|
Management Of Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory demyelinating disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS). Several therapies for it exist, although there is no known cure. The most common initial course of the disease is the relapsing-remitting subtype, which is characterized by unpredictable attacks (relapses) followed by periods of relative remission with no new signs of disease activity. After some years, many of the people who have this subtype begin to experience neurologic decline without acute relapses. When this happens it is called secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Other, less common, courses of the disease are the primary progressive (decline from the beginning without attacks) and the progressive-relapsing (steady neurologic decline and superimposed attacks). Different therapies are used for patients experiencing acute attacks, for patients who have the relapsing-remitting subtype, for patients who have the progressive subtypes, for patients without ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Specific symptoms can include double vision, blindness in one eye, muscle weakness, and trouble with sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In the relapsing forms of MS, between attacks, symptoms may disappear completely, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. While the cause is unclear, the underlying mechanism is thought to be either destruction by the immune system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disease-modifying Treatment
A disease-modifying treatment, disease-modifying drug, or disease-modifying therapy is a treatment that delays or slows the progression of a disease by targeting its underlying cause. They are distinguished from symptomatic treatments that treat the symptoms of a disease but do not address its underlying cause. Examples * Disease-modifying osteoarthritis drug * Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) comprise a category of otherwise unrelated disease-modifying drugs defined by their use in rheumatoid arthritis to slow down disease progression. The term is often used in contrast to nonsteroidal ... References {{Reflist Medical treatments Medical terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teriflunomide
Teriflunomide, sold under the brand name Aubagio, is the active metabolite of leflunomide. Teriflunomide was investigated in the Phase III clinical trial TEMSO as a medication for multiple sclerosis (MS). The study was completed in July 2010. 2-year results were positive. However, the subsequent TENERE head-to-head comparison trial reported that "although permanent discontinuations f therapywere substantially less common among MS patients who received teriflunomide compared with interferon beta-1a, relapses were more common with teriflunomide." The drug was approved for use in the United States in September 2012 and for use in the European Union in August 2013. Mechanisms of action Teriflunomide is an immunomodulatory drug inhibiting pyrimidine de novo synthesis by blocking the enzyme dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. It is uncertain whether this explains its effect on MS lesions. Teriflunomide inhibits rapidly dividing cells, including activated T cells, which are thought to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fingolimod
Fingolimod, sold under the brand name Gilenya, is an immunomodulating medication, mostly used for treating multiple sclerosis (MS). Fingolimod is a sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator, which sequesters lymphocytes in lymph nodes, preventing them from contributing to an autoimmune reaction. It has been reported to reduce the rate of relapses in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis by approximately one-half over a two-year period. Medical uses Fingolimod is used in the treatment of the relapsing form of multiple sclerosis. Its effect in those with primary progressive MS is not clear. It may also be used in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Adverse effects The most common side effects of fingolimod have been head colds, headache, increased gamma-glutamyl transfer (≤15%), diarrhea (13%), nausea (13%), abdominal pain (11%) and fatigue. A few cases of skin cancer have been reported, which has also been reported in patients taking natalizumab (Tysabri), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitoxantrone
Mitoxantrone (INN, BAN, USAN; also known as Mitozantrone in Australia; trade name Novantrone) is an anthracenedione antineoplastic agent. Uses Mitoxantrone is used to treat certain types of cancer, mostly acute myeloid leukemia. It improves the survival rate of children suffering from acute lymphoblastic leukemia relapse. The combination of mitoxantrone and prednisone is approved as a second-line treatment for metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Until recently this combination was the first line of treatment; however, a combination of docetaxel and prednisone improves survival rates and lengthens the disease-free period. Mitoxantrone is also used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS), most notably the subset of the disease known as secondary-progressive MS. In the absence of a cure, mitoxantrone is effective in slowing the progression of secondary-progressive MS and extending the time between relapses in both relapsing-remitting MS and progressive-relapsing MS. Side eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glatiramer Acetate
Glatiramer acetate (also known as Copolymer 1, Cop-1), sold under the brand name Copaxone among others, is an immunomodulator medication used to treat multiple sclerosis. Glatiramer acetate is approved in the United States to reduce the frequency of relapses, but not for reducing the progression of disability. Observational studies, but not randomized controlled trials, suggest that it may reduce progression of disability. While a conclusive diagnosis of multiple sclerosis requires a history of two or more episodes of symptoms and signs, glatiramer acetate is approved to treat a first episode anticipating a diagnosis. It is also used to treat relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. It is administered by subcutaneous injection. It is a mixture of random-sized peptides that are composed of the four amino acids found in myelin basic protein, namely glutamic acid, lysine, alanine, and tyrosine. Myelin basic protein is the antigen in the myelin sheaths of the neurons that stimulates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocrelizumab
Ocrelizumab, sold under the brand name Ocrevus, is a medication used for the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS). It is a humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody. It targets CD20 marker on B lymphocytes and hence is an immunosuppressive drug. Ocrelizumab binds to an epitope that overlaps with the epitope to which rituximab binds. It was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in March 2017, and the first FDA approved drug for the primary progressive form of MS; it was discovered and developed and is marketed by Hoffmann–La Roche's subsidiary Genentech under the trade name Ocrevus. With the approval, the FDA also required the company to conduct several Phase IV clinical trials to better understand whether the drug is safe and effective in young people, cancer risks, and effects on pregnant women and children they might bear. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication. Medical uses In the US, ocrelizumab is indicated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alemtuzumab
Alemtuzumab, sold under the brand names Campath and Lemtrada among others, is a medication used to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and multiple sclerosis. In CLL, it has been used as both a first line and second line treatment. In MS it is generally only recommended if other treatments have not worked. It is given by injection into a vein. It is a monoclonal antibody that binds to CD52, a protein present on the surface of mature lymphocytes, but not on the stem cells from which these lymphocytes are derived. After treatment with alemtuzumab, these CD52-bearing lymphocytes are targeted for destruction. Alemtuzumab was approved for medical use in the United States in 2001. (Mab)Campath was withdrawn from the markets in the US and Europe in 2012, to prepare for a higher-priced relaunch of Lemtrada aimed at multiple sclerosis. Medical uses Chronic lymphocytic leukemia Alemtuzumab is used for the treatment of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) in people who have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natalizumab
Natalizumab, sold under the brand name Tysabri among others, is a medication used to treat multiple sclerosis and Crohn's disease. It is a humanized monoclonal antibody against the cell adhesion molecule α4-integrin. It is given by intravenous infusion every 28 days. The drug is believed to work by reducing the ability of inflammatory immune cells to attach to and pass through the cell layers lining the intestines and blood–brain barrier. Natalizumab has proven effective in treating the symptoms of both diseases, preventing relapse, vision loss, cognitive decline and significantly improving quality of life in people with multiple sclerosis, as well as increasing rates of remission and preventing relapse in multiple sclerosis. Natalizumab, is a monoclonal antibody which targets a protein called α4β1 integrin on white blood cells involved in inflammation. By attaching to integrin, natalizumab is thought to stop white blood cells from entering the brain and spinal cord tiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
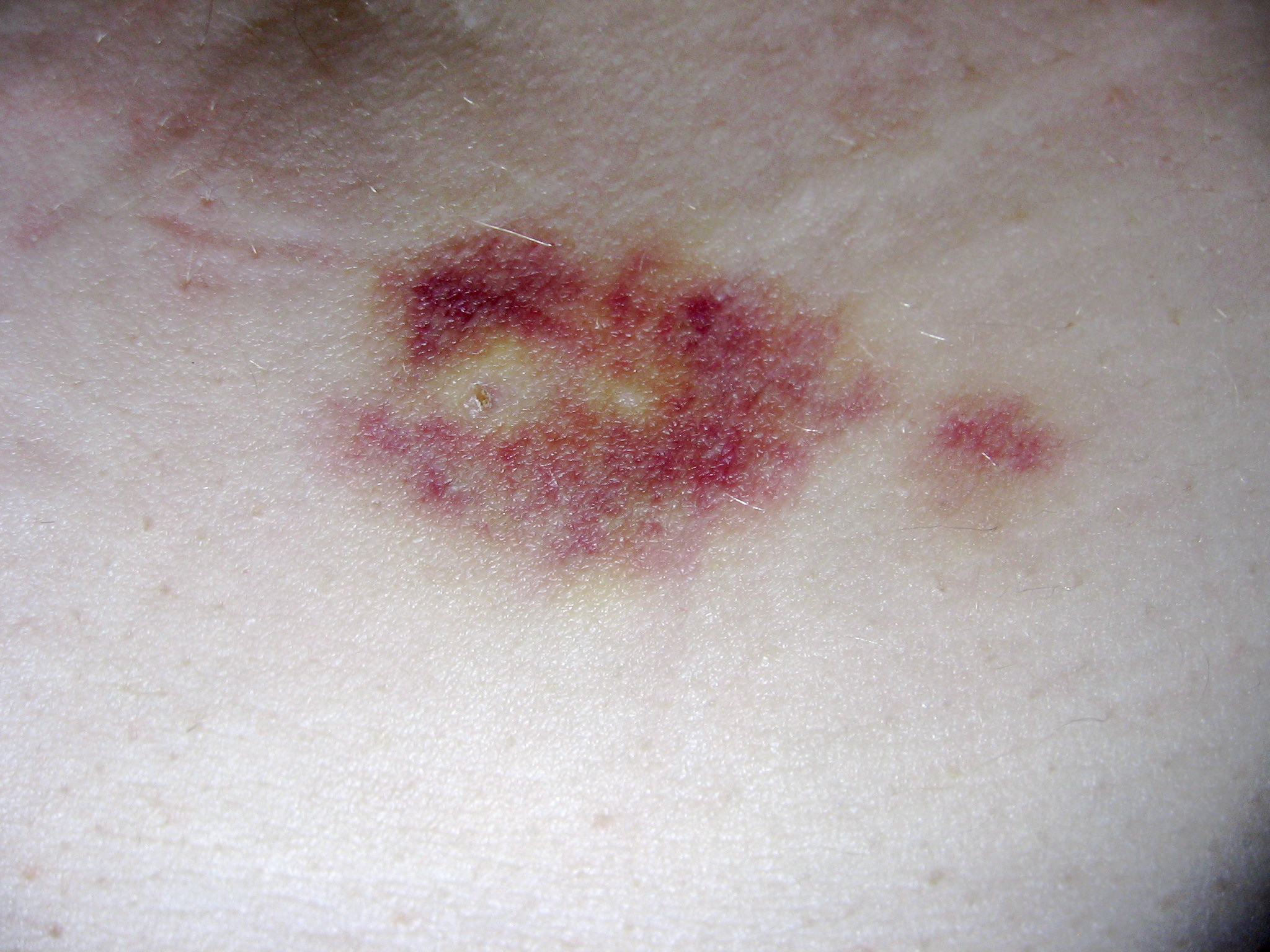
Interferon Beta-1b
Interferon beta-1b is a cytokine in the interferon family used to treat the relapsing-remitting and secondary-progressive forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). It is approved for use after the first MS event. Closely related is interferon beta 1a, also indicated for MS, with a very similar drug profile. Mechanism of action Interferon beta balances the expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory agents in the brain, and reduces the number of inflammatory cells that cross the blood brain barrier. Overall, therapy with interferon beta leads to a reduction of neuron inflammation. Moreover, it is also thought to increase the production of nerve growth factor and consequently improve neuronal survival. Side effects Interferon beta-1b is available only in injectable forms, and can cause skin reactions at the injection site that may include cutaneous necrosis. Skin reactions vary greatly in their clinical presentation. They usually appear within the first month of treatment albeit their freque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferon Beta-1a
Interferon beta-1a (also interferon beta 1-alpha) is a cytokine in the interferon family used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS). It is produced by mammalian cells, while interferon beta-1b is produced in modified '' E. coli''. Some research indicates that interferon injections may result in an 18–38% reduction in the rate of MS relapses. Interferon beta has not been shown to slow the advance of disability. Interferons are not a cure for MS (there is no known cure); the claim is that interferons may slow the progress of the disease if started early and continued for the duration of the disease. Medical uses Clinically isolated syndrome The earliest clinical presentation of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis is the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS), that is, a single attack of a single symptom. During a CIS, there is a subacute attack suggestive of demyelination which should be included in the spectrum of MS phenotypes. Treatment with interferons after an initial attac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Health, Labour And Welfare (Japan)
The is a cabinet level ministry of the Japanese government. It is commonly known as in Japan. The ministry provides services on health, labour and welfare. It was formed with the merger of the former Ministry of Health and Welfare or and the Ministry of Labour or . The Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare is a member of the Cabinet and is chosen by the Prime Minister, typically from among members of the Diet. Organization The ministry contains the following sections as of 2019: * The Minister's Secretariat (including the Statistics and Information Department) * The Health Policy Bureau * The Health Service Bureau * Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau (including the Food Safety Department) * The Labour Standards Bureau (including the Industrial Safety and Health Department, Workers Compensation Department, and Workers' Life Department) * The Employment Security Bureau (including the Employment Measures for the Elderly and Persons with Disabilities Department) * The Hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |