|
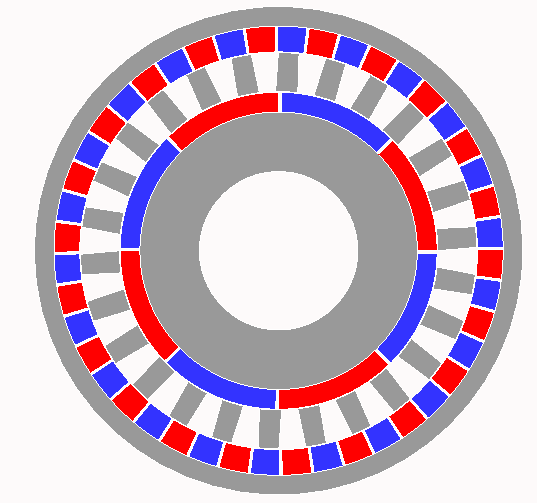
Magnetic Gear
A magnetic gear resembles the traditional mechanical gear in geometry and function, using magnets instead of teeth. As two opposing magnets approach each other, they repel; when placed on two rings the magnets will act like teeth. As opposed to conventional hard contact backlash in a spur gear, where a gear may rotate freely until in contact with the next gear, the magnetic gear has a springy backlash. As a result magnetic gears are able to apply pressure no matter the relative angle. Although they provide a motion ratio as a traditional gear, such gears work without touching and are immune to wear of mating surfaces, have no noise, and may slip without damage. A magnetically coupled gear can be used in a vacuum without lubrication, or operations involving hermetically sealed barriers. This can be an advantage in explosive or otherwise hazardous environments where leaks constitute a real danger. Design Magnetic gear systems typically use permanent magnets. They may also u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gear
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic principle behind the operation of gears is analogous to the basic principle of levers. A gear may also be known informally as a cog. Geared devices can change the speed, torque, and direction of a power source. Gears of different sizes produce a change in torque, creating a mechanical advantage, through their ''gear ratio'', and thus may be considered a simple machine. The rotational speeds, and the torques, of two meshing gears differ in proportion to their diameters. The teeth on the two meshing gears all have the same shape. Two or more meshing gears, working in a sequence, are called a gear train or a '' transmission''. The gears in a transmission are analogous to the wheels in a crossed, belt pulley system. An advantage of gears is tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permanent Magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, cobalt, etc. and attracts or repels other magnets. A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include the elements iron, nickel and cobalt and their alloys, some alloys of rare-earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weakly to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in the hole in the center of the coil. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet. The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field. Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, electromechanical solen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycloidal Drive
A cycloidal drive or cycloidal speed reducer is a mechanism for reducing the speed of an input shaft by a certain ratio. Cycloidal speed reducers are capable of relatively high ratios in compact sizes with very low backlash. The input shaft drives an eccentric bearing that in turn drives the cycloidal disc in an eccentric, cycloidal motion. The perimeter of this disc is geared to a stationary ring gear and has a series of output shaft pins or rollers placed through the face of the disc. These output shaft pins directly drive the output shaft as the cycloidal disc rotates. The radial motion of the disc is not translated to the output shaft. Theory of operation The input shaft is mounted eccentrically to a rolling-element bearing (typically a cylindrical roller bearing), causing the cycloidal disc to wobble in a circle. The cycloidal disc will independently rotate around the bearing as it is pushed against the ring gear. This is similar to planetary gearing. The direction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicyclic Gearing
An epicyclic gear train (also known as a planetary gearset) consists of two gears mounted so that the center of one gear revolves around the center of the other. A carrier connects the centers of the two gears and rotates the planet and sun gears mesh so that their pitch circles roll without slip. A point on the pitch circle of the planet gear traces an epicycloid curve. In this simplified case, the sun gear is fixed and the planetary gear(s) roll around the sun gear. An epicyclic gear train can be assembled so the planet gear rolls on the inside of the pitch circle of a fixed, outer gear ring, or ring gear, sometimes called an ''annular gear''. In this case, the curve traced by a point on the pitch circle of the planet is a hypocycloid. The combination of epicycle gear trains with a planet engaging both a sun gear and a ring gear is called a ''planetary gear train''.J. J. Uicker, G. R. Pennock and J. E. Shigley, 2003, ''Theory of Machines and Mechanisms,'' Oxford University Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gearbox
Propulsion transmission is the mode of transmitting and controlling propulsion power of a machine. The term ''transmission'' properly refers to the whole drivetrain, including clutch, gearbox, prop shaft (for rear-wheel drive vehicles), differential, and final drive shafts. In the United States the term is sometimes used in casual speech to refer more specifically to the gearbox alone, and detailed usage differs. The transmission reduces the higher engine speed to the slower wheel speed, increasing torque in the process. Transmissions are also used on pedal bicycles, fixed machines, and where different rotational speeds and torques are adapted. Often, a transmission has multiple gear ratios (or simply "gears") with the ability to switch between them as the speed varies. This switching may be done manually (by the operator) or automatically (by a control unit). Directional (forward and reverse) control may also be provided. Single-ratio transmissions also exist, which simply chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque Multiplier
A torque multiplier is a tool used to provide a mechanical advantage in applying torque to turn bolts, nuts or other items designed to be actuated by application of torque, particularly where there are relatively high torque requirements. Description Torque multipliers are often used instead of extended handles, often called "cheater bars". Extended handles use leverage instead of gear reduction to achieve torque. This torque is transmitted through the driving tool and could become dangerous in the case of a sudden catastrophic failure of the drive tool with the extended handle attached. Torque multipliers only have a fraction of the final torque pressure on the drive tool making them a safer choice. Torque multipliers typically employ an epicyclic gear train having one or more stages. Each stage of gearing multiplies the torque applied. In epicyclic gear systems, torque is applied to the input gear or ‘sun’ gear. A number of planet gears are arranged around and engaged wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Devices
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Magnetism is one aspect of the combined phenomena of electromagnetism. The most familiar effects occur in ferromagnetic materials, which are strongly attracted by magnetic fields and can be magnetization, magnetized to become permanent magnets, producing magnetic fields themselves. Demagnetizing a magnet is also possible. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic; the most common ones are iron, cobalt, and nickel and their alloys. The rare-earth metals neodymium and samarium are less common examples. The prefix ' refers to iron because permanent magnetism was first observed in lodestone, a form of natural iron ore called magnetite, Fe3O4. All substances exhibit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |