|
Maizuru Naval Arsenal
was one of four principal naval shipyards owned and operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy. History The Maizuru Naval District was established at Maizuru, Kyoto Prefecture in 1889, as the fourth of the naval districts responsible for the defense of the Japanese home islands. After the establishment of the navy base, a ship repair facility was established in 1901 with a dry dock. With the addition of equipment and facilities for ship production by 1903, the Maizuru Naval Arsenal was officially established. Additional dry docks were completed in 1904 and 1914. When the No. 3 dry dock was completed in 1914, it was the largest in Japan at the time. In 1923, after the Washington Naval Treaty, there were discussions within the Navy Ministry about closing the facility, and it was largely mothballed until 1936. Afterwards, it reopened and expanded, building ships, aircraft and weapons for the military. It specialized mostly in destroyer-size and smaller vessels. Post WW II In the pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Marine United
(informally JMU) is a Japanese ship building marine engineering and service company headquartered in Yokohama, Japan. It's Japan’s second largest shipbuilder after Imabari Shipbuilding, with shipyard facilities in Kure, Hiroshima, Yokohama, Nagasu, Kumamoto, Maizuru, Kyoto and Mie prefectures. JMU's products include the design, manufacture, purchase and sale of both merchant and naval ships, offshore engineering and ship life cycle services. History Osaka Iron Works (Hitachi Zosen) established in 1881. Nippon Kokan (NKK) established by Asano zaibatsu in 1912. Both united and became Universal Shipbuilding Corporation in 2002. Ishikawajima Shipyard established in 1853. Uraga Dock ( Sumitomo Heavy Industries) established in 1893. Both united and became IHI Marine United in 2002, part of Ishikawajima-Harima Heavy Industries Co., Ltd., later renamed IHI Corporation Universal Shipbuilding Corporation and IHI Marine United Inc. united and became Japan Marine United in 2013. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defunct Companies Of Japan
{{Disambiguation ...
Defunct (no longer in use or active) may refer to: * ''Defunct'' (video game), 2014 * Zombie process or defunct process, in Unix-like operating systems See also * * :Former entities * End-of-life product * Obsolescence Obsolescence is the state of being which occurs when an object, service, or practice is no longer maintained or required even though it may still be in good working order. It usually happens when something that is more efficient or less risky r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shipbuilding Companies Of Japan
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to before recorded history. Shipbuilding and ship repairs, both commercial and military, are referred to as "naval engineering". The construction of boats is a similar activity called boat building. The dismantling of ships is called ship breaking. History Pre-history The earliest known depictions (including paintings and models) of shallow-water sailing boats is from the 6th to 5th millennium BC of the Ubaid period of Mesopotamia. They were made from bundled reeds coated in bitumen and had bipod masts. They sailed in shallow coastal waters of the Persian Gulf. 4th millennium BC Ancient Egypt Evidence from Ancient Egypt shows that the early Egyptians knew how to assemble planks of wood into a ship hull as early as 3100 BC. Egyptian potte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornell University Press
The Cornell University Press is the university press of Cornell University; currently housed in Sage House, the former residence of Henry William Sage. It was first established in 1869, making it the first university publishing enterprise in the United States, but was inactive from 1884 to 1930. The press was established in the College of the Mechanic Arts (as mechanical engineering was called in the 19th century) because engineers knew more about running steam-powered printing presses than literature professors. Since its inception, The press has offered work-study financial aid: students with previous training in the printing trades were paid for typesetting and running the presses that printed textbooks, pamphlets, a weekly student journal, and official university publications. Today, the press is one of the country's largest university presses. It produces approximately 150 nonfiction titles each year in various disciplines, including anthropology, Asian studies, biologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JDS Kashima (TV-3508)
JS ''Kashima'' (TV-3508) is a training ship of the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF). Built to a unique design during the mid-1990s, ''Kashima'' is flagship of the JMSDF Training Fleet. The name ''Kashima'' comes from the famous Shinto Kashima Shrine in Ibaraki prefecture, located to the northeast of Tokyo. Development and design ''Kashima'' is of a unique design referred to as the "''Kashima'' class cadet training ship". She is long, with a beam of , and a draft of . ''Kashima'' has a full load displacement of 4,050 tons. She is powered by a combined diesel or gas (CODOG) system, which uses two Mitsubishi S16U-MTK diesel engines for cruising, and two Kawasaki-Rolls-Royce Spey SM1C gas turbines (providing 26,150 shaft horsepower each): a diesel and a gas turbine are connected to each of the two controllable-pitch propeller shafts. The ship is armed with a single Otobreda 76 mm gun and two triple 324 mm torpedo tube sets. Four saluting cannon are also carried. '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matsu-class Destroyer
The were a class of destroyer built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) in the late stages of World War II. The class was also designated the . Although sometimes termed Destroyer escorts, they were larger and more capable than contemporary United States Navy destroyer escorts or the Imperial Japanese Navy ''kaibōkan'' vessels. Background Even by 1942, the Imperial Japanese Navy General Staff realized that attrition of its destroyer force was not sustainable. There was a growing need for a simplified design which could be quickly mass-produced, and which could serve primarily as convoy escorts and as destroyer-transports in front-line locations, but would still be capable of working with the fleet if necessary. Emphasis was placed on anti-aircraft guns and anti-submarine weapons, and radar, as operations against surface targets was deemed unlikely. Forty-two vessels were ordered and work began in August 1943. In the middle of 1944, the orders for twenty-four of these vessels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Destroyer Shimakaze
Three warships of Japan have borne the name : * , a destroyer launched in 1920, renamed ''Patrol Boat No.1'' in 1940 and sunk in 1943. * , a one-off World War II period super-destroyer launched in 1942 and sunk in 1944 * , a guided missile destroyer commissioned in 1988 and operated by the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF). See also * ''Shimakaze'' (CL-59), a operated by the Japan Coast Guard The is the coast guard of Japan. The Japan Coast Guard consists of about 13,700 personnel and is responsible for the protection of the coastline of Japan under the oversight of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. Th ... (JCG). * , a projected class of destroyers that was cancelled in 1942. {{DEFAULTSORT:Shimakaze Imperial Japanese Navy ship names Japanese Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enoki-class Destroyer
The were a class of six destroyers of the Imperial Japanese Navy. As with the previous , all were named after trees. As ''Enoki'' and ''Nara'' were both commissioned on the same day, the class is also referred to as the . Background With most of Japan’s destroyers deployed to the Mediterranean Sea as part of Japan’s contribution to the war effort against Imperial Germany under the Anglo-Japanese Alliance, the Imperial Japanese Navy approached the Diet of Japan for an emergency procurement budget, similar to that awarded during the Russo-Japanese War for the production of the destroyers. The funding was awarded from the fiscal 1917 budget, but mindful of the fact that the ''Kamikaze''-class destroyers had not actually been completed until after the end of the previous war, the government stipulated that the emergency budget be used up within a six-month period. The order for six vessels was split between the four major naval shipyards: one to Yokosuka Naval Arsenal, two to K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wakatake-class Destroyer
The were a class of eight second-class destroyers of the Imperial Japanese Navy. Background The medium-sized ''Wakatake''-class destroyers were a follow-on to the as part of the Imperial Japanese Navy's 8-6 Fleet Program from fiscal 1921 as a lower cost accompaniment to the larger s. The class was originally planned to consist of thirteen vessels, but due to the Washington Naval Treaty, as well as budgetary limitations, the orders for the last four were cancelled in 1922, with the final number being reduced to eight when ''No.14'' was also cancelled. The ''Wakatake'' class was the last class to be rated "second class" and all future destroyers were designed larger. It was planned that the ''Wakatake''-class ships should have names, but upon completion they were given numbers. This proved to be extremely unpopular with the crews and was a constant source of confusion in communications, so in 1928, names were assigned. Design The ''Wakatake''-class destroyers were essentially sli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
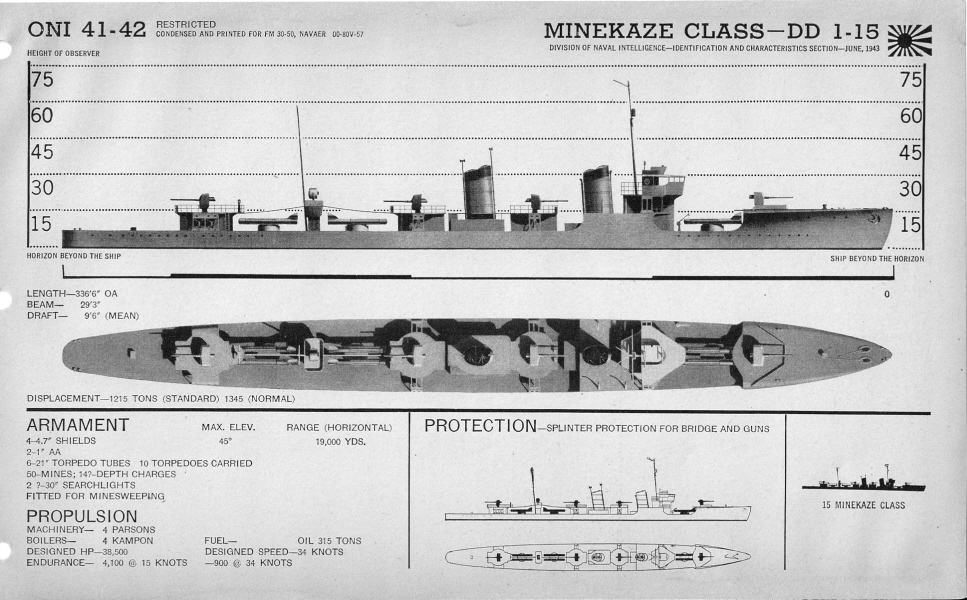
Minekaze-class Destroyer
The was a class of fifteen 1st-class destroyers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy. Obsolete by the beginning of the Pacific War, the ''Minekaze''-class ships were then relegated to mostly secondary roles, serving throughout the war as patrol vessels, high speed transports, target control vessels, and as ''kaiten'' (suicide torpedo) carriers. Most ultimately were lost to U.S. and British submarines. The basic design of the ''Minekaze'' was used for the next three classes of Japanese destroyers, a total of 36 ships. Background Construction of the large-sized ''Minekaze''-class destroyers was authorized as part of the Imperial Japanese Navy's 8-4 Fleet Program from fiscal 1917–1920, as an accompaniment to the medium-sized with which they shared many common design characteristics. Equipped with powerful engines, these vessels were capable of high speeds and were intended as escorts for the projected s, which were ultimately never built. Two vessels were authorized in fiscal 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaba-class Destroyer
The were a class of ten destroyers of the Imperial Japanese Navy. Each was named after a variety of tree. Background At the outbreak of World War I, the Imperial Japanese Navy had a total of two modern destroyers capable of overseas deployment: the and . It was clear that this force would not enable Japan to fulfill its obligations under the Anglo-Japanese Alliance, so the Japanese government pushed through an Emergency Naval Expansion Budget in fiscal 1914 to allow for the construction of ten new destroyers. As speed was of the essence, the orders were given to both government and civilian shipyards (as was the case with the construction of the Russo-Japanese War vintage ''Kamikaze''-class). Twelve more vessels were built by the same shipyards in Japan per an order from the French Navy, where they were designated the Tribal class (or ''Arabe'' class) named , , , , , , , , , , , and . The ''Arabe'' class were the most advanced destroyers in the French inventory in World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)