|
Manga Sewa
Manga Sewa (died 1884) was a Yalunka paramount chief in British Sierra Leone who blew up a magazine and much of Falaba, the capital of Solimana, killing himself, his family and other leaders, rather than let it fall to Samori Toure's army. Early life and career Manga Sewa was born in Falaba, Solimana chiefdom, in the Northern Province of British Sierra Leone to Yalunka parents. His father was a Yalunka paramount chief of Solimana, a prosperous chieftaincy. Its capital, Falaba, was on the rich trading routes leading to the coast. Manga Sewa's father had a number of wives and dozens of children. Touré 1884 attack Manga Sewa became paramount chief of Solimana, a state in Northern Province. He was from one of the ruling families of the chieftaincy and would have been chief for life. In the Beyla region of Guinea, Samori Toure (c.1830-1900), of the Touré clan, had expanded his influence; by 1878 he proclaimed himself ''faama'' (military leader) of his own Wassoulou Empire. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yalunka People
The Yalunka, or Dialonké, are a Mandé-speaking people who were one of the original inhabitants of the Futa Jallon (french: Fouta Djallon, links=no), a mountainous region in Guinea, West Africa. The Yalunka people live primarily in Guinea, particularly in Faranah, while smaller communities are found in Kouroussa. Additional Yalunka are also located in northeastern Sierra Leone, southeastern Senegal, and southwestern Mali. The Yalunka are a branch of the Mandé peoples and are closely related to the Susu people. Some scholars classify the two as one group, The Yalunka are notable for having first converted to Islam, but then renouncing Islam en masse when Muslim Fula people began dominating their region. In the eighteenth century, many of the Yalunka's were displaced from the Futa Jallon. The Yalunka fought against the Fula jihads, left Futa Jallon, migrating south to the foothills of the mountains in Mamou or east to live amongst the Mandinka people of Upper Guinea, others mig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribal Chief
A tribal chief or chieftain is the leader of a tribal society or chiefdom. Tribe The concept of tribe is a broadly applied concept, based on tribal concepts of societies of western Afroeurasia. Tribal societies are sometimes categorized as an intermediate stage between the band society of the Paleolithic stage and civilization with centralized, super-regional government based in cities. Anthropologist Elman Service distinguishes two stages of tribal societies: simple societies organized by limited instances of social rank and prestige, and more stratified societies led by chieftains or tribal kings (chiefdoms). Stratified tribal societies led by tribal kings are thought to have flourished from the Neolithic stage into the Iron Age, albeit in competition with urban civilisations and empires beginning in the Bronze Age. In the case of tribal societies of indigenous peoples existing within larger colonial and post-colonial states, tribal chiefs may represent their tribe or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Sierra Leone
The Colony and Protectorate of Sierra Leone (informally British Sierra Leone) was the British colonial administration in Sierra Leone from 1808 to 1961, part of the British Empire from the abolitionism era until the decolonisation era. The Crown colony, which included the area surrounding Freetown, was established in 1808. The protectorate was established in 1896 and included the interior of what is today known as Sierra Leone. The motto of the colony and protectorate was (Latin for "Free under the protection of Britain"). This motto was included on Sierra Leone's later flag and coat of arms. History Origins In the 1780s, London was home to several thousand freed slaves and Black Pioneers, who had gained their freedom fighting on the side of the British in the American Revolutionary War. After several avenues to employment were closed to them, many of the Black Poor ended up destitute, and received support from the Committee for the Relief of the Black Poor. This Committee ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
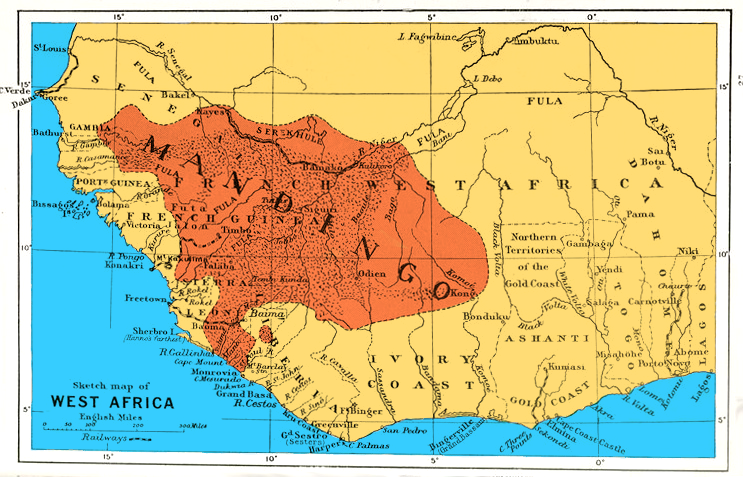
Falaba
{{Infobox settlement , official_name = Falaba , other_name = , native_name = , nickname = , settlement_type = , motto = , image_skyline = , imagesize = , image_caption = , image_flag = , flag_size = , image_seal = , seal_size = , image_shield = , shield_size = , image_blank_emblem = , blank_emblem_type = , blank_emblem_size = , image_map = , mapsize = , map_caption = , image_map1 = , mapsize1 = , map_caption1 = , image_dot_map = , dot_mapsize = , dot_map_caption = , dot_x = , dot_y = , pushpin_map = Sierra Leone , pushpin_label_position =bottom , pushpin_map_caption =Location in Sierra Leone , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Sierra Leon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solimana (state)
Solimana was a minor West African state of the nineteenth century with a capital at the fortress town of Falaba. Situated on rich slave-trading routes in what is now Sierra Leone, Solimana was visited in 1822 by Alexander Gordon Laing and in 1869 by William Winwood Reade, making it nominally British. In 1884, Mandinka conqueror Samori joined the king of Kaliere in attacking Solimana, then under the rule of Manga Sewa. After Samori's general N'fa Ali destroyed a number of surrounding villages, the Mandinka forces began a five-month siege of Falaba itself. With the city's residents starved nearly to death, Manga Sewa gathered his family in Falaba's gunpowder magazine and lit a torch, simultaneously killing himself and breaching Falaba's walls. The territory of Solimana was then briefly assimilated into Samori's Wassoulou Empire The Wassoulou Empire, sometimes referred to as the Mandinka Empire, was a short-lived (1878–1898) empire of West Africa built from the conques ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samori Ture
Samory Toure ( – June 2, 1900), also known as Samori Toure, Samory Touré, or Almamy Samore Lafiya Toure, was a Muslim cleric, a military strategist, and the founder and leader of the Wassoulou Empire, an Islamic empire that was in present-day north and south-eastern Guinea and included part of north-eastern Sierra Leone, part of Mali, part of northern Côte d'Ivoire and part of southern Burkina Faso. Samori Ture was a deeply religious Muslim of the Maliki jurisprudence of Sunni Islam. Toure resisted French colonial rule in West Africa from 1882 until his capture in 1898. Samori Toure was the great-grandfather of Guinea's first president, Ahmed Sékou Touré. Early life and career Samori Ture was Mandinka, born in c. 1830 in Manyambaladugu (in the Kankan region). Kankan is the second capital city located in eastern part of Guinea West, the son of Dyula traders. He grew up as West Africa was being transformed through growing contacts and trade with the Europeans in commodities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Province, Sierra Leone
The Northern Province (commonly referred to as Northern Sierra Leone or simply the North) is one of the five provincial divisions of Sierra Leone. It is located in the Northern geographic region of Sierra Leone. It comprises the following four Districts: Bombali, Falaba, Koinadugu and Tonkolili. The Northern Province covers an area of with a population of 2,502,865, based on the 2015 Sierra Leone national censu Its Administrative centre, administrative and economic center is Makeni. The North borders the Western Area to the West, the Republic of Guinea to the north-east, the Eastern Province and Southern Province to the south-east. Geography Overview The Northern province is mainly a hilly wooded area with mountainous area farther inland. The region has ranges of Mountains, Hills, Valleys and Wetlands; comprising unique and endangered species. The region is a political stronghold of the All People's Congress (APC) political party. The APC currently controls all the elected s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, the Gambia and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the largest ethnic-linguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family and a ''lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. Over 99% of Mandinka adhere to Islam. They are predominantly subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia and the Casamance region in Senegal to Iv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuranko People
The Kuranko, also called Koranko, Kolanko, Kooranko, Koronko, Kouranko, Kulanko, Kurako, Kuronko, Kuranké, or Karanko, are a Mande people living in Guinea and Sierra Leone. The Koranko occupy a large section in a mountainous region within northeastern Sierra Leone and southern Guinea. Within this geographical region, different dialects, as well as distinct social groupings can be found. In general, the Koranko are a peaceful people who have maintained a separate ethnic identity, despite years of tribal mixings. Each Kuranko village is led by a chief and a group of elders. The Koranko speak the Kuranko language (or Koranko), a dialect of the Mande branch of the Niger–Congo language family. The Kuranko are nominally an Islamic people, but many people in this isolated area still follow traditional religious beliefs, identifying as Muslim without adhering to all the strict protocols of that religion. The Kuranko speak a language similar to the Manding languages, and their langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jihad
Jihad (; ar, جهاد, jihād ) is an Arabic word which literally means "striving" or "struggling", especially with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it can refer to almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with God's guidance, such as struggle against one's evil inclinations, proselytizing, or efforts toward the moral betterment of the Muslim community (''Ummah''), though it is most frequently associated with war. In classical Islamic law (''sharia''), the term refers to armed struggle against unbelievers, while modernist Islamic scholars generally equate military ''jihad'' with defensive warfare. In Sufi circles, spiritual and moral jihad has been traditionally emphasized under the name of ''greater jihad''. The term has gained additional attention in recent decades through its use by various insurgent Islamic extremist, militant Islamist, and terrorist individuals and organizations whose ideology is based on the Islamic notion of ''jihad''. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fouta Djallon
Fouta Djallon ( ff, 𞤊𞤵𞥅𞤼𞤢 𞤔𞤢𞤤𞤮𞥅, Fuuta Jaloo; ar, فوتا جالون) is a Highland (geography), highland region in the center of Guinea, roughly corresponding with Middle Guinea, in West Africa. Etymology The Fulani people call the region in the Pular language. The origin of the name is from the Fula language, Fula word for any region inhabited by , plus the name of the original inhabitants, the Yalunka people (french: Djallonké, links=no). History Since the 17th century, the Fouta Djallon region has been a stronghold of Islam. Early revolutionaries led by Karamokho Alfa and Ibrahim Sori set up a federation divided into nine provinces. Several succession crises weakened the central power located in Timbo, Guinea, Timbo until 1896, when the last Almamy, Bubakar Biro, was defeated by the French army in the Battle of Porédaka. The Fulɓe of Fouta Djallonke spearheaded the expansion of Islam in the region.Mats Widgren, "Slaves: Inequality and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)