|
Manchurian Mixed Forests
The Manchurian mixed forests ecoregion (WWF ID: PA0426) covers the forested hills surrounding the river plains of northern China, Russia, North Korea, and South Korea. The ecoregion supports a number of rare species due to the relative isolation, the diversity of habitat, with mixed forests of deciduous Mongolian oak and conifers of Korean pine. Because mountains rise above the region on three sides, with plains and wetlands below, the area supports high biodiversity as a transition zone. Location and description The ecoregion occupies the middle-elevation slopes of three surrounding mountain ranges: the eastern slopes of the Greater Khingan Mountains, the southern slopes of the Lesser Khingan, and the western slopes of the Changbai Mountains. The southern section of the ecoregion surrounds the higher Changbai Mountains mixed forests ecoregion, while the middle section encircles most of the lower-elevation Northeast China Plain deciduous forests ecoregion, and the northern hal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palearctic Realm
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa. The realm consists of several bioregions: the Euro-Siberian region; the Mediterranean Basin; the Sahara and Arabian Deserts; and Western, Central and East Asia. The Palaearctic realm also has numerous rivers and lakes, forming several freshwater ecoregions. The term 'Palearctic' was first used in the 19th century, and is still in use as the basis for zoogeographic classification. History In an 1858 paper for the ''Proceedings of the Linnean Society'', British zoologist Philip Sclater first identified six terrestrial zoogeographic realms of the world: Palaearctic, Aethiopian/Afrotropic, Indian/Indomalayan, Australasian, Nearctic, and Neotropical. The six indicated general groupings of fauna, based on shared biogeography and large-scale geographic barriers to migration. Alfred Wallace ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
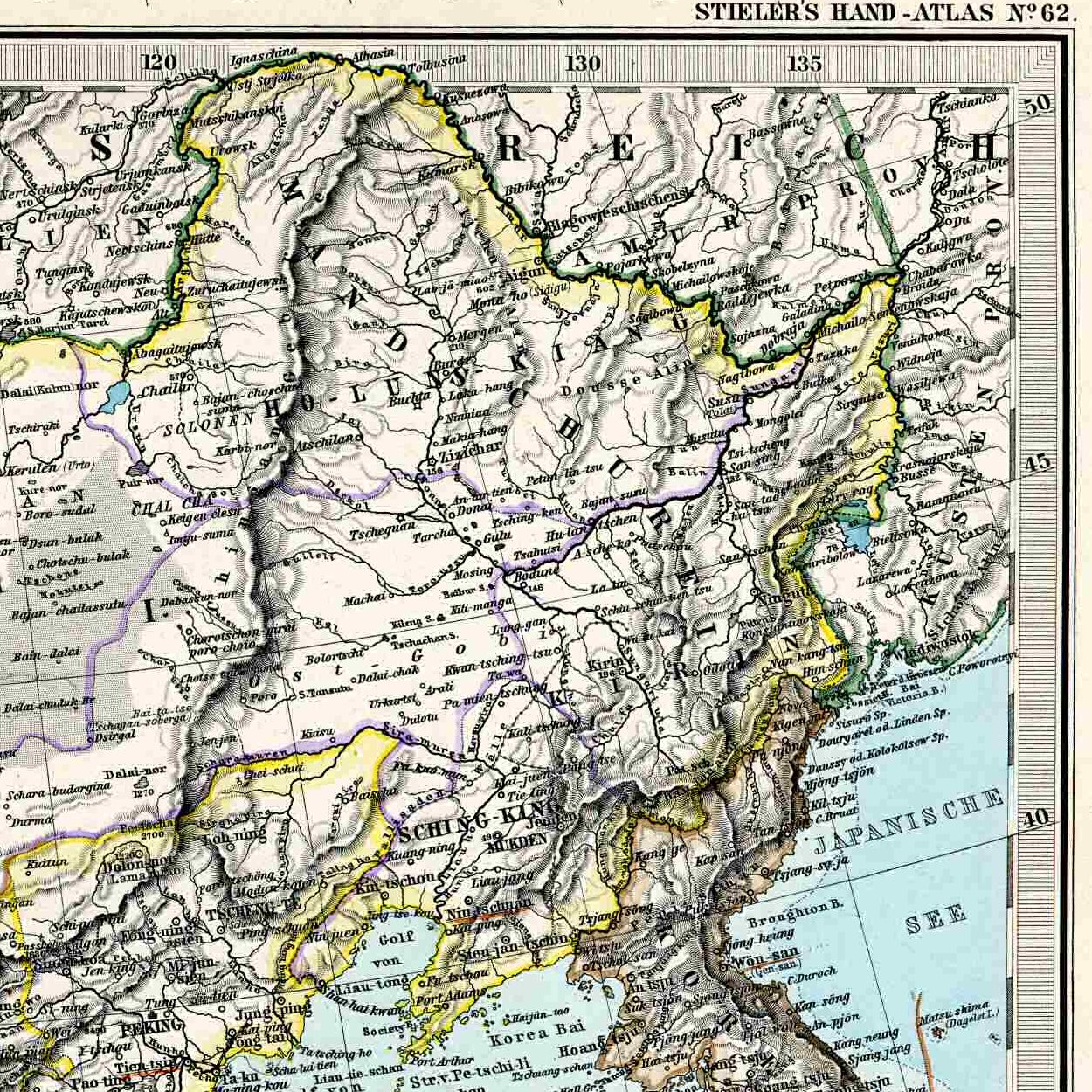
Lesser Khingan
Lesser Khingan (; russian: Малый Хинган, ''Maly Khingan'') is a mountain range in China's Heilongjiang province and the adjacent parts of Russia's Amur Oblast and Jewish Autonomous Oblast.Малый Хинган '''' in 30 vols. — Ch. ed. . - 3rd ed. - M. Soviet Encyclopedia, 1969-1978. (in Russian) In Russia, the range is part of the . Geo ...
|
Land Of The Leopard National Park
Land of the Leopard National Park is a national park in Primorsky Krai in the Russian Far East, covering an area of west of Razdolnaya River. It was gazetted in April 2012. It was established to protect the Amur leopard which was at the time the world's rarest cat with an estimated population of 30 individuals. The park was created from the merger of Kedrovaya Pad Nature Reserve, Barsovy Federal Wildlife Refuge and Borisovkoye Plateau Regional Wildlife Refuge, and a new territory along the border with China. History By the beginning of the 21st century the Amur leopard population was on the verge of extinction. As a result of poaching and fires, the vast habitat of the beast had shrunk to a narrow stripe in the southwest of Primorsky Krai. By then, a Kedrovaya Pad nature reserve and several breeding grounds existed here, but only expansion of the protected area and integrated management of the existing natural territories could solve the problem of conserving the rare cat. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Area
Protected areas or conservation areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognized natural, ecological or cultural values. There are several kinds of protected areas, which vary by level of protection depending on the enabling laws of each country or the regulations of the international organizations involved. Generally speaking though, protected areas are understood to be those in which human presence or at least the exploitation of natural resources (e.g. firewood, non-timber forest products, water, ...) is limited. The term "protected area" also includes marine protected areas, the boundaries of which will include some area of ocean, and transboundary protected areas that overlap multiple countries which remove the borders inside the area for conservation and economic purposes. There are over 161,000 protected areas in the world (as of October 2010) with more added daily, representing between 10 and 15 percent of the world's land surface area. As of 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinus Sylvestris
''Pinus sylvestris'', the Scots pine (UK), Scotch pine (US) or Baltic pine, is a species of tree in the pine family Pinaceae that is native to Eurasia. It can readily be identified by its combination of fairly short, blue-green leaves and orange-red bark. Description ''Pinus sylvestris'' is an evergreen coniferous tree growing up to in height and in trunk diameter when mature, exceptionally over tall and in trunk diameter on very productive sites. The tallest on record is a tree over 210 years old tree growing in Estonia which stands at . The lifespan is normally 150–300 years, with the oldest recorded specimens in Lapland, Northern Finland over 760 years. The bark is thick, flaky and orange-red when young to scaly and gray-brown in maturity, sometimes retaining the former on the upper portion.Trees for LifeSpecies profile: Scots pine/ref> The habit of the mature tree is distinctive due to its long, bare and straight trunk topped by a rounded or flat-topped mass of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulmus Laciniata
''Ulmus laciniata'' (Trautv.) Mayr, known variously as the Manchurian, cut-leaf, or lobed elm, is a deciduous tree native to the humid ravine forests of Japan, Korea, northern China, eastern Siberia and Sakhalin, growing alongside ''Cercidiphyllum japonicum'', ''Aesculus turbinata'', and ''Pterocarya rhoifolia'',Sasaki, Y. (1979) Der Verband Pterocaryon rhoifoliae in Japan. In: Vegetation und Landschaft Japans. Eds: Miyawaki, A., and Okuda, S. ''Bull. Yokohama Phytosoc. Soc. Japan.'' 16, 1979. pp. 213-226Ohwi, J. (1984). Flora of Japan. Qian, H., Krestov, P., Fu, P.-Y., Wang, Q.-L., Song, J.-S. & Chourmouzis, C. Phytogeography of Northeast Asia. http://www.biosoil.ru/files/00000052.pdf at elevations of 700–2200 m, though sometimes lower in more northern latitudes, notably in Hokkaido. The tree is similar to the Wych elm ''Ulmus glabra'', and was originally treated as such by Houtzagers and Henry, but later accorded species status of its own largely by reason of the enormous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tilia Amurensis
''Tilia amurensis'', the Amur lime or Amur linden, is a species of ''Tilia'' native to eastern Asia. It differs from the better-known ''Tilia cordata'' in having somewhat smaller leaves, bracts and cymes. It is an important timber tree in Russia, China and Korea, and is occasionally planted as a street tree in cities with colder climates. Description ''Tilia amurensis'' is a medium sized shade tree which can grow up to tall. The appearance is quite similar to ''Tilia japonica ''Tilia japonica'', the Japanese lime or Japanese linden, is a species of ''Tilia'' native to eastern China and Japan, preferring to grow in mountains up to 2000m. It superficially resembles the better-known '' Tilia cordata'', the small-leaved l ...'' besides the difference in size of leaves, bracts and a shorter cyme. ''Tilia amurensis'' is a hermaphrodite which means it contains both female and male organs and is mainly pollinated by insects. Habitat ''T. amurensis'' prefer a medium moisture leve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraxinus Mandschurica
''Fraxinus mandshurica'', the Manchurian ash, is a species of ''Fraxinus'' native to northeastern Asia in northern China (Gansu, Hebei, Heilongjiang, Henan, Hubei, Jilin, Liaoning, Shaanxi, Shanxi), Korea, Japan and southeastern Russia ( Sakhalin Island). It is a medium-sized to large deciduous tree reaching 30 m tall, with a trunk up to 50 cm in diameter. The leaves are 25–40 cm long, pinnate compound, with 7–13 leaflets, the leaflets 5–20 cm long and 2–5 cm broad, subsessile on the leaf rachis, and with a serrated margin. They turn to a golden-yellow in early autumn, and the tree is usually early to change color. The flowers are produced in early spring, before the new leaves, in compact panicles; they are inconspicuous with no petals, and are wind-pollinated. The fruit is a samara comprising a single seed 1–2 cm long with an elongated apical wing 2.5–4 cm long and 5–7 mm broad. It is closely related to ''Fraxinus nigra'' (Blac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quercus Mongolica
''Quercus mongolica'', commonly known as Mongolian oak, is a species of oak native to Japan, China, Korea, Mongolia, and Siberia. The species can grow to be tall. The flavono-ellagitannin The Flavono-ellagitannins or complex tannins are a class of tannins formed from the complexation of an ellagitannin with a flavonoid. Flavono-ellagitannins can be found in '' Quercus mongolica var. grosseserrata''. Examples * Acutissimin A * Ac ...s mongolicin A and B can be found in ''Quercus mongolica var. grosseserrata''. LXXI. Isolation and characterization of mongolicins A and B, novel flavono-ellagitannins from ''Quercus mongolica'' var. ''grosseserrata''. Ishimaru K, Ishimatsu M, Nonaka G, Mihashi K, Iwase Y and Nishioka I, Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1988, volume 36, number 9, pages 3312– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picea Obovata
''Picea obovata'', the Siberian spruce, is a spruce native to Siberia, from the Ural Mountains east to Magadan Oblast, and from the Arctic tree line south to the Altay Mountains in northwestern Mongolia. Description and uses It is a medium-sized evergreen tree growing to 15–35 m tall, and with a trunk diameter of up to 1.5 m, and a conical crown with drooping branchlets. The shoots are orange-brown, with variably scattered to dense pubescence. The leaves are needle-like, 1–2 cm long, rhombic in cross-section, shiny green to grayish-green with inconspicuous stomatal lines; the leaves subtending a bud are distinctively angled out at a greater angle than the rest of the leaves (a character shared by only two or three other spruces). The cones are cylindric-conic, 5–10 cm long and 1.5–2 cm broad, green or purple, maturing glossy brown 4–6 months after pollination, and have stiff, smoothly rounded scales. It is an important timber tree in Russia, the wood bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abies Holophylla
''Abies holophylla'', also called needle fir or Manchurian fir, is a species of fir native to mountainous regions of northern Korea, southern Ussuriland, and China in the provinces of Heilongjiang, Jilin, and Liaoning. It is an evergreen coniferous tree growing to tall and in trunk diameter with a narrowly conical crown of horizontal spreading branches. The bark is scaly and gray-brown with resin blisters. The leaves ("needles") are flattened, long and thick, spread at right angles from the shoot, and end in a point. They spread on two sides, but not flat like for example in silver fir. Usually they more or less rise up forming with the shoot a V-shape empty compartment above it. Unlike in silver fir, the leaves here are sharp and prickly, without any indentation at the top. They are bright green above and whitish-green below with 2 whitish strips, each of which is formed by 7–10 wax-covered stomatal bands. The shoots are glabrous, shiny yellow-gray when young and tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinus Koraiensis
''Pinus koraiensis'' is a species of pine known commonly as the Korean pine. It is native to eastern Asia: Korea, northeastern China, Mongolia, the temperate rainforests of the Russian Far East, and central Japan. In the north of its range, it grows at moderate elevations, typically , whereas further south, it is a mountain tree, growing at elevation in Japan. Other common names include Chinese pinenut. Description It is a member of the white pine group, ''Pinus'', section ''Quinquefoliae''. In its native habitat and growing conditions it can reach in height. Cultivated specimens may grow up to tall. It is pyramidal in shape, younger specimens with ascending branches and older trees with more horizontal branches that reach ground level. The gray or brownish bark flakes off to reveal reddish inner bark. Its branches are lined with bundles of five blue-green needles each up to and bear brown cones up to long. Uses and conservation The nuts of this tree are edible and sold comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)