|
Madhava's Sine Table
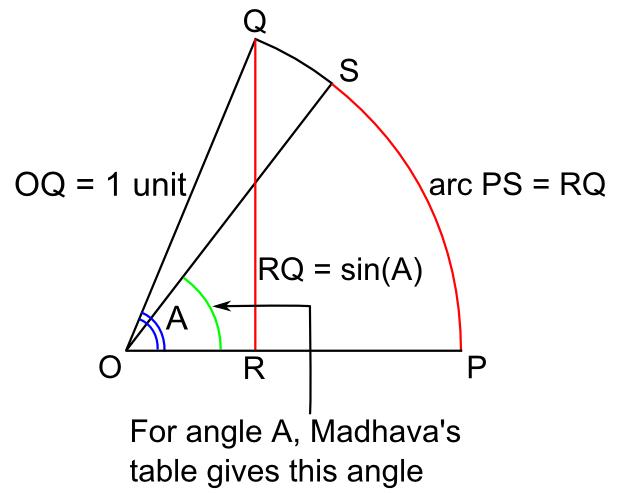
Madhava's sine table is the table of trigonometric sines of various angles constructed by the 14th century Kerala mathematician-astronomer Madhava of Sangamagrama. The table lists the trigonometric sines of the twenty-four angles 3.75°, 7.50°, 11.25°, ..., and 90.00° (angles that are integral multiples of 3.75°, i.e. 1/24 of a right angle, beginning with 3.75 and ending with 90.00). The table is encoded in the letters of Devanagari using the Katapayadi system. This gives the entries in the table an appearance of the verses of a poem in Sanskrit. Madhava's original work containing the sine table has not yet been traced. The table is seen reproduced in the ''Aryabhatiyabhashya'' of Nilakantha Somayaji''The Aryabhatiam of Aryabhattacharya with the Bhashya of Nilakantha Somasutvan, Part1-Gaṇitapāda,'' Edited by K. Sambasiva Sastri, Trivandrum Sanskrit Series No.101. p. 55. https://archive.org/details/Trivandrum_Sanskrit_Series_TSS http://www.sanskritebooks.org/2013/02/t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table (information)
A table is an arrangement of information or data, typically in rows and columns, or possibly in a more complex structure. Tables are widely used in communication, research, and data analysis. Tables appear in print media, handwritten notes, computer software, architectural ornamentation, traffic signs, and many other places. The precise conventions and terminology for describing tables vary depending on the context. Further, tables differ significantly in variety, structure, flexibility, notation, representation and use. Information or data conveyed in table form is said to be in tabular format (adjective). In books and technical articles, tables are typically presented apart from the main text in numbered and captioned floating blocks. Basic description A table consists of an ordered arrangement of rows and columns. This is a simplified description of the most basic kind of table. Certain considerations follow from this simplified description: * the term row has several c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantrasamgraha
Tantrasamgraha, or Tantrasangraha, (literally, ''A Compilation of the System'') is an important astronomical treatise written by Nilakantha Somayaji, an astronomer/mathematician belonging to the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics. The treatise was completed in 1501 CE. It consists of 432 verses in Sanskrit divided into eight chapters. Tantrasamgraha had spawned a few commentaries: ''Tantrasamgraha-vyakhya'' of anonymous authorship and '' Yuktibhāṣā'' authored by Jyeshtadeva in about 1550 CE. Tantrasangraha, together with its commentaries, bring forth the depths of the mathematical accomplishments the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics, in particular the achievements of the remarkable mathematician of the school Sangamagrama Madhava. In his ''Tantrasangraha'', Nilakantha revised Aryabhata's model for the planets Mercury and Venus. His equation of the centre for these planets remained the most accurate until the time of Johannes Kepler in the 17th century.G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherpu
Cherpu is a suburb of Thrissur city in the Kerala State of South India. It is 12 kilometres south of Thrissur town and is on the Thriprayar road. It is dotted by a number of temples and has quite a few rivers flowing by its vicinity. The village occupies a prominent place in the Kerala's cultural map as Cherpu is one of the main venues of the state's classical percussion ensembles like chenda melam and panchavadyam, staged as they are during temple festivals called pooram. Naturally, Cherpu is the birthplace of many leading (as well as lesser known) practitioners of ethnic Kerala instruments like chenda, ilathalam, kombu, kuzhal, timila, maddalam and edakka. Cherpu has two major poorams—Peruvanam Pooram and Arattupuzha Pooram. Peruvanam, otherwise traditionally known as one of the leading Namboodiri villages of Kerala, has today many of its people employed in the manufacture of furniture and gold ornaments. Legend has it that Peruvanam village was one of the settlements cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karanapaddhati
Karanapaddhati is an astronomical treatise in Sanskrit attributed to Puthumana Somayaji, an astronomer-mathematician of the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics. The period of composition of the work is uncertain. C.M. Whish, a civil servant of the East India Company, brought this work to the attention of European scholars for the first time in a paper published in 1834. The book is divided into ten chapters and is in the form of verses in Sanskrit. The sixth chapter contains series expansions for the value of the mathematical constant π, and expansions for the trigonometric sine, cosine and inverse tangent functions. Author and date of Karanapaddhati Nothing definite is known about the author of Karanapaddhati. The last verse of the tenth chapter of Karanapaddhati describes the author as a Brahamin residing in a village named Sivapura. Sivapura is an area surrounding the present day Thrissur in Kerala, India. The period in which Somayaji lived is also uncertain. Ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhūtasaṃkhyā System
The Bhūtasaṃkhyā system is a method of recording numbers in Sanskrit using common nouns having connotations of numerical values. The method was introduced already in astronomical texts in antiquity, but it was expanded and developed during the medieval period. A kind of rebus system, bhūtasaṃkhyā has also been called the "concrete number notation". For example, the number "two" was associated with the word "eye" as every human being has two eyes. Thus every Sanskrit word having the meaning "eye" was used to denote "two". All words synonymous with the meaning "earth" could be used to signify the number "one" as there is only one earth, etc. In the more expansive examples of application, concepts, ideas and objects from all parts of the Sanskrit lexicon were harvested to generate number-connoting words, resulting in a kind of kenning system for numbers. Thus, every Sanskrit word indicating an "arrow" has been used to denote "five" as Kamadeva, the Hindu deity of love ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madhava Value Of Pi
Mādhava means Lord Krishna an incarnation of Vishnu. It may also refer to: *a Sanskrit patronymic, "descendant of Madhu (a man of the Yadu tribe)". ** especially of Krishna, see Madhava (Vishnu) *** an icon of Krishna ** Madhava of Sangamagrama, fourteenth-century Indian mathematician ** Madhvacharya, philosopher in the Vaishnavism tradition ** Madhava Vidyaranya, Advaita saint and brother of Sayana ** Venkata Madhava, 10th to 12th century commentator of the Rigveda ** Madhavdeva, 16th-century proponent of Ekasarana dharma, neo-Vaishnavism of Assam *relating to springtime; the first month of spring, see Chaitra *a name of Krishna *Madhava or Madhava-kara, an Indian physician of the 7th or early 8th century See also *Madhavan (other) *Madhavi (other) *Magha (month) Maagha (Hindi: माघ ''maagh'') is a month of the Hindu calendar. In India's national civil calendar, it's the eleventh month of the year, corresponding to January/February in the Gregorian c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Āryabhaṭīya
''Aryabhatiya'' (IAST: ') or ''Aryabhatiyam'' ('), a Sanskrit astronomical treatise, is the ''magnum opus'' and only known surviving work of the 5th century Indian mathematician Aryabhata. Philosopher of astronomy Roger Billard estimates that the book was composed around 510 CE based on historical references it mentions. Structure and style Aryabhatiya is written in Sanskrit and divided into four sections; it covers a total of 121 verses describing different moralitus via a mnemonic writing style typical for such works in India (see definitions below): 1. Gitikapada (13 verses): large units of time—kalpa, manvantara, and yuga—which present a cosmology different from earlier texts such as Lagadha's Vedanga Jyotisha (ca. 1st century BCE). There is also a table of ine (jya), given in a single verse. The duration of the planetary revolutions during a mahayuga is given as 4.32 million years. 2. Ganitapada (33 verses): covering mensuration (kṣetra vyāvahāra); arithmetic and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is of an arcminute, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcsecond (mas) and microarcsecond (μas), for instance, are commonly used in astron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minute Of Arc
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is of an arcminute, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcsecond (mas) and microarcsecond (μas), for instance, are commonly used in ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpendicular
In elementary geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at a right angle (90 degrees or π/2 radians). The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the ''perpendicular symbol'', ⟂. It can be defined between two lines (or two line segments), between a line and a plane, and between two planes. Perpendicularity is one particular instance of the more general mathematical concept of '' orthogonality''; perpendicularity is the orthogonality of classical geometric objects. Thus, in advanced mathematics, the word "perpendicular" is sometimes used to describe much more complicated geometric orthogonality conditions, such as that between a surface and its '' normal vector''. Definitions A line is said to be perpendicular to another line if the two lines intersect at a right angle. Explicitly, a first line is perpendicular to a second line if (1) the two lines meet; and (2) at the point of intersection the straight angle on one side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is constant. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is called the radius. Usually, the radius is required to be a positive number. A circle with r=0 (a single point) is a degenerate case. This article is about circles in Euclidean geometry, and, in particular, the Euclidean plane, except where otherwise noted. Specifically, a circle is a simple closed curve that divides the plane into two regions: an interior and an exterior. In everyday use, the term "circle" may be used interchangeably to refer to either the boundary of the figure, or to the whole figure including its interior; in strict technical usage, the circle is only the boundary and the whole figure is called a '' disc''. A circle may also be defined as a special ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)