maniates ( el, Μανιάτες) are the inhabitants of Mani Peninsula, located in western Laconia and eastern Messenia, in the southern Peloponnese, Greece. They were also formerly known as Mainotes and the peninsula as ''Maina''. The Maniots claim to be the descendants of the ancient Spartans and they have often been described as such. The terrain is mountainous and inaccessible (until recently many Mani villages could be accessed only by sea), and the regional name "Mani" is thought to have meant originally "dry" or "barren". The name "Maniot" is a derivative meaning "of Mani". In the early modern period, Maniots had a reputation as fierce and proudly independent warriors, who practiced piracy and fierce blood feuds. For the most part, the Maniots lived in fortified villages (and "house-towers") where they defended their lands against the armies of William II Villehardouin and later against those of the Ottoman Empire. Names The surnames of the Maniots unifo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
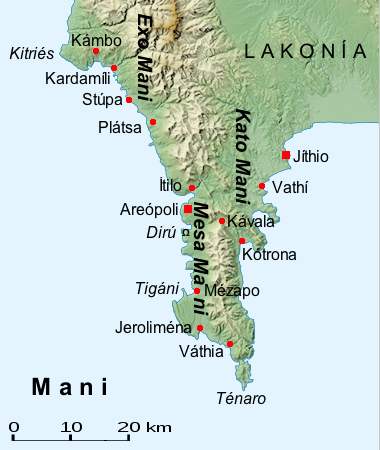
Mani Peninsula
The Mani Peninsula ( el, Μάνη, Mánē), also long known by its medieval name Maina or Maïna (Μαΐνη), is a geographical and cultural region in Southern Greece that is home to the Maniots (Mανιάτες, ''Maniátes'' in Greek), who claim descent from the ancient Spartans. The capital city of Mani is Areopoli. Mani is the central peninsula of the three which extend southwards from the Peloponnese in southern Greece. To the east is the Laconian Gulf, to the west the Messenian Gulf. The Mani peninsula forms a continuation of the Taygetos mountain range, the western spine of the Peloponnese. Etymology The name "Mani" may come from the Albanian language, albanian word mani meaning mullbery Geography The terrain is mountainous and inaccessible. Until recent years many Mani villages could be reached only by sea. Today a narrow and winding road extends along the west coast from Kalamata to Areopoli, then south to Akrotainaro (the pointed cape, which is the southernmost poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and contains 15,693 lines in its most widely accepted version, and was written in dactylic hexameter. Set towards the end of the Trojan War, a ten-year siege of the city of Troy by a coalition of Mycenaean Greek states, the poem depicts significant events in the siege's final weeks. In particular, it depicts a fierce quarrel between King Agamemnon and a celebrated warrior, Achilles. It is a central part of the Epic Cycle. The ''Iliad'' is often regarded as the first substantial piece of European literature. The ''Iliad'', and the ''Odyssey'', were likely written down in Homeric Greek, a literary amalgam of Ionic Greek and other dialects, probably around the late 8th or early 7th century BC. Homer's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalogue Of Ships
The Catalogue of Ships ( grc, νεῶν κατάλογος, ''neōn katálogos'') is an epic catalogue in Book 2 of Homer's ''Iliad'' (2.494–759), which lists the contingents of the Achaean army that sailed to Troy. The catalogue gives the names of the leaders of each contingent, lists the settlements in the kingdom represented by the contingent, sometimes with a descriptive epithet that fills out a half-verse or articulates the flow of names and parentage and place, and gives the number of ships required to transport the men to Troy, offering further differentiations of weightiness. A similar, though shorter, Catalogue of the Trojans and their allies follows (2.816–877). A similar catalogue appears in the Pseudo-Apollodoran ''Bibliotheca''. Historical background In the debate since antiquity over the Catalogue of Ships, the core questions have concerned the extent of historical credibility of the account, whether it was composed by Homer himself, to what extent it reflec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the most revered and influential authors in history. Homer's ''Iliad'' centers on a quarrel between King Agamemnon and the warrior Achilles during the last year of the Trojan War. The ''Odyssey'' chronicles the ten-year journey of Odysseus, king of Ithaca, back to his home after the fall of Troy. The poems are in Homeric Greek, also known as Epic Greek, a literary language which shows a mixture of features of the Ionic and Aeolic dialects from different centuries; the predominant influence is Eastern Ionic. Most researchers believe that the poems were originally transmitted orally. Homer's epic poems shaped aspects of ancient Greek culture and education, fostering ideals of heroism, glory, and honor. To Plato, Homer was simply the one who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William II Villehardouin
William of Villehardouin (french: Guillaume de Villehardouin; Kalamata, 1211 – 1 May 1278) was the fourth prince of Achaea in Frankish Greece, from 1246 to 1278. The younger son of Prince Geoffrey I, he held the Barony of Kalamata in fief during the reign of his elder brother Geoffrey II. William ruled Achaea as regent for his brother during Geoffrey's military campaigns against the Greeks of Nicaea, who were the principal enemies of his overlord, the Latin Emperor of Constantinople Baldwin II. William succeeded his childless brother in the summer of 1246. Conflicts between Nicaea and Epirus enabled him to complete the conquest of the Morea in about three years. He captured Monemvasia and built three new fortresses, forcing two previously autonomous tribes, the Tzakones and Melingoi, into submission. He participated in the unsuccessful Egyptian crusade of Louis IX of France, who rewarded him with the right to issue currency in the style of French ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feud
A feud , referred to in more extreme cases as a blood feud, vendetta, faida, clan war, gang war, or private war, is a long-running argument or fight, often between social groups of people, especially families or clans. Feuds begin because one party perceives itself to have been attacked, insulted, injured, or otherwise wronged by another. Intense feelings of resentment trigger an initial retribution, which causes the other party to feel greatly aggrieved and vengeful. The dispute is subsequently fuelled by a long-running cycle of retaliatory violence. This continual cycle of provocation and retaliation usually makes it extremely difficult to end the feud peacefully. Feuds can persist for generations and may result in extreme acts of violence. They can be interpreted as an extreme outgrowth of social relations based in family honor. Until the early modern period, feuds were considered legitimate legal instruments and were regulated to some degree. For example, Montenegrin cultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, vessels used for piracy are pirate ships. The earliest documented instances of piracy were in the 14th century BC, when the Sea Peoples, a group of ocean raiders, attacked the ships of the Aegean and Mediterranean civilisations. Narrow channels which funnel shipping into predictable routes have long created opportunities for piracy, as well as for privateering and commerce raiding. Historic examples include the waters of Gibraltar, the Strait of Malacca, Madagascar, the Gulf of Aden, and the English Channel, whose geographic structures facilitated pirate attacks. The term ''piracy'' generally refers to maritime piracy, although the term has been generalized to refer to acts committed on land, in the air, on computer networks, and (in scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warrior
A warrior is a person specializing in combat or warfare, especially within the context of a tribal or clan-based warrior culture society that recognizes a separate warrior aristocracies, class, or caste. History Warriors seem to have been present in the earliest pre-state societies. Scholars have argued that horse-riding Yamnaya warriors from the Pontic–Caspian steppe played a key role during the Indo-European migrations and the diffusion of Indo-European languages across Eurasia. Most of the basic weapons used by warriors appeared before the rise of most hierarchical systems. Bows and arrows, clubs, spears, swords, and other edged weapons were in widespread use. However, with the new findings of metallurgy, the aforementioned weapons had grown in effectiveness. When the first hierarchical systems evolved 5000 years ago, the gap between the rulers and the ruled had increased. Making war to extend the outreach of their territories, rulers often forced men from lower orders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_Homer_and_his_Guide_(1874).jpg)