|
Makwana
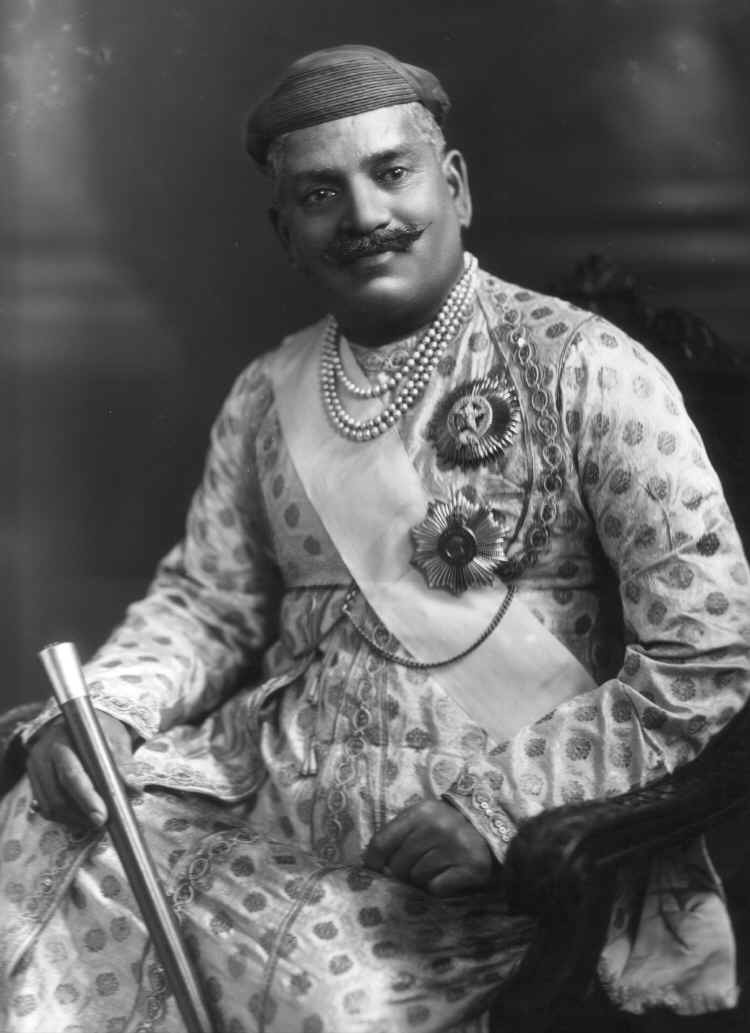
The Makwana, or Makawana is a clan ( Gotra) of the Koli caste found in the Indian state of Gujarat. The Makwana clan is mostly found among Talpada Kolis, Chunvalia Koli and Ghedia Kolis. In 1931 census of Baroda State, there were 20,700 Kolis of Makwana clan in the Baroda state's territory. Makwana Kolis mostly belong to the Hindu faith but a minor number of them converted to Islam during the reign of the invading Mughal power in Gujarat. Estates Here are list of Princely States ruled by Makwana Kolis, * Katosan State The Katosan is a town and former Princely State in Jotana Taluka of Mehsana district, Gujarat, India. The Bhagwanji Koli of Katosan state who was a able ruler of Katosan, raised the Kolis of Katosan Thana against British Raj during Rebellio ... * Gabat * Punadra Notable * Savshibhai Makwana References {{Reflist Koli clans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savshibhai Makwana
Savshibhai Kanjibhai Makwana became a member of the 13th Lok Sabha of India from Surendranagar Lok Sabha seat of Gujarat. Makwana is a member of the Indian National Congress Party And won by 25,990 votes. Makwana belong to the Koli caste of Gujarat. Savshibhai Makwana wrote a book in Gujarati language Gujarati (; gu, ગુજરાતી, Gujarātī, translit-std=ISO, label=Gujarati script, ) is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Indian state of Gujarat and spoken predominantly by the Gujarati people. Gujarati is descended from Old Gu ... named ''Zadna Parakha Far Par Thi''. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Makwana, Savshibhai Koli people People from Surendranagar district India MPs 1999–2004 1932 births Living people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katosan State
The Katosan is a town and former Princely State in Jotana Taluka of Mehsana district, Gujarat, India. The Bhagwanji Koli of Katosan state who was a able ruler of Katosan, raised the Kolis of Katosan Thana against British Raj during Rebellion of 1857 in Gujarat but he was forced by Rehvari Rajputs and Marwadi Banias to putt down the arms against British rule but he refused and fought against local Rajput chiefs and British officials. History Katosan was a Fourth Class princely state and taluka, comprising five more villages, covering ten square miles in Mahi Kantha Agency, ruled by Makwana Koli chieftains who used the title of Thakor. It had a combined population of 5,510 in 1901, yielding a state revenue of 26,617 Rupees (some three quarters from land), paying a tribute of 4,893 Rupees to the Gaikwar Baroda State, supplemented by fixed tribute sums for Baroda from individual villages belonging entirely to Katosan state: 430 Rupees from Nadasa, 623 Rupees from Jakasna, 96 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punadra
Punadra is a town in the Gandhinagar List of districts of Gujarat, district of Gujarat in Western India, Western India. History Punadra was a Fourth Class princely state and taluka, comprising ten more villages, covering eleven square miles in Mahi Kantha Agency and ruled by Makwana (clan), Makwana Koli people, Koli Tribal chief, chieftains of Jhala (clan), Jhala Dynasty having Thakor title during the British Raj under the colonial Mahi Kantha Agency. The Koli rulers of Punadra were converted to Islam by Mahmud Begada. They are brothers of Dabha, Gujarat, Dabha State, Ramas State and Khadal State. It had a combined population of 2,662 in 1901, yielding a state revenue of 15,598 Rupees (mostly from land), paying a tribute of 375 Rupees to the Gaekwad dynasty, Gaekwad Baroda State. Places of interest The village has an old fort from the time of Mahmud Begada (1459–1511). References {{coord, 23, 06, N, 72, 58, E, display=title, region:IN_type:city_source:GNS-enwik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thakor
Thakor also known as Thakarda is subcaste of Koli community of Gujarat. Koli forms the largest caste-cluster, comprising 24% of the total population of the state. Koli Thakors in Gujarat placed in Other Backward Class including all of the Koli Community of state during the power of former Koli chief minister Madhav Singh Solanki. Koli Thakors are mostly businessmen or land-owners. Clans Some of the clans of Koli Thakors are here *Makwana *Parmar *Solanki *Jhala * Chauhan * Vaghela Organisation * Kshatriya Koli Thakor Samaj * Sree Smasth Chunvalia Koli Thakor Velnath Pragati Mandal * Chunvalia Koli Thakor Seva Trust, Surendranagar Notable Thakor * Alpesh Thakor, Member of legislative assembly from Radhanpur * Geni Thakor, Member of legislative assembly *Jagdish Thakor, Gujarat Congress President *Vikram Thakor *Madhav Singh Solanki See also * Koli rebellions * List of Koli people * List of Koli states and clans The Koli is an Indian caste found in Rajasthan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabat State
Gabat also spelled Gubut is a village and former petty princely state in Gujarat, western India. The village is in Bayad Taluka of Sabarkantha District. History The Seventh Class state and taluka, in Mahi Kantha, included eight more villages, covering in total ten square miles. It was ruled by Kshatriya Makwana Koli Chieftains who held the Thakor Thakor also known as Thakarda is subcaste of Koli community of Gujarat. Koli forms the largest caste-cluster, comprising 24% of the total population of the state. Koli Thakors in Gujarat placed in Other Backward Class including all of the Koli ... title. In 1901, Gabat had a combined population of 604, yielding 2,831 Rupees state revenue (1903-4, mostly from land) and paying 43 Rupees tribute to Idar State. Sources and external links Imperial Gazetteer on dsal.uchicago.edu - Mahi Kantha {{coord missing, Gujarat Princely states of Gujarat Koli princely states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jhala (clan)
Jhala is a Rajput clan. They are found in Rajasthan and Gujarat state of India. The clan is also found among Koli castes as Jala. The Jhalawar state ruled by Jhala Rajputs in Rajasthan was a 17-gun salute state, the princely state of Dhrangadhra was a 13-gun salute state in the 1920s, when it was ruled by members of the Jhala dynasty. At that time, Jhalas also governed in the 11-gun salute state of Wankaner and in the 9-gun salute states of Limbdi and Wadhwan, as well as in the non-salute states of Lakhtar During the British Raj period, Lakhtar State, in the present-day Indian state of Gujarat, was a non-salute princely state and was governed by members of a Jhala Jhala (Hindi: झाला, ) is a term in Hindustani classical music which denote ..., Sayla and Chuda. References Further reading * Koli clans Rajput clans of Gujarat {{India-ethno-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic (Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in the 8th and 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely State
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Raj, British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to a subsidiary alliance and the suzerainty or paramountcy of the the Crown, British crown. There were officially 565 princely states when India and Pakistan became independent in 1947, but the great majority had contracted with the viceroy to provide public services and tax collection. Only 21 had actual state governments, and only four were large (Hyderabad State, Mysore State, Kashmir and Jammu (princely state), Jammu and Kashmir State, and Baroda State). They Instrument of accession, acceded to one of the two new independent nations between 1947 and 1949. All the princes were eventually pensioned off. At the time of the British withdrawal, 565 princely states were officially recognised in the Indian subcontinent, apart from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely State
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Raj, British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to a subsidiary alliance and the suzerainty or paramountcy of the the Crown, British crown. There were officially 565 princely states when India and Pakistan became independent in 1947, but the great majority had contracted with the viceroy to provide public services and tax collection. Only 21 had actual state governments, and only four were large (Hyderabad State, Mysore State, Kashmir and Jammu (princely state), Jammu and Kashmir State, and Baroda State). They Instrument of accession, acceded to one of the two new independent nations between 1947 and 1949. All the princes were eventually pensioned off. At the time of the British withdrawal, 565 princely states were officially recognised in the Indian subcontinent, apart from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroda State
Baroda State was a state in present-day Gujarat, ruled by the Gaekwad dynasty of the Maratha Confederacy from its formation in 1721 until its accession to the newly formed Dominion of India in 1949. With the city of Baroda (Vadodara) as its capital, during the British Raj its relations with the British were managed by the Baroda Residency. The revenue of the state in 1901 was Rs. 13,661,000. Baroda formally acceded to the Dominion of India, on 1 May 1949, prior to which an interim government was formed in the state. History Early history Baroda derives its native name ''Vadodara'' from the Sanskrit word ''vatodara'', meaning 'in the heart of the Banyan (''Vata'') tree. It also has another name, ''Virakshetra'' or ''Virawati'' (land of warriors), mentioned alongside ''Vadodara'' by the 17th century Gujarati poet Premanand Bhatt, native to the city. Its name has been mentioned as ''Brodera'' by early English travellers and merchants, from which its later name Baroda was d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census In British India
The Census of India prior to independence was conducted periodically from 1865 to 1941. The censuses were primarily concerned with administration and faced numerous problems in their design and conduct ranging from the absence of house numbering in hamlets to cultural objections on various grounds to dangers posed by wild animals to census personnel. The censuses were designed more for social engineering and to further the British agenda for governance than to uncover the underlying structure of the population. The sociologist Michael Mann called the census exercise "more telling of the administrative needs of the British than of the social reality for the people of British India". The differences in the nature of Indian society during the British Raj from the value system and the societies of the West were highlighted by the inclusion of "caste", "religion", "profession" and "age" in the data to be collected, as the collection and analysis of that information had a considerable im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patel
The Patel is an Indian surname or title, predominantly found in the state of Gujarat representing the community of land-owning farmers and later (with the British East India Company) businessmen, agriculturalists and merchants. Traditionally the title is a status name referring to the village chieftains during medieval times, and was later retained as successive generations stemmed out into communities of landowners, including Patidars, Kolis, Kurmis, some Parsis and Muslims. There are roughly 500,000 Patels outside India, including about 150,000 in the United Kingdom and about 150,000 in the United States. Nearly 1 in 10 people of Indian origin in the US is a Patel. Etymology The term ''patel'' derives from the word Patidar, literally "one who holds (owned) pieces of land called ''patis'', implying a higher economic status than that of the landless, ultimately from Sanskrit ''paṭṭakīla'', with the ending ''-dar'' (from Sanskrit "धार"—supporting, containing, holdi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |