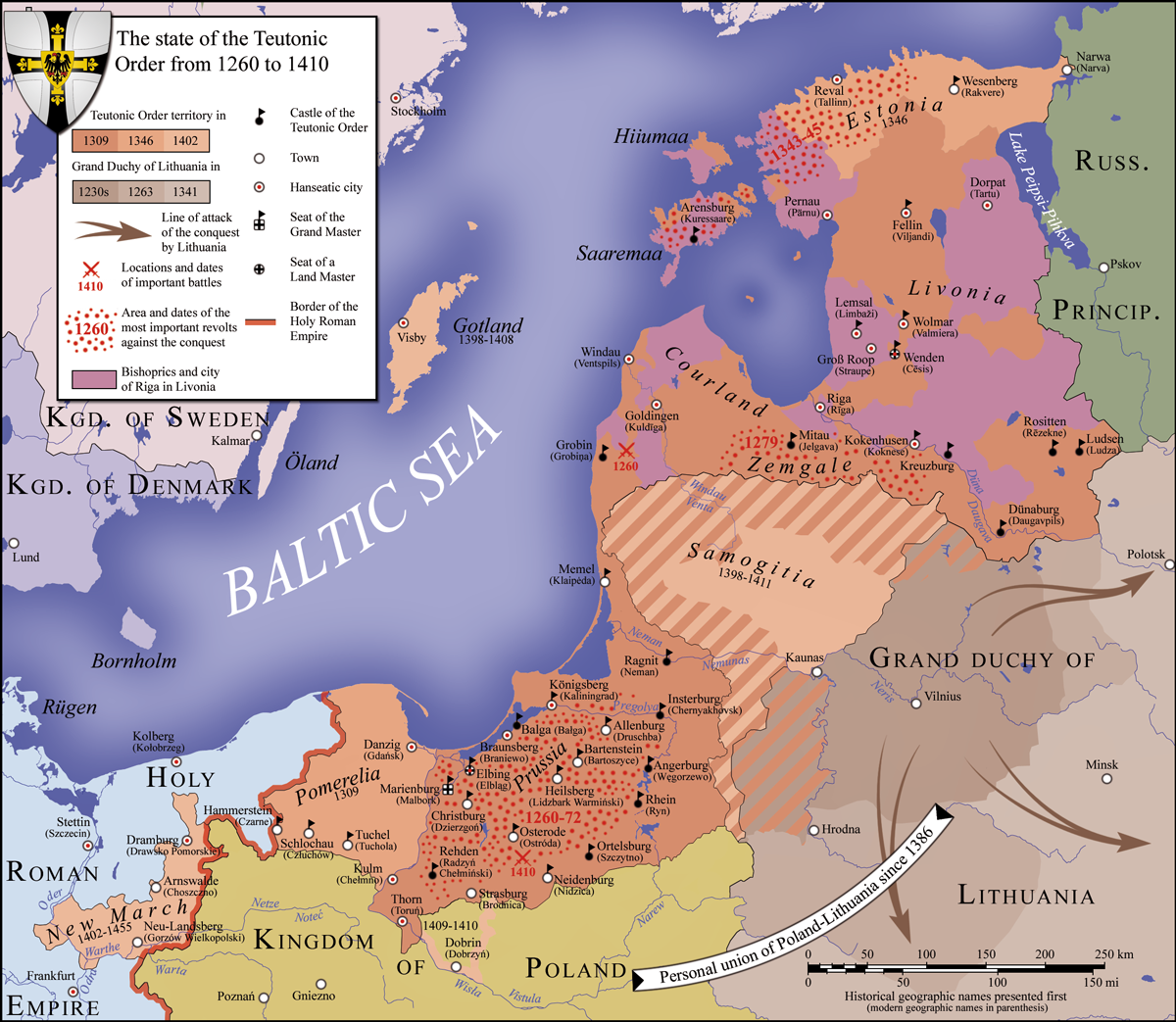
|
Mamonovo
Mamonovo (russian: Мамоново), prior to 1945 known by its German name Heiligenbeil ( pl, Święta Siekierka or ''Świętomiejsce''; lt, Šventpilis; Prussian: ''Swintamīstan''), is a town in Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia. Population figures: Etymology Mamonovo is named after a Soviet Commander, Nikolay Mamonov, killed in action near Pułtusk on October 26, 1944, who was posthumously awarded the title Hero of the Soviet Union on March 24, 1945. History Under the Teutonic Knights Heiligenstadt was built near an Old Prussian settlement. It was later renamed Heiligenbeil after a holy axe used by Augustinian monks, established in the area by Grand Master Winrich von Kniprode after the Battle of Rudau, to cut down an oak tree worshiped by pagan Prussians. It came under the bishopric of Warmia, then to the territory of Natangia. Since 1440, the town was a founding member of the anti-Teutonic Prussian Confederation, upon the request of which, Polish King Casimir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label= Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1871); following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's Free State of Prussia, until 1945. Its capital city was Königsberg (present-day Kaliningrad). East Prussia was the main part of the region of Prussia along the southeastern Baltic Coast. The bulk of the ancestral lands of the Baltic Old Prussians were enclosed within East Prussia. During the 13th century, the native Prussians were conquered by the crusading Teutonic Knights. After the conquest the indigenous Balts were gradually converted to Christianity. Because of Germanization and colonisation over the following centuries, Germans became the dominant ethnic group, while Masurians and Lithuanians formed minorities. From the 13th century, East Prussia was pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heiligenbeil Concentration Camp
Heiligenbeil was a subcamp of the German Stutthof concentration camp, operated from September 1944 to January 1945. It was named after the town Heiligenbeil (now Mamonovo, Russia). Its prisoners were 1,100 Jewish women and 100 Jewish men. The prisoners were subjected to Forced labour. The commanders of the subcamp were SS-Unterscharführer Hermann Kleiss (in September–October 1944), SS-Oberscharführer Johann Mayer (October–November 1944), SS-Hauptscharführer Ernst Thulke (October 1944–January 1945) and SS-Sturmscharführer __NOTOC__ (, ) was a Nazi rank of the Waffen-SS that existed between 1934 and 1945. The rank was the most senior enlisted rank in the Waffen-SS, the equivalent of a regimental sergeant major, in other military organizations. Rank usage ''Sturm ... Wolförer (January 1945). References External links Stutthof concentration camp Subcamps of Nazi concentration camps {{Holocaust-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Rudau
The Battle of Rudau (german: Schlacht bei Rudau, lt, Rūdavos mūšis) was a medieval pitched battle fought between the Teutonic Knights and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania on 17 or 18 February 1370 near Rudau village, north of Königsberg (now Melnikovo village in the Kaliningrad oblast). According to the Teutonic chronicler Wigand of Marburg and the Livonian chronicle of Hermann de Wartberge, the Lithuanians suffered a great defeat. Background The Teutonic Knights had waged a crusade against the pagan Lithuanians since the 1290s in order to Christianize the country. Each side would organize military expeditions against each other and then retaliate. In August 1369 the Knights burned a Lithuanian fort in the mouth of the Nevėžis River; 109 people perished in the fire. During truce negotiations Kęstutis, brother and right-hand man of the Grand Duke Algirdas, warned the Prussian Marshal Henning Schindekop that he would organize a retaliation. This gave time for the Kni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian Confederation
The Prussian Confederation (german: Preußischer Bund, pl, Związek Pruski) was an organization formed on 21 February 1440 at Kwidzyn (then officially ''Marienwerder'') by a group of 53 nobles and clergy and 19 cities in Prussia, to oppose the arbitrariness of the Teutonic Knights. It was based on an earlier similar organization, the Lizard Union established in 1397 by the nobles of Chełmno Land. In 1454, the leader of the Confederation, Johannes von Baysen (Jan Bażyński), formally asked King Casimir IV Jagiellon, to incorporate Prussia into the Kingdom of Poland. This marked the beginning of the Thirteen Years' War between the Order's State and Poland, with the cities co-financing the military costs of the latter. Background According to the 1411 First Peace of Thorn which followed the Teutonic Knights' defeat in the Battle of Grunwald, the Teutonic Order had to pay high reparations to the Kingdom of Poland. The monastic state imposed high taxes on the cities to ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winrich Von Kniprode
Winrich von Kniprode was the 22nd Grand Master of the Teutonic Order. He was the longest serving Grand Master, holding the position for 31 years (1351–1382). Winrich von Kniprode was born in 1310 in Monheim am Rhein near Cologne. He served as the Komtur of Danzig (1338–1341) and Balga (1341–1343). In 1341 he was promoted to the Grand Marshal. Winrich was elected Grand Master in 1351. He constantly fought with the Grand Duchy of Lithuania to gain access to Livonia. He achieved a victory in the Battle of Rudau. Winrich died in 1382 and was buried in Marienburg Castle in the mausoleum A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the interment space or burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be con ... under the Chapel of St. Anna. References * Friedrich Borchert: "Die Hochmeister des Deutschen Ordens in Preußen." In: ''Preußische Allgeme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million Military personnel, personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Air warfare of World War II, Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) constituted the German state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1866 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick II "the Great".Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Frederick the Great 1712–30." In Frederick the Great and the Rise of Prussia, 9–10. 3rd ed. Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ducal Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (german: Herzogtum Preußen, pl, Księstwo Pruskie, lt, Prūsijos kunigaikštystė) or Ducal Prussia (german: Herzogliches Preußen, link=no; pl, Prusy Książęce, link=no) was a duchy in the region of Prussia established as a result of secularization of the Monastic Prussia, the territory that remained under the control of the State of the Teutonic Order until the Protestant Reformation in 1525. Overview The duchy became the first Protestant state when Albert, Duke of Prussia formally adopted Lutheranism in 1525. It was inhabited by a German, Polish (mainly in Masuria), and Lithuanian-speaking (mainly in Lithuania Minor) population. In 1525, during the Protestant Reformation, in accordance to the Treaty of Kraków, the Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, Albert, secularized the order's prevailing Prussian territory (the Monastic Prussia), becoming Albert, Duke of Prussia. As the region had been a part of the Kingdom of Poland since the Second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal allegiance, services and/or payments. The fees were often lands, land revenue or revenue-producing real property like a watermill, held in feudal land tenure: these are typically known as fiefs or fiefdoms. However, not only land but anything of value could be held in fee, including governmental office, rights of exploitation such as hunting, fishing or felling trees, monopolies in trade, money rents and tax farms. There never did exist one feudal system, nor did there exist one type of fief. Over the ages, depending on the region, there was a broad variety of customs using the same basic legal principles in many variations. Terminology In ancient Rome, a "benefice" (from the Latin noun , meaning "benefit") was a gift of land () f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466)
The Thirteen Years' War (german: Dreizehnjähriger Krieg; pl, wojna trzynastoletnia), also called the War of the Cities, was a conflict fought in 1454–1466 between the Prussian Confederation, allied with the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, and the State of the Teutonic Order. The war began as an uprising by Prussian cities and local nobility to win independence from the Teutonic Knights. In 1454 Casimir IV married Elisabeth of Habsburg and the Prussian Confederation asked Poland's King Casimir IV Jagiellon for help and offered to accept the king as protector instead of the Teutonic Order. When the King assented, war broke out between supporters of the Prussian Confederation, backed by Poland, and backers of government by the Teutonic Knights. The Thirteen Years' War ended in the victory of the Prussian Confederation and Poland and in the Second Peace of Thorn (1466). This was soon followed by the War of the Priests (1467–1479), a drawn-out dispute over the independ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's Fair (''Jarmark Świętojański''), traditional Saint Martin's croissants and a local dialect. Among its most important heritage sites are the Renaissance Old Town, Town Hall and Gothic Cathedral. Poznań is the fifth-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. As of 2021, the city's population is 529,410, while the Poznań metropolitan area (''Metropolia Poznań'') comprising Poznań County and several other communities is inhabited by over 1.1 million people. It is one of four historical capitals of medieval Poland and the ancient capital of the Greater Poland region, currently the administrative capital of the province called Greater Poland Voivodeship. Poznań is a center of trade, sports, education, technology an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Of The Kingdom Of Poland
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, including the Kingdom of Poland proper. The Polish Crown was at the helm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1569 to 1795. Major political events The Kingdom of Poland has been traditionally dated back to c. 966, when Mieszko I and his pagan Slavic realm joined Christian Europe ( Baptism of Poland), establishing the state of Poland, a process started by his Polan Piast dynasty ancestors. His oldest son and successor, Prince Bolesław I Chrobry, Duke of Poland, became the first crowned King of Poland in 1025. Union of Krewo The Union of Krewo was a set of prenuptial agreements made in the Kreva Castle on August 13, 1385. Once Jogaila confirmed the prenuptial agreements on August 14, 1385, Poland and Lithuania formed a pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |