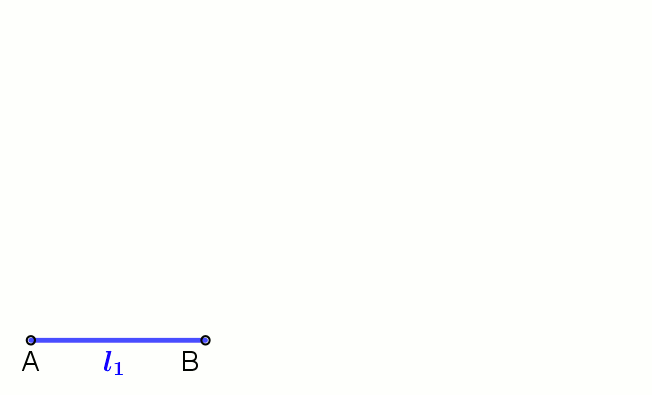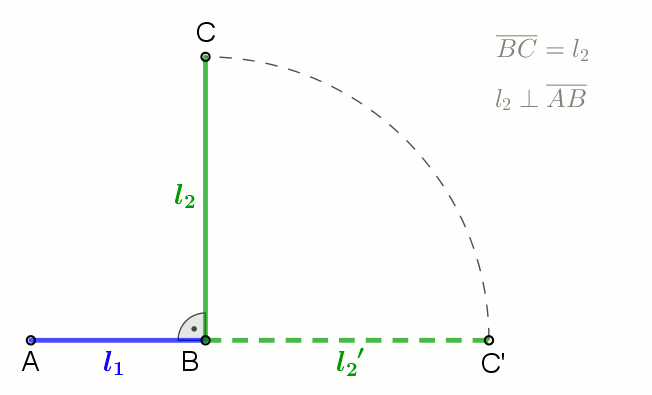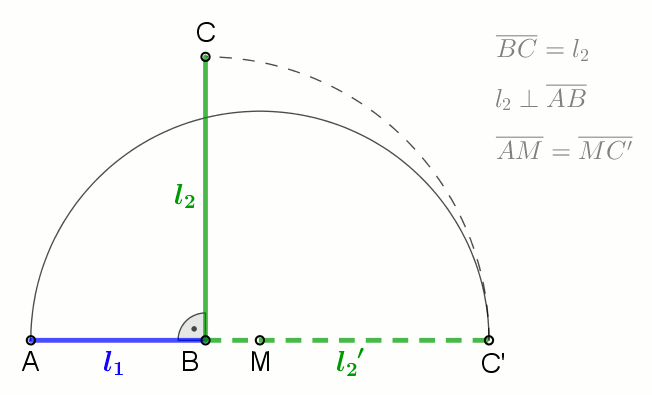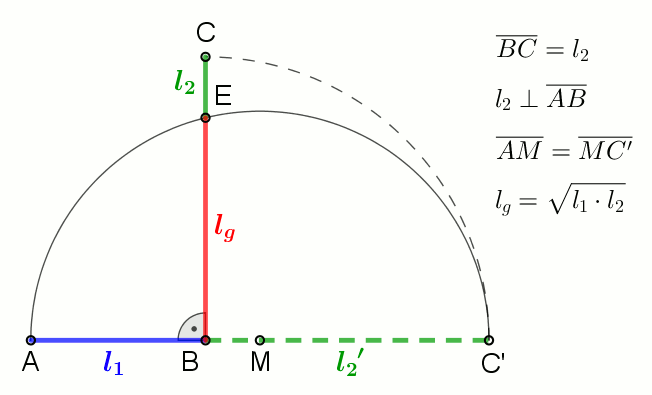|
Mahler's Inequality
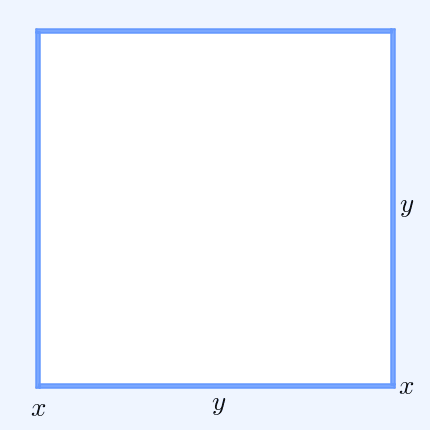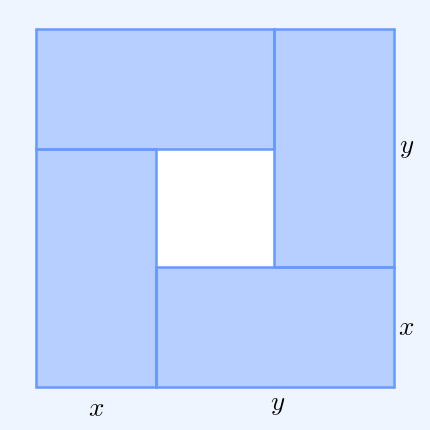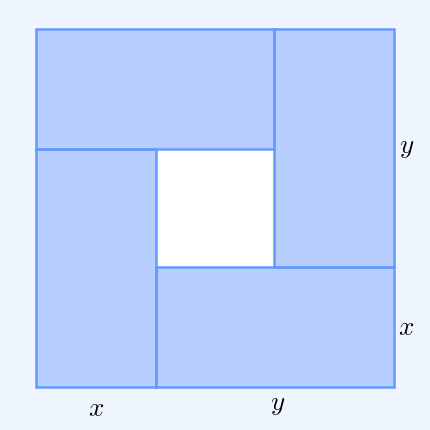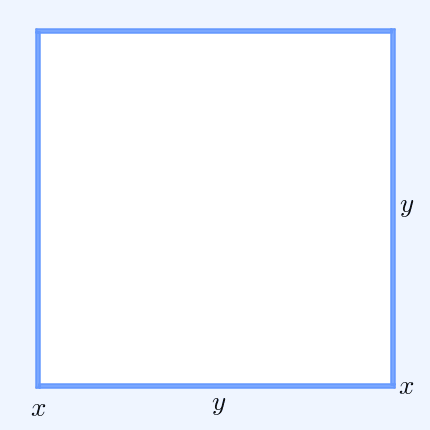
In mathematics, Mahler's inequality, named after Kurt Mahler, states that the geometric mean of the term-by-term sum of two finite sequences of positive numbers is greater than or equal to the sum of their two separate geometric means: :\prod_^n (x_k + y_k)^ \ge \prod_^n x_k^ + \prod_^n y_k^ when ''x''''k'', ''y''''k'' > 0 for all ''k''. Proof By the inequality of arithmetic and geometric means, we have: :\prod_^n \left(\right)^ \le \sum_^n , and : \prod_^n \left(\right)^ \le \sum_^n . Hence, :\prod_^n \left(\right)^ + \prod_^n \left(\right)^ \le n = 1. Clearing denominators then gives the desired result. See also *Minkowski inequality References Minkowski inequalityin the ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics The ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics'' (also ''EOM'' and formerly ''Encyclopaedia of Mathematics'') is a large reference work in mathematics. Overview The 2002 version contains more than 8,000 entries covering most areas of mathematics at a graduat ...'' Inequalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurt Mahler
Kurt Mahler FRS (26 July 1903, Krefeld, Germany – 25 February 1988, Canberra, Australia) was a German mathematician who worked in the fields of transcendental number theory, diophantine approximation, ''p''-adic analysis, and the geometry of numbers. Career Mahler was a student at the universities in Frankfurt and Göttingen, graduating with a Ph.D. from Johann Wolfgang Goethe University of Frankfurt am Main in 1927; his advisor was Carl Ludwig Siegel. He left Germany with the rise of Adolf Hitler and accepted an invitation by Louis Mordell to go to Manchester. However, at the start of World War II he was interned as an enemy alien in Central Camp in Douglas, Isle of Man, where he met Kurt Hirsch, although he was released after only three months. He became a British citizen in 1946. Mahler held the following positions: *University of Groningen ** Assistant 1934–1936 *University of Manchester ** Assistant Lecturer at 1937–1939, 1941–1944 ** Lecturer, 1944–1947; Senior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Mean
In mathematics, the geometric mean is a mean or average which indicates a central tendency of a set of numbers by using the product of their values (as opposed to the arithmetic mean which uses their sum). The geometric mean is defined as the th root of the product of numbers, i.e., for a set of numbers , the geometric mean is defined as :\left(\prod_^n a_i\right)^\frac = \sqrt /math> or, equivalently, as the arithmetic mean in logscale: :\exp For instance, the geometric mean of two numbers, say 2 and 8, is just the square root of their product, that is, \sqrt = 4. As another example, the geometric mean of the three numbers 4, 1, and 1/32 is the cube root of their product (1/8), which is 1/2, that is, \sqrt = 1/2. The geometric mean applies only to positive numbers. The geometric mean is often used for a set of numbers whose values are meant to be multiplied together or are exponential in nature, such as a set of growth figures: values of the human population or inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inequality Of Arithmetic And Geometric Means
In mathematics, the inequality of arithmetic and geometric means, or more briefly the AM–GM inequality, states that the arithmetic mean of a list of non-negative real numbers is greater than or equal to the geometric mean of the same list; and further, that the two means are equal if and only if every number in the list is the same (in which case they are both that number). The simplest non-trivial case – i.e., with more than one variable – for two non-negative numbers and , is the statement that :\frac2 \ge \sqrt with equality if and only if . This case can be seen from the fact that the square of a real number is always non-negative (greater than or equal to zero) and from the elementary case of the binomial formula: :\begin 0 & \le (x-y)^2 \\ & = x^2-2xy+y^2 \\ & = x^2+2xy+y^2 - 4xy \\ & = (x+y)^2 - 4xy. \end Hence , with equality precisely when , i.e. . The AM–GM inequality then follows from taking the positive square root of both sides and then dividing both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clearing Denominators
In mathematics, the method of clearing denominators, also called clearing fractions, is a technique for simplifying an equation equating two expressions that each are a sum of rational expressions – which includes simple fractions. Example Consider the equation : \frac x 6 + \frac y = 1. The smallest common multiple of the two denominators 6 and 15''z'' is 30''z'', so one multiplies both sides by 30''z'': : 5xz + 2y = 30z. \, The result is an equation with no fractions. The simplified equation is not entirely equivalent to the original. For when we substitute and in the last equation, both sides simplify to 0, so we get , a mathematical truth. But the same substitution applied to the original equation results in , which is mathematically meaningless. Description Without loss of generality, we may assume that the right-hand side of the equation is 0, since an equation may equivalently be rewritten in the form . So let the equation have the form :\sum_^n \frac = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minkowski Inequality
In mathematical analysis, the Minkowski inequality establishes that the L''p'' spaces are normed vector spaces. Let ''S'' be a measure space, let and let ''f'' and ''g'' be elements of L''p''(''S''). Then is in L''p''(''S''), and we have the triangle inequality :\, f+g\, _p \le \, f\, _p + \, g\, _p with equality for if and only if ''f'' and ''g'' are positively linearly dependent, i.e., for some or . Here, the norm is given by: :\, f\, _p = \left( \int , f, ^p d\mu \right)^ if ''p'' q, then \, f\, _\leq\, f\, _. Reverse inequality When p< 1 the reverse inequality holds: : We further need the restriction that both and are non-negative, as we can see from the example and : . The reverse inequality follows from the same argument as the standard Minkowski, but uses that Holder's inequality is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Of Mathematics
The ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics'' (also ''EOM'' and formerly ''Encyclopaedia of Mathematics'') is a large reference work in mathematics. Overview The 2002 version contains more than 8,000 entries covering most areas of mathematics at a graduate level, and the presentation is technical in nature. The encyclopedia is edited by Michiel Hazewinkel and was published by Kluwer Academic Publishers until 2003, when Kluwer became part of Springer. The CD-ROM contains animations and three-dimensional objects. The encyclopedia has been translated from the Soviet ''Matematicheskaya entsiklopediya'' (1977) originally edited by Ivan Matveevich Vinogradov and extended with comments and three supplements adding several thousand articles. Until November 29, 2011, a static version of the encyclopedia could be browsed online free of charge online. This URL now redirects to the new wiki incarnation of the EOM. ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics'' wiki A new dynamic version of the encyclopedia is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inequalities
Inequality may refer to: Economics * Attention inequality, unequal distribution of attention across users, groups of people, issues in etc. in attention economy * Economic inequality, difference in economic well-being between population groups * Spatial inequality, the unequal distribution of income and resources across geographical regions * Income inequality metrics, used to measure income and economic inequality among participants in a particular economy * International inequality, economic differences between countries Healthcare * Health equity, the study of differences in the quality of health and healthcare across different populations Mathematics * Inequality (mathematics), a relation between two values when they are different Social sciences * Educational inequality, the unequal distribution of academic resources to socially excluded communities * Gender inequality, unequal treatment or perceptions of individuals due to their gender * Participation inequality, the pheno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |