|
Madilog
The ''Madilog'' by Iljas Hussein (the pen name of Tan Malaka), first published in 1943, official first edition 1951, is the magnum opus of Tan Malaka, the Indonesian national hero and is the most influential work in the history of modern Indonesian philosophy. ''Madilog'' is an Indonesian acronym that stands for ''Materialisme Dialektika Logika'' (literally, Materialism Dialectics Logics). It is a synthesis of Marxist dialectical materialism and Hegelian logic. Madilog was written in Batavia where Malaka was hiding during the Japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies, disguised as a tailor. If Malaka's essay "Naar de Republiek Indonesië" ("Towards a Republic of Indonesia") published in 1928, under the Dutch East Indies government, stands as a formulation of the national identity of Indonesia, then ''Madilog'' stands as an anticlimax of his ideas in the sense of building the Indonesian character in modern society. Although ''Madilog'' is based on Marxism, it neither i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tan Malaka
Tan Malaka (2 June 1897 – 21 February 1949) was an Indonesian teacher, Marxist, philosopher, founder of Struggle Union (Persatuan Perjuangan) and Murba Party, independent guerrilla, Indonesian fighter, and national hero. ''Tempo'' credited him as Father of the Republic of Indonesia (Indonesian: ''Bapak Republik Indonesia''). Early life Family and childhood Tan Malaka's full name was Ibrahim Gelar Datuk Sutan Malaka. His given name was ''Ibrahim'', but he was known both as a child and as an adult as Tan Malaka, an honorary and semi-aristocratic name, he inherited from his mother's aristocratic background. He was born in present-day Nagari Pandam Gadang, Suliki, Lima Puluh Kota Regency, West Sumatra, which was then under the rule of the Dutch East Indies. His date of birth in unclear, and varies from source to source, but is likely sometime between 1894 and 1897. His father was HM. Rasad Caniago, an agricultural employee, and Rangkayo Sinah Simabur, a daughter of a respec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Translations
Dutch commonly refers to: * Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands * Dutch people () * Dutch language () Dutch may also refer to: Places * Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States * Pennsylvania Dutch Country People Ethnic groups * Germanic peoples, the original meaning of the term ''Dutch'' in English ** Pennsylvania Dutch, a group of early Germanic immigrants to Pennsylvania * Dutch people, the Germanic group native to the Netherlands Specific people * Dutch (nickname), a list of people * Johnny Dutch (born 1989), American hurdler * Dutch Schultz (1902–1935), American mobster born Arthur Simon Flegenheimer * Dutch Mantel, ring name of American retired professional wrestler Wayne Maurice Keown (born 1949) * Dutch Savage, ring name of professional wrestler and promoter Frank Stewart (1935–2013) Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional characters * Dutch (''Black Lagoon''), an African-American character from the Japanese manga and anime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (; ; 27 August 1770 – 14 November 1831) was a German philosopher. He is one of the most important figures in German idealism and one of the founding figures of modern Western philosophy. His influence extends across the entire range of contemporary philosophical topics, from metaphysical issues in epistemology and ontology, to political philosophy, the philosophy of history, philosophy of art, philosophy of religion, and the history of philosophy. Born in 1770 in Stuttgart during the transitional period between the Enlightenment and the Romantic movement in the Germanic regions of Europe, Hegel lived through and was influenced by the French Revolution and the Napoleonic wars. His fame rests chiefly upon ''The Phenomenology of Spirit'', ''The Science of Logic'', and his lectures at the University of Berlin on topics from his ''Encyclopedia of the Philosophical Sciences''. Throughout his work, Hegel strove to address and correct the probl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demographics Of Indonesia
The population of Indonesia was 270.20 million according to the 2020 national census, an increase from 237.64 in 2010. Indonesia is the fourth most populous country in the world. Approximately 55% of Indonesia's population resides on Java, which is the most populous island in the world. Despite a fairly effective family planning program that has been in place since 1967, Indonesia's average population growth per year was over 1.1% for the decade ending in 2020, nearly having 13% population growth for that decade. At this rate, Indonesia's population is projected to surpass the population of the United States if the population growth is not maintained . Indonesia has a relatively young population compared to Western nations, though it is aging as the country's birth rate has slowed and its life expectancy has increased. The median age was 30.2 years in 2017. Indonesia includes numerous ethnic, cultural and linguistic groups, some of which are related to each other. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Indonesia
More than 700 living languages are spoken in Indonesia. These figures indicate that Indonesia has about 10% of the world's languages, establishing its reputation as the second most linguistically diverse nation in the world after Papua New Guinea. Most languages belong to the Austronesian language family, while there are over 270 Papuan languages spoken in eastern Indonesia. The language most widely spoken as a native language is Javanese. Languages in Indonesia are classified into nine categories: national language, locally used indigenous languages, regional lingua francas, foreign and additional languages, heritage languages, languages in the religious domain, English as a lingua franca, and sign languages. National language The official language of Indonesia is Indonesian (locally known as ''bahasa Indonesia''), a standardised form of Malay, which serves as the lingua franca of the archipelago. The vocabulary of Indonesian borrows heavily from regional languages of In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesian Archipelago
The islands of Indonesia, also known as the Indonesian Archipelago ( id, Kepulauan Indonesia) or Nusantara, may refer either to the islands comprising the country of Indonesia or to the geographical groups which include its islands. History The exact number of islands comprising Indonesia varies among definitions and sources. According to the Law No 9/1996 on Maritime Territory of Indonesia, of 17,508 officially listed islands within the territory of the Republic of Indonesia. According to a geospatial survey conducted between 2007 and 2010 by the National Coordinating Agency for Survey and Mapping (Bakorsurtanal), Indonesia has 13,466 islands. However, according to earlier survey in 2002 by National Institute of Aeronautics and Space (LAPAN), the Indonesian archipelago has 18,307 islands, and according to the CIA ''World Factbook'', there are 17,508 islands. The discrepancy of the numbers of Indonesian islands was because that the earlier surveys include "tidal islands"; s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logical Positivism
Logical positivism, later called logical empiricism, and both of which together are also known as neopositivism, is a movement in Western philosophy whose central thesis was the verification principle (also known as the verifiability criterion of meaning). This theory of knowledge asserted that only statements verifiable through direct observation or logical proof are meaningful in terms of conveying truth value, information or factual content. Starting in the late 1920s, groups of philosophers, scientists, and mathematicians formed the Berlin Circle and the Vienna Circle, which, in these two cities, would propound the ideas of logical positivism. Flourishing in several European centres through the 1930s, the movement sought to prevent confusion rooted in unclear language and unverifiable claims by converting philosophy into "scientific philosophy", which, according to the logical positivists, ought to share the bases and structures of empirical sciences' best examples, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy Of Science
Philosophy of science is a branch of philosophy concerned with the foundations, methods, and implications of science. The central questions of this study concern what qualifies as science, the reliability of scientific theories, and the ultimate purpose of science. This discipline overlaps with metaphysics, ontology, and epistemology, for example, when it explores the relationship between science and truth. Philosophy of science focuses on metaphysical, epistemic and semantic aspects of science. Ethical issues such as bioethics and scientific misconduct are often considered ethics or science studies rather than the philosophy of science. There is no consensus among philosophers about many of the central problems concerned with the philosophy of science, including whether science can reveal the truth about unobservable things and whether scientific reasoning can be justified at all. In addition to these general questions about science as a whole, philosophers of science consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 pamphlet ''The Communist Manifesto'' and the four-volume (1867–1883). Marx's political and philosophical thought had enormous influence on subsequent intellectual, economic, and political history. His name has been used as an adjective, a noun, and a school of social theory. Born in Trier, Germany, Marx studied law and philosophy at the universities of Bonn and Berlin. He married German theatre critic and political activist Jenny von Westphalen in 1843. Due to his political publications, Marx became stateless and lived in exile with his wife and children in London for decades, where he continued to develop his thought in collaboration with German philosopher Friedrich Engels and publish his writings, researching in the British Mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
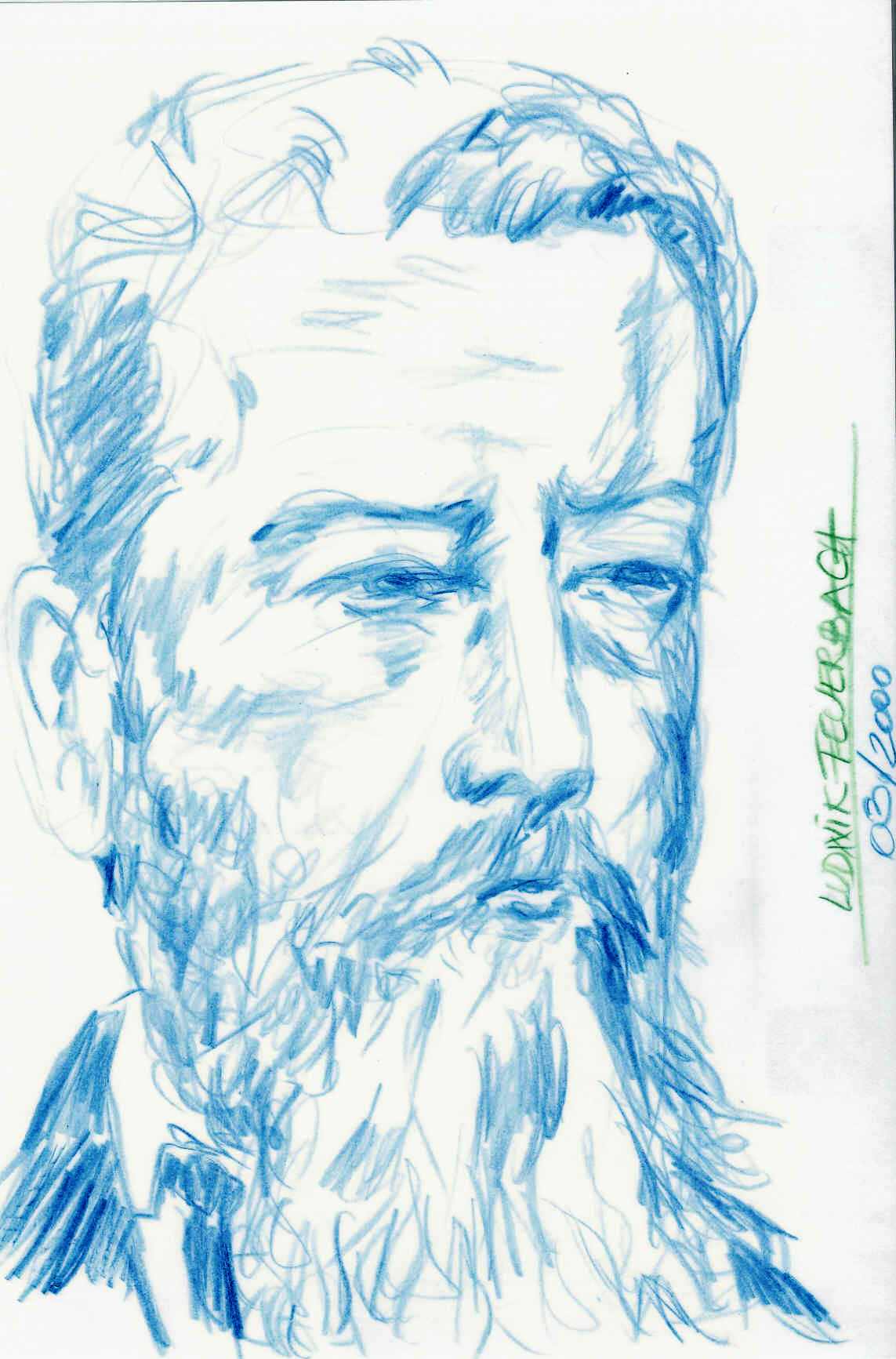
Ludwig Feuerbach
Ludwig Andreas von Feuerbach (; 28 July 1804 – 13 September 1872) was a German anthropologist and philosopher, best known for his book ''The Essence of Christianity'', which provided a critique of Christianity that strongly influenced generations of later thinkers, including Charles Darwin, Karl Marx, Sigmund Freud, Friedrich Engels, Richard Wagner, and Friedrich Nietzsche. An associate of Young Hegelian circles, Feuerbach advocated atheism and anthropological materialism. Many of his philosophical writings offered a critical analysis of religion. His thought was influential in the development of historical materialism,Nicholas Churchich, ''Marxism and Alienation'', Fairleigh Dickinson University Press, 1990, p. 57: "Although Marx has rejected Feuerbach's abstract materialism," Lenin says that Feuerbach's views "are consistently materialist," implying that Feuerbach's conception of causality is entirely in line with dialectical materialism." where he is often recognized as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hegel
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (; ; 27 August 1770 – 14 November 1831) was a German philosopher. He is one of the most important figures in German idealism and one of the founding figures of modern Western philosophy. His influence extends across the entire range of contemporary philosophical topics, from metaphysical issues in epistemology and ontology, to political philosophy, the philosophy of history, philosophy of art, philosophy of religion, and the history of philosophy. Born in 1770 in Stuttgart during the transitional period between the Enlightenment and the Romantic movement in the Germanic regions of Europe, Hegel lived through and was influenced by the French Revolution and the Napoleonic wars. His fame rests chiefly upon ''The Phenomenology of Spirit'', ''The Science of Logic'', and his lectures at the University of Berlin on topics from his ''Encyclopedia of the Philosophical Sciences''. Throughout his work, Hegel strove to address and correct the problema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of people),Anthony D. Smith, Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Theory, Ideology, History''. Polity (publisher), Polity, 2010. pp. 9, 25–30; especially with the aim of gaining and maintaining the nation's sovereignty (self-governance) over its homeland to create a nation-state. Nationalism holds that each nation should govern itself, free from outside interference (self-determination), that a nation is a natural and ideal basis for a polity, and that the nation is the only rightful source of political power. It further aims to build and maintain a single national identity, based on a combination of shared social characteristics such as culture, ethnicity, geographic location, language, politics (or the government), religion, traditions and belief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |