|
Magnus Stenbock
Count Magnus Stenbock (22 May 1665 – 23 February 1717) was a Swedish field marshal ('' Fältmarskalk'') and Royal Councillor. A renowned commander of the Carolean Army during the Great Northern War, he was a prominent member of the Stenbock family. He studied at Uppsala University and joined the Swedish Army during the Nine Years' War, where he participated in the Battle of Fleurus in 1690. After the battle, he was appointed lieutenant colonel, entered Holy Roman service as Adjutant General, and married Eva Magdalena Oxenstierna, daughter of statesman Bengt Gabrielsson Oxenstierna. Returning to Swedish service he received colonelcy of a regiment in Wismar, and later became colonel of the Kalmar and then Dalarna regiments. During the Great Northern War, Stenbock served under King Charles XII in his military campaigns in the Baltic and Polish fronts. As director of the General War Commissariat, Stenbock collected substantial funds and supplies for the maintenance of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excellency
Excellency is an honorific style given to certain high-level officers of a sovereign state, officials of an international organization, or members of an aristocracy. Once entitled to the title "Excellency", the holder usually retains the right to that courtesy throughout their lifetime, although in some cases the title is attached to a particular office, and is held only for the duration of that office. Generally people addressed as ''Excellency'' are heads of state, heads of government, governors, ambassadors, Roman Catholic bishops and high-ranking ecclesiastics and others holding equivalent rank (e.g., heads of international organizations). Members of royal families generally have distinct addresses (Majesty, Highness, etc.) It is sometimes misinterpreted as a title of office in itself, but in fact is an honorific that precedes various titles (such as Mr. President, and so on), both in speech and in writing. In reference to such an official, it takes the form ''His'' or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I of Russia, Frederick IV of Denmark–Norway and Augustus II the Strong of Saxony– Poland–Lithuania. Frederick IV and Augustus II were defeated by Sweden, under Charles XII, and forced out of the alliance in 1700 and 1706 respectively, but rejoined it in 1709 after the defeat of Charles XII at the Battle of Poltava. George I of Great Britain and the Electorate of Hanover joined the coalition in 1714 for Hanover and in 1717 for Britain, and Frederick William I of Brandenburg-Prussia joined it in 1715. Charles XII led the Swedish army. Swedish allies included Holstein-Gottorp, several Polish magnates under Stanislaus I Leszczyński (1704–1710) and Cossacks under the Ukrainian Hetman Ivan Mazepa (1708–17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privy Council Of Sweden
The Council of the Realm, or simply The Council ( sv, Riksrådet or sv, Rådet: sometimes in la, Senatus Regni Sueciae), was a cabinet of medieval origin, consisting of magnates ( sv, stormän) which advised, and at times co-ruled with, the King of Sweden. The 1634 Instrument of Government, Sweden's first written constitution in the modern sense, stipulated that the King must have a council, but he was free to choose whomever he might find suitable for the job, as long as they were of Swedish birth. At the introduction of absolutism, Charles XI had the equivalent organ named as Royal Council ( sv, Kungligt råd). In the Age of Liberty, the medieval name was reused, but after the bloodless revolution of Gustav III, the old organ was practically abolished. The 1809 Instrument of Government, created a Council of State, also known as the King in Council ( sv, Konungen i Statsrådet) which became the constitutionally mandated cabinet where the King had to make all state decisio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Marshal
Field marshal (or field-marshal, abbreviated as FM) is the most senior military rank, ordinarily senior to the general officer ranks. Usually, it is the highest rank in an army and as such few persons are appointed to it. It is considered as a five-star rank (OF-10) in modern-day armed forces in many countries. Promotion to the rank of field marshal in many countries historically required extraordinary military achievement by a general (a wartime victory). However, the rank has also been used as a divisional command rank and also as a brigade command rank. Examples of the different uses of the rank include Austria-Hungary, Pakistan, Prussia/Germany, India and Sri Lanka for an extraordinary achievement; Spain and Mexico for a divisional command ( es, link=no, mariscal de campo); and France, Portugal and Brazil for a brigade command (french: link=no, maréchal de camp, pt, marechal de campo). Origins The origin of the term dates to the early Middle Ages, originally meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxenstierna
Oxenstierna ( , ) is a Swedish noble family, originally from Småland in southern Sweden which can be traced up to the middle of the 14th century. The Oxenstierna family held vast estates in Södermanland and Uppland during the late Middle Ages and Renaissance. In the 15th century, the family at times held the position of Regent of Sweden during the turbulent civil wars of the Kalmar Union. The family began to adopt its armorial designation of Oxenstierna as a personal surname towards the end of the 16th century. In the case of earlier members of the family, the surname has been retroactively applied by historians. Notable Oxenstierna family members Several members of the family, most notably the influential Lord High Chancellor Axel Oxenstierna, rose to prominence, high political office and titles during the age of the Swedish Empire in the 17th century. The family's most notable members include the following (in chronological order): * Jöns Bengtsson (Oxenstierna) the El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Tönning
During the Great Northern War, the fortress of Tönning (Tønning) in the territory of Holstein-Gottorp, an ally of the Swedish Empire, was besieged twice. Denmark-Norway was forced to lift the first siege in 1700, but a combined force of the anti-Swedish coalition successfully besieged and took Tönning in 1713–1714. 1700 The first siege was one of the first military actions of the Great Northern War. Denmark-Norway, Saxe- Poland-Lithuania and Russia had agreed on invading the Swedish Empire on three fronts, and accordingly, Danish forces moved into Holstein-Gottorp,Frost (2000), p.228 allied and dynastically tied to Sweden,Frost (2000), p.227 and laid siege to Tönning in March 1700. The siege had to be lifted when Charles XII of Sweden, backed by the Maritime Powers, in a surprise move deployed an army in front of Copenhagen, forcing Frederik IV of Denmark-Norway out of the war by the Peace of Travendal on 18 August 1700.Frost (2000), p.229 Denmark re-entered the war onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Gadebusch
The Battle of Gadebusch or Wakenstädt (20 December 1712) was Sweden's final great victory in the Great Northern War. It was fought by the Swedes to prevent the Siege of Stralsund (1711–1715), loss of the city of Stralsund to Denmark, Danish and Saxony, Saxon forces. Prelude During 1712, all of Sweden's Dominions of Sweden, dominions south of the Baltic Sea, apart from forts, had been conquered by the allies Denmark, Saxony, and Russia. In the Baltic the Danish admiral Ulrik Christian Gyldenløve, Gyldenløve patrolled with a squadron to disrupt Swedish supply lines to the Continent. It was vital for Sweden not to lose Stralsund, as it was the gateway to campaigns in Poland. While a Danish army moved in the region of Hamburg, a large Russian-Saxon force stood south of Stralsund. Stenbock could hardly attack this force with a frontal assault, but hoped that by moving west towards Mecklenburg it could be encirclement, encircled or scattered. Such a movement would also prevent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Helsingborg
The Battle of Helsingborg was the last major engagement of the Great Northern War to take place on Swedish soil, and resulted in a decisive victory of a Swedish force of 14,000 men under the command of Magnus Stenbock against a Danish force of equal strength under the command of Jørgen Rantzau, ensuring that Denmark's final effort to regain the Scanian territories that it had lost to Sweden in 1658 failed. The battle was fought on March 10, 1710, in the province of Scania, just outside the city of Helsingborg, and directly on the Ringstorp heights just north-east of the city.''Svenska slagfält'', Lars Ericson, Martin Hårdstedt, Per Iko, Ingvar Sjöblom och Gunnar Åselius, Wahlström & Widstrand 2003, .Marklund (2008), pp. 206−208Eriksson (2007), pp. 205−209 Denmark-Norway had been forced out of the Great Northern War by the Treaty of Traventhal in 1700, but had long planned on reopening hostilities with the goal of reconquering the lost provinces Scania, Halland and Ble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Grodno (1706)
The Battle of Grodno (1706) refers to the battle during the Great Northern War. Grodno was a city of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth at this time. Background Battle The blockade of Grodno by the 31,000 men (21,000 Swedes, 10,000 Poles) strong Swedish–Polish army took place between January and March 1706 (3,000 Swedes had already died due to frostbite prior to the arrival). In the city and close vicinity there were about 41,000 Russian and Saxon troops under the command of General Field-Marshall Ogilvy as well as general Repnin. On 13 January 1706 the Swedish army coming from Poland crossed the Neman River and squeezed out the Russian cavalry units of Menshikov towards Minsk, cutting of all connections to Russia for the Grodno garrison. The situation of the Russian troops was made even more difficult after the allied Polish-Lithuanian king Augustus II quickly left Grodno in Polish direction, taking four Russian dragoon regiments with him. As a result, the Grodno garri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Thorn (1703)
The siege of Thorn was set during the Great Northern War, between Sweden and Saxony from May to October 14, 1703. The Swedish army was commanded by Charles XII of Sweden and the Saxon by General von Kanitz. The siege ended with a victory for Sweden, and the whole garrison surrendered to the Swedes. References * Karl Hoburg: Die Belagerungen der Stadt und Festung Thorn seit dem 17. Jahrhundert, Lambeck Verlag, Thorn 1844 * Anders Fryxell: Lebensgeschichte Karl's des Zwölften, Königs von Schweden, Band 1, Braunschweig 1861 Thorn Thorn Thorn(s) or The Thorn(s) may refer to: Botany * Thorns, spines, and prickles, sharp structures on plants * ''Crataegus monogyna'', or common hawthorn, a plant species Comics and literature * Rose and Thorn, the two personalities of two DC Com ... Thorn 1703 Thorn 1703 History of Toruń {{Poland-battle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
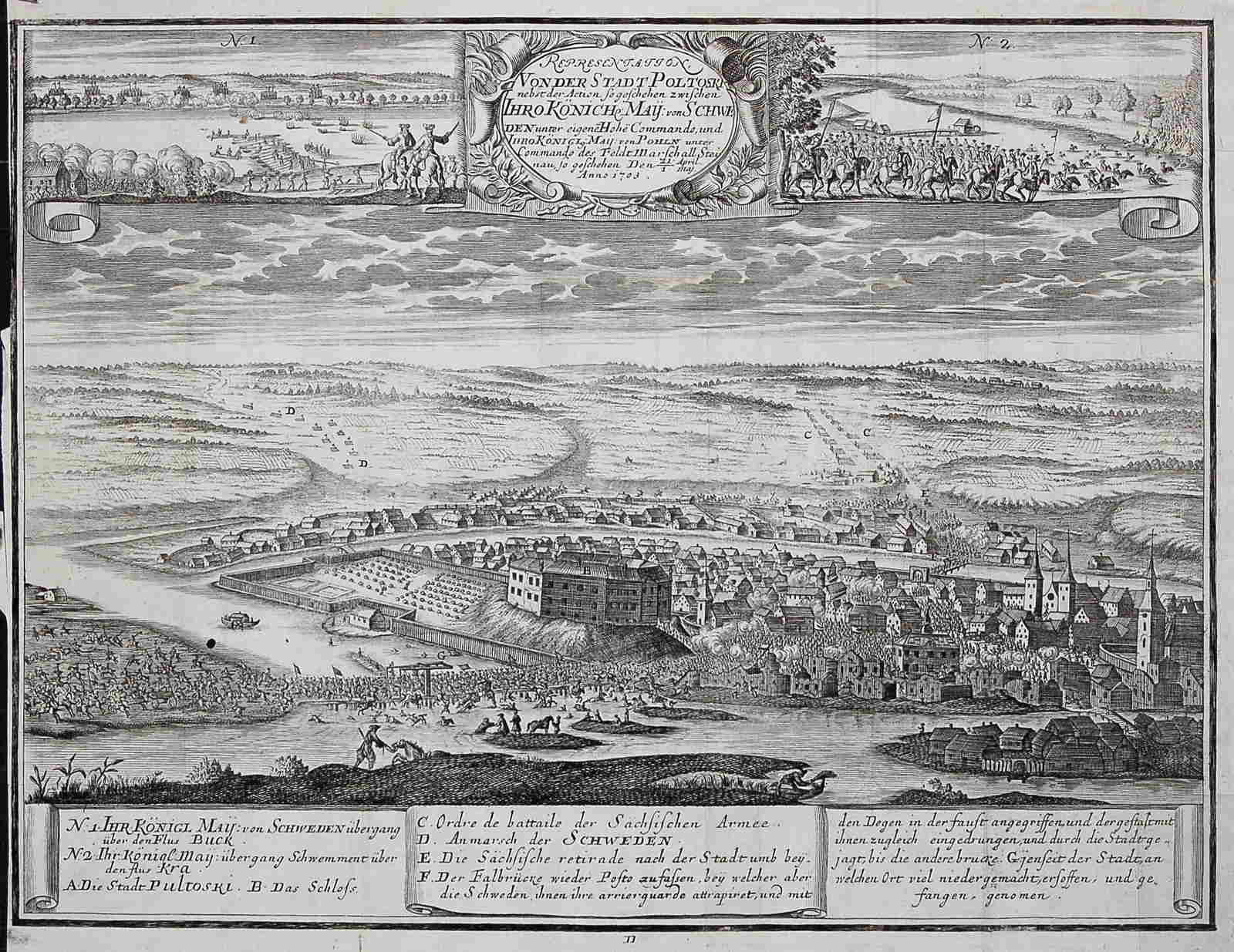
Battle Of Pułtusk (1703)
The Battle of Pułtusk took place on April 21, 1703 in Pułtusk during the Great Northern War. The Swedish army under the command of Charles XII defeated the Saxon army under Adam Heinrich von Steinau. Charles later went on to take Toruń (Thorn) in December.Tucker, S.C., 2010, A Global Chronology of Conflict, Vol. Two, Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO, LLC, p. 691. Background In the first months of 1703 the war in Poland ceased. In March, Charles XII broke with his army in the direction of Warsaw, which he reached at the beginning of April. At the beginning of April 1703 August II left Dresden for Thorn and Marienburg in order to begin the new campaign from there. After the defeat in the previous year in the Battle of Klissow, August II used the time to build a new Saxon-Lithuanian army. This army camped at Pułtusk. Charles XII decided to attack. He rode out of Warsaw with 3,000 cavalry. Because of the many waterways that had to be passed, he left behind infantry and artillery. With th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kliszów
The Battle of Kliszów (also spelled Klissow or Klezow) took place on July 19, 1702, near Kliszów in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth during the Great Northern War. A numerically superior Polish–Saxon army led by king Augustus II the Strong was defeated by a Swedish army half its size under the command of king Charles XII of Sweden. During the second year of the war, following the Swedish victories at Narva and Düna, Charles XII launched a campaign against the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. His aim was to outmaneuver Augustus II's Saxon troops and create dissension in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth to depose Augustus II as king of Poland. In May 1702, Charles XII captured the capital of Warsaw. While there, the Swedish king received intelligence about Augustus II being in Kraków and assembling a large Saxon army. He chose to pursue Augustus II and called for Swedish reinforcements in order to assemble an army capable of defeating the Saxon army in a decisive bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |