|
Mammalian Gestation
In mammals, pregnancy is the period of reproduction during which a female carries one or more live offspring from implantation in the uterus through gestation. It begins when a fertilized zygote implants in the female's uterus, and ends once it leaves the uterus. Fertilization and implantation During copulation, the male inseminates the female. The spermatozoon fertilizes an ovum or various ova in the uterus or fallopian tubes, and this results in one or multiple zygotes. Sometimes, a zygote can be created by humans outside of the animal's body in the artificial process of in-vitro fertilization. After fertilization, the newly formed zygote then begins to divide through mitosis, forming an embryo, which implants in the female's endometrium. At this time, the embryo usually consists of 50 cells. Development After implantation A blastocele is a small cavity on the center of the embryo, and the developing embryonary cells will grow around it. Then, a flat layer cell forms on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System . School ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germ Layer
A germ layer is a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans (animals that are sister taxa to the sponges) produce two or three primary germ layers. Some animals, like cnidarians, produce two germ layers (the ectoderm and endoderm) making them diploblastic. Other animals such as bilaterians produce a third layer (the mesoderm) between these two layers, making them triploblastic. Germ layers eventually give rise to all of an animal’s tissues and organs through the process of organogenesis. History Caspar Friedrich Wolff observed organization of the early embryo in leaf-like layers. In 1817, Heinz Christian Pander discovered three primordial germ layers while studying chick embryos. Between 1850 and 1855, Robert Remak had further refined the germ cell layer (''Keimblatt'') concept, stating that the external, internal and middle layers form respectively the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrulation
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of cells), or in mammals the blastocyst is reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula. Before gastrulation, the embryo is a continuous epithelial sheet of cells; by the end of gastrulation, the embryo has begun differentiation to establish distinct cell lineages, set up the basic axes of the body (e.g. dorsal-ventral, anterior-posterior), and internalized one or more cell types including the prospective gut. In triploblastic organisms, the gastrula is trilaminar (three-layered). These three germ layers are the ectoderm (outer layer), mesoderm (middle layer), and endoderm (inner layer).Mundlos 2009p. 422/ref>McGeady, 2004: p. 34 In diploblastic organisms, such as Cnidaria and Ctenophora, the gastrula has only ectoderm and endoderm. The two layers are also sometimes referred to as the ''hypoblast'' and ''epiblast''. Sponges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbilical Cord
In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or ''funiculus umbilicalis'') is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and (in humans) normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps low-oxygen, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta. Structure and development The umbilical cord develops from and contains remnants of the yolk sac and allantois. It forms by the fifth week of development, replacing the yolk sac as the source of nutrients for the embryo. The cord is not directly connected to the mother's circulatory system, but instead joins the placenta, which transfers materials t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood, and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leucocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ''Bindegewebe'') was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as a distinct class in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hollow vessel", with ''-cyte'' translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Blood vessels are needed to sustain life, because all of the body's tissues rely on their functionality. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', meaning relating to the blood vessels, is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning vessel. Some structures – such as cartilage, the epithelium, and the lens and cornea of the eye – do not contain blood vessels and are labeled ''avascular''. Etymology * artery: late Middle English; from Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorionic Villi
Chorionic villi are villi that sprout from the chorion to provide maximal contact area with maternal blood. They are an essential element in pregnancy from a histomorphologic perspective, and are, by definition, a product of conception. Branches of the umbilical arteries carry embryonic blood to the villi. After circulating through the capillaries of the villi, blood returns to the embryo through the umbilical vein. Thus, villi are part of the border between maternal and fetal blood during pregnancy. Structure Villi can also be classified by their relations: * Floating villi float freely in the intervillous space. They exhibit a bi-layered epithelium consisting of cytotrophoblasts with overlaying syncytium ( syncytiotrophoblast). * Anchoring (stem) villi stabilize mechanical integrity of the placental-maternal interface. Development The chorion undergoes rapid proliferation and forms numerous processes, the chorionic villi, which invade and destroy the uterine decidua and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniotic Cavity
The amniotic sac, also called the bag of waters or the membranes, is the sac in which the embryo and later fetus develops in amniotes. It is a thin but tough transparent pair of membranes that hold a developing embryo (and later fetus) until shortly before birth. The inner of these membranes, the amnion, encloses the amniotic cavity, containing the amniotic fluid and the embryo. The outer membrane, the chorion, contains the amnion and is part of the placenta. On the outer side, the amniotic sac is connected to the yolk sac, the allantois, and via the umbilical cord, the placenta. The yolk sac, amnion, chorion, and allantois are the four extraembryonic membranes that lie outside of the embryo and are involved in providing nutrients and protection to the developing embryo. They form from the inner cell mass; the first to form is the yolk sac followed by the amnion which grows over the developing embryo. The amnion remains an important extraembryonic membrane throughout prenatal dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate maternal and fetal circulations, and is an important endocrine organ, producing hormones that regulate both maternal and fetal physiology during pregnancy. The placenta connects to the fetus via the umbilical cord, and on the opposite aspect to the maternal uterus in a species-dependent manner. In humans, a thin layer of maternal decidual (endometrial) tissue comes away with the placenta when it is expelled from the uterus following birth (sometimes incorrectly referred to as the 'maternal part' of the placenta). Placentas are a defining characteristic of placental mammals, but are also found in marsupials and some non-mammals with varying levels of development. Mammalian placentas probably first evolved about 150 million to 200 million years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
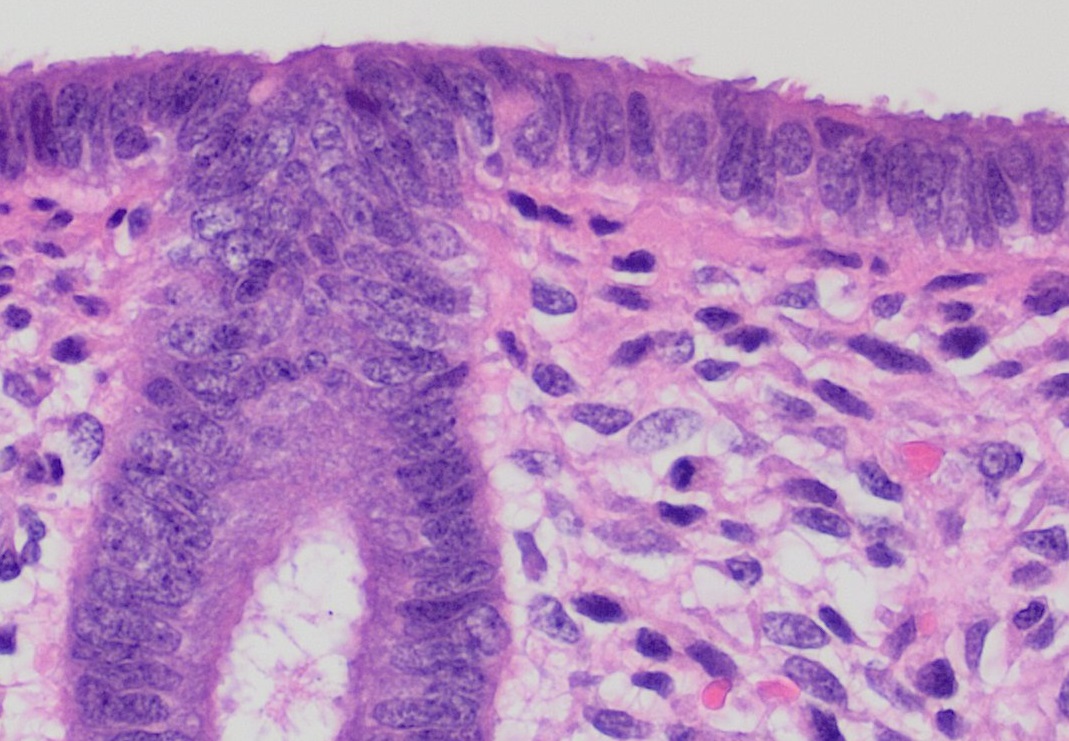
Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |