|
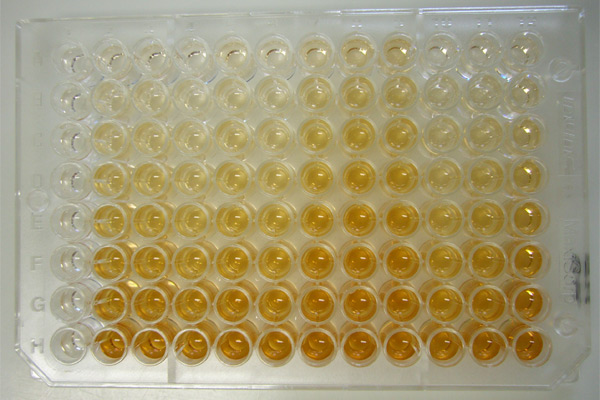
Magnetic Immunoassay
Magnetic immunoassay (MIA) is a type of diagnostic immunoassay using magnetic beads as labels in lieu of conventional enzymes (ELISA), radioisotopes (RIA) or fluorescent moieties ( fluorescent immunoassays) to detect a specified analyte. MIA involves the specific binding of an antibody to its antigen, where a magnetic label is conjugated to one element of the pair. The presence of magnetic beads is then detected by a magnetic reader (magnetometer) which measures the magnetic field change induced by the beads. The signal measured by the magnetometer is proportional to the analyte (virus, toxin, bacteria, cardiac marker, etc.) concentration in the initial sample. Magnetic labels Magnetic beads are made of nanometric-sized iron oxide particles encapsulated or glued together with polymers. These magnetic beads range from 35 nm up to 4.5 μm. The component magnetic nanoparticles range from 5 to 50 nm and exhibit a unique quality referred to as superparamagnetism in the presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoassay
An immunoassay (IA) is a biochemical test that measures the presence or concentration of a macromolecule or a small molecule in a solution through the use of an antibody (usually) or an antigen (sometimes). The molecule detected by the immunoassay is often referred to as an "analyte" and is in many cases a protein, although it may be other kinds of molecules, of different sizes and types, as long as the proper antibodies that have the required properties for the assay are developed. Analytes in biological liquids such as serum or urine are frequently measured using immunoassays for medical and research purposes. Immunoassays come in many different formats and variations. Immunoassays may be run in multiple steps with reagents being added and washed away or separated at different points in the assay. Multi-step assays are often called separation immunoassays or heterogeneous immunoassays. Some immunoassays can be carried out simply by mixing the reagents and sample and making a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunologic Tests
An immunoassay (IA) is a biochemical test that measures the presence or concentration of a macromolecule or a small molecule in a solution through the use of an antibody (usually) or an antigen (sometimes). The molecule detected by the immunoassay is often referred to as an "analyte" and is in many cases a protein, although it may be other kinds of molecules, of different sizes and types, as long as the proper antibodies that have the required properties for the assay are developed. Analytes in biological liquids such as serum or urine are frequently measured using immunoassays for medical and research purposes. Immunoassays come in many different formats and variations. Immunoassays may be run in multiple steps with reagents being added and washed away or separated at different points in the assay. Multi-step assays are often called separation immunoassays or heterogeneous immunoassays. Some immunoassays can be carried out simply by mixing the reagents and sample and making a phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potato Virus X
Potato virus X (PVX) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family ''Alphaflexiviridae'' and the order ''Tymovirales''. PVX is found mainly in potatoes and is only transmitted mechanically. There are no insect or fungal vectors for this virus. This virus causes mild or no symptoms in most potato varieties, but when Potato virus Y is present, synergy between these two viruses causes severe symptoms in potatoes. The virion has helical symmetry and a deeply grooved, highly hydrated surface and is made of a single-stranded positive-sense RNA genome of approximately 6.4 kb. This is wrapped in approximately 1300 units of a single coat protein (CP) type, with 8.9 CP units per helix turn. The genome is capped at the 5′-end and poly-adenylated at the 3′-terminus. It contains five open reading frames (ORFs) encoding five proteins: the RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRP), the movement proteins encoded by three overlapping ORFs that form the Triple Gene Block module (TGBp1, TGBp2, and TGBp3), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grapevine Fanleaf Virus
Grapevine fanleaf virus (GFLV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family ''Secoviridae''. It infects grapevines, causing chlorosis of the leaves and lowering the fruit quality.P. Andret-Link ''et al.'' Journal of Plant Pathology (2004), 86(3), 183–195 Because of its effect on grape yield, GFLV is a pathogen of commercial importance. It is transmitted via a nematode vector, ''Xiphinema index ''Xiphinema index'', the California dagger nematode, is a species of plant-parasitic nematodes. History A major pest of grapes, the California dagger nematode provided the first example of a nematode acting as a vector for a viral plant diseas ...''. This nematode acquires the virus through feeding on roots of an infected plant, and passes it on in the same manner. Host and Symptoms: The host for Grapevine fanleaf virus or GFLV is the vitis species. This includes V. vinifera, V. rupestris, and hybrids. The symptoms of GFLV are “distortion of leaves and may cause unusual chlorotic (yell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochip
In molecular biology, biochips are engineered substrates ("miniaturized laboratories") that can host large numbers of simultaneous biochemical reactions. One of the goals of biochip technology is to efficiently screen large numbers of biological analytes, with potential applications ranging from disease diagnosis to detection of bioterrorism agents. For example, digital microfluidic biochips are under investigation for applications in biomedical fields. In a digital microfluidic biochip, a group of (adjacent) cells in the microfluidic array can be configured to work as storage, functional operations, as well as for transporting fluid droplets dynamically. History The development started with early work on the underlying sensor technology. One of the first portable, chemistry-based sensors was the glass pH electrode, invented in 1922 by Hughes. The basic concept of using exchange sites to create permselective membranes was used to develop other ion sensors in subsequent years. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Flow Test
A lateral flow test (LFT), is an assay also known as a lateral flow device (LFD), lateral flow immunochromatographic assay, or rapid test. It is a simple device intended to detect the presence of a target substance in a liquid sample without the need for specialized and costly equipment. LFTs are widely used in medical diagnostics in the home, at the point of care, and in the laboratory. For instance, the home pregnancy test is an LFT that detects a specific hormone. These tests are simple and economical and generally show results in around five to thirty minutes. Many lab-based applications increase the sensitivity of simple LFTs by employing additional dedicated equipment. Because the target substance is often a biological antigen, many lateral flow tests are rapid antigen tests (RAT or ART). LFTs operate on the same principles of affinity chromatography as the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). In essence, these tests run the liquid sample along the surface of a pad w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrocellulose
Nitrocellulose (also known as cellulose nitrate, flash paper, flash cotton, guncotton, pyroxylin and flash string, depending on form) is a highly flammable compound formed by nitrating cellulose through exposure to a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid. One of its first major uses was as guncotton, a replacement for gunpowder as propellant in firearms. It was also used to replace gunpowder as a low-order explosive in mining and other applications. In the form of collodion it was also a critical component in an early photographic emulsion, the use of which revolutionized photography in the 1860s. Production The process uses a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid to convert cellulose into nitrocellulose. The quality of the cellulose is important. Hemicellulose, lignin, pentosans, and mineral salts give inferior nitrocelluloses. In precise chemical terms, nitrocellulose is not a nitro compound, but a nitrate ester. The glucose repeat unit (anhydroglucose) within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Néel
Louis Eugène Félix Néel (22 November 1904 – 17 November 2000) was a French physicist born in Lyon who received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1970 for his studies of the magnetic properties of solids. Biography Néel studied at the Lycée du Parc in Lyon and was accepted at the École Normale Supérieure in Paris. He obtained the degree of Doctor of Science at the University of Strasbourg. He was corecipient (with the Swedish astrophysicist Hannes Alfvén) of the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1970 for his pioneering studies of the magnetic properties of solids. His contributions to solid state physics have found numerous useful applications, particularly in the development of improved computer memory units. About 1930 he suggested that a new form of magnetic behavior might exist; called antiferromagnetism, as opposed to ferromagnetism. Above a certain temperature (the Néel temperature) this behaviour stops. Néel pointed out (1948) that materials could also exist showing fer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand (commonly a protein) in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the protein to be measured. ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries. In the most simple form of an ELISA, antigens from the sample to be tested are attached to a surface. Then, a matching antibody is applied over the surface so it can bind the antigen. This antibody is linked to an enzyme and then any unbound antibodies are removed. In the final step, a substance containing the enzyme's substrate is added. If there was binding, the subsequent reaction produces a detectable signal, most commonly a color change. Performing an ELISA involves at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
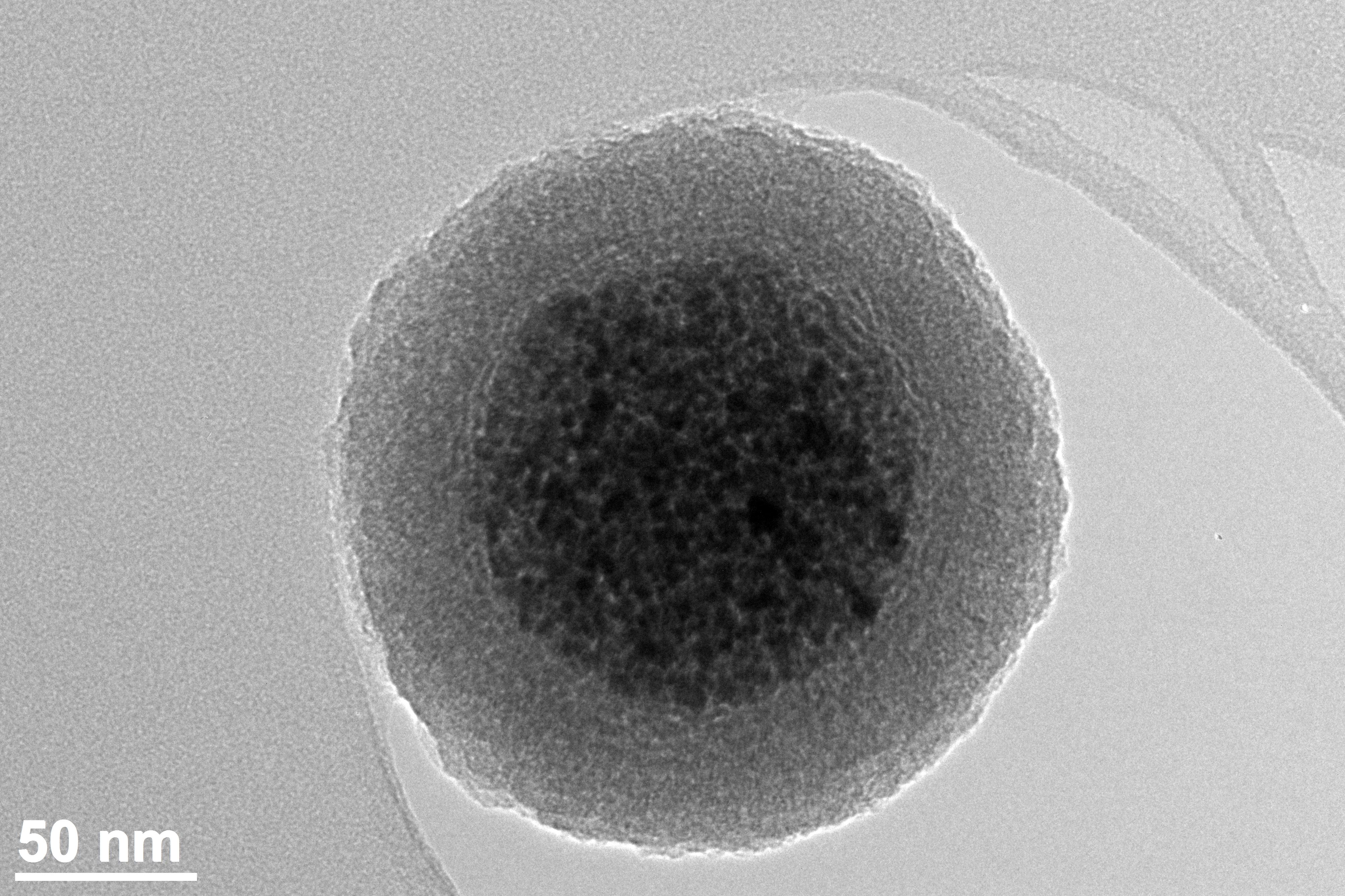
Superparamagnetism
Superparamagnetism is a form of magnetism which appears in small ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic nanoparticles. In sufficiently small nanoparticles, magnetization can randomly flip direction under the influence of temperature. The typical time between two flips is called the Néel relaxation time. In the absence of an external magnetic field, when the time used to measure the magnetization of the nanoparticles is much longer than the Néel relaxation time, their magnetization appears to be in average zero; they are said to be in the superparamagnetic state. In this state, an external magnetic field is able to magnetize the nanoparticles, similarly to a paramagnet. However, their magnetic susceptibility is much larger than that of paramagnets. The Néel relaxation in the absence of magnetic field Normally, any ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material undergoes a transition to a paramagnetic state above its Curie temperature. Superparamagnetism is different from this standard transi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Nanoparticles
Magnetic nanoparticles are a class of nanoparticle that can be manipulated using magnetic fields. Such particles commonly consist of two components, a magnetic material, often iron, nickel and cobalt, and a chemical component that has functionality. While nanoparticles are smaller than 1 micrometer in diameter (typically 1–100 nanometers), the larger microbeads are 0.5–500 micrometer in diameter. Magnetic nanoparticle clusters that are composed of a number of individual magnetic nanoparticles are known as magnetic nanobeads with a diameter of 50–200 nanometers. Magnetic nanoparticle clusters are a basis for their further magnetic assembly into magnetic nanochains. The magnetic nanoparticles have been the focus of much research recently because they possess attractive properties which could see potential use in catalysis including nanomaterial-based catalysts, biomedicine and tissue specific targeting, antimicrobial agents, magnetically tunable colloidal photonic crystals, mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |