|
Macromolecular Cages
Macromolecular cages have three dimensional chambers surrounded by a molecular framework. Macromolecular cage architectures come in various sizes ranging from 1-50 nm and have varying topologies as well as functions. They can be synthesized through covalent bonding or self-assembly through non-covalent interactions. Most macromolecular cages that are formed through self-assembly are sensitive to pH, temperature, and solvent polarity. Metal Organic Polyhedra Metal Organic Polyhedra (MOPs) comprise a specific type of self-assembled macromolecular cage that is formed through unique coordination and is typically chemically and thermally stable. MOPs have cage-like frameworks with an enclosed cavity. The discrete self-assembly of metal ions and organic scaffolds to form MOPs into highly symmetrical architectures, is a modular process and has various applications. The self-assembly of various subunits that result in high symmetry is a common occurrence in biological systems. Spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
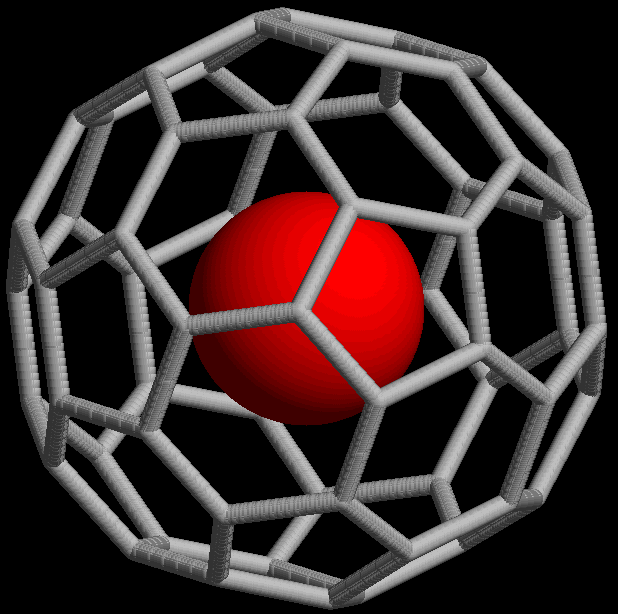
Endohedral Fullerene
Endohedral fullerenes, also called endofullerenes, are fullerenes that have additional atoms, ions, or clusters enclosed within their inner spheres. The first lanthanum C60 complex called La@C60 was synthesized in 1985. The @ (at sign) in the name reflects the notion of a small molecule trapped inside a shell. Two types of endohedral complexes exist: endohedral metallofullerenes and non-metal doped fullerenes. Notation In a traditional chemical formula notation, a buckminsterfullerene (C60) with an atom (M) was simply represented as MC60 regardless of whether M was inside or outside the fullerene. In order to allow for more detailed discussions with minimal loss of information, a more explicit notation was proposed in 1991, where the atoms listed to the left of the @ sign are situated inside the network composed of the atoms listed to the right. The example above would then be denoted M@C60 if M were inside the carbon network. A more complex example is K2(K@C59B), which denotes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDB 2ba0 EBI
PDB may refer to: * Chess Problem Database Server (PDB Server) * 1,4-Dichlorobenzene (paradichlorobenzene) * Party of German-speaking Belgians, (German: '), a political party and predecessor of the ProDG * PDB (Palm OS), a container format for record databases in Palm OS, Garnet OS and Access Linux Platform * ''Pee Dee Belemnite'', a standard for stable Carbon-13 and Oxygen-18 isotopes; see * Pluggable database, such as an Oracle Database in a multitenancy environment * Potato dextrose broth, a common microbiological growth media * Pousette-Dart Band * President's Daily Brief or Briefing or Bulletin, a top-secret intelligence document produced each morning for the U.S. President * Program database, a file format for storing debugging information * Promised Day Brigade, an Iraqi Shia organisation * Protein Data Bank * Protein Data Bank (file format) The Protein Data Bank (PDB) file format is a textual file format describing the three-dimensional structures of molecules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization
Atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) is an example of a reversible-deactivation radical polymerization. Like its counterpart, ATRA, or atom transfer radical addition, ATRP is a means of forming a carbon-carbon bond with a transition metal catalyst. Polymerization from this method is called atom transfer radical addition polymerization (ATRAP). As the name implies, the atom transfer step is crucial in the reaction responsible for uniform polymer chain growth. ATRP (or transition metal-mediated living radical polymerization) was independently discovered by Mitsuo Sawamoto and by Krzysztof Matyjaszewski and Jin-Shan Wang in 1995. ::The following scheme presents a typical ATRP reaction: Overview of ATRP ATRP usually employs a transition metal complex as the catalyst with an alkyl halide as the initiator (R-X). Various transition metal complexes, namely those of Cu, Fe, Ru, Ni, and Os, have been employed as catalysts for ATRP. In an ATRP process, the dormant species is activated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copolymer
In polymer chemistry, a copolymer is a polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. The polymerization of monomers into copolymers is called copolymerization. Copolymers obtained from the copolymerization of two monomer species are sometimes called ''bipolymers''. Those obtained from three and four monomers are called ''terpolymers'' and ''quaterpolymers'', respectively. Copolymers can be characterized by a variety of techniques such as NMR spectroscopy and size-exclusion chromatography to determine the molecular size, weight, properties, and composition of the material. Commercial copolymers include acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), styrene/butadiene co-polymer (SBR), nitrile rubber, styrene-acrylonitrile, styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) and ethylene-vinyl acetate, all of which are formed by chain-growth polymerization. Another production mechanism is step-growth polymerization, which is used to produce the nylon-12/6/66 copolymer of nylon 12, nylon 6 and nylon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-Xylene
''p''-Xylene ( ''para''-xylene) is an aromatic hydrocarbon. It is one of the three isomers of dimethylbenzene known collectively as xylenes. The ''p-'' stands for ''para-'', indicating that the two methyl groups in ''p''-xylene occupy the diametrically opposite substituent positions 1 and 4. It is in the positions of the two methyl groups, their arene substitution pattern, that it differs from the other isomers, ''o''-xylene and ''m''-xylene. All have the same chemical formula C6H4(CH3)2. All xylene isomers are colorless and highly flammable. The odor threshold of ''p''-xylene is 0.62 parts per million (ppm). Production The production of ''p''-xylene is industrially significant, with annual demand estimated at 37 million tons in 2014, and still on the increase. ''p''-Xylene is produced by catalytic reforming of petroleum naphtha as part of the BTX aromatics (benzene, toluene and the xylene isomers) extracted from the catalytic reformate. The ''p''-xylene is then separated out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogenolysis
Hydrogenolysis is a chemical reaction whereby a carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom single bond is cleaved or undergoes lysis (breakdown) by hydrogen.Ralph Connor, Homer Adkins. Hydrogenolysis Of Oxygenated Organic Compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1932; 54(12); 4678–4690. The heteroatom may vary, but it usually is oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. A related reaction is hydrogenation, where hydrogen is added to the molecule, without cleaving bonds. Usually hydrogenolysis is conducted catalytically using hydrogen gas. History The term "hydrogenolysis" was coined by Carleton Ellis in reference to hydrogenolysis of carbon–carbon bonds. Earlier, Paul Sabatier had already observed the hydrogenolysis of benzyl alcohol to toluene, and as early as 1906, Padoa and Ponti had observed the hydrogenolysis of furfuryl alcohol. Homer Burton Adkins and Ralph Connor were the first to call the carbon–oxygen bond cleavage "hydrogenolysis". In the petrochemical industry In petroleum refineries, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Click Chemistry
In chemical synthesis, click chemistry is a class of biocompatible small molecule reactions commonly used in bioconjugation, allowing the joining of substrates of choice with specific biomolecules. Click chemistry is not a single specific reaction, but describes a way of generating products that follow examples in nature, which also generates substances by joining small modular units. In many applications, click reactions join a biomolecule and a reporter molecule. Click chemistry is not limited to biological conditions: the concept of a "click" reaction has been used in chemoproteomic, pharmacological, and various biomimetic applications. However, they have been made notably useful in the detection, localization and qualification of biomolecules. Click reactions occur in one pot, are not disturbed by water, generate minimal and inoffensive byproducts, and are "spring-loaded"—characterized by a high thermodynamic driving force that drives it quickly and irreversibly to high yi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaperonin
HSP60, also known as chaperonins (Cpn), is a family of heat shock proteins originally sorted by their 60kDa molecular mass. They prevent misfolding of proteins during stressful situations such as high heat, by assisting protein folding. HSP60 belong to a large class of molecules that assist protein folding, called molecular chaperones. Newly made proteins usually must fold from a linear chain of amino acids into a three-dimensional tertiary structure. The energy to fold proteins is supplied by non-covalent interactions between the amino acid side chains of each protein, and by solvent effects. Most proteins spontaneously fold into their most stable three-dimensional conformation, which is usually also their functional conformation, but occasionally proteins mis-fold. Molecular chaperones catalyze protein refolding by accelerating partial unfolding of misfolded proteins, aided by energy supplied by the hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Chaperonin proteins may also tag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes. Numerous human pathogenic viruses in circulation are encased in lipid bilayers, and they infect their target cells by causing the viral envelope and cell membrane to fuse. Although there are effective vaccines against some of these viruses, there is no preventative or curative medicine for the majority of them. In most cases, the known vaccines operate by inducing antibodies that prevent the pathogen from entering cells. This happens in the case of enveloped viruses when the antibodies bind to the viral envelope proteins. The membrane fusion event that triggers viral entrance is caused by the viral fusion protein. Many enveloped viruses only have one protein visible on the surface of the particle, which is required for both mediating adhesion to the cell surface and for the subsequent membrane fusi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clathrin Cage
Clathrin is a protein that plays a major role in the formation of coated vesicles. Clathrin was first isolated and named by Barbara Pearse in 1976. It forms a triskelion shape composed of three clathrin heavy chains and three light chains. When the triskelia interact they form a polyhedral lattice that surrounds the vesicle, hence the protein's name, which is derived from the Latin ''clathrum'' meaning lattice. Coat-proteins, like clathrin, are used to build small vesicles in order to transport molecules within cells. The endocytosis and exocytosis of vesicles allows cells to communicate, to transfer nutrients, to import signaling receptors, to mediate an immune response after sampling the extracellular world, and to clean up the cell debris left by tissue inflammation. The endocytic pathway can be hijacked by viruses and other pathogens in order to gain entry to the cell during infection. Structure The clathrin triskelion is composed of three clathrin heavy chains in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclease
A nuclease (also archaically known as nucleodepolymerase or polynucleotidase) is an enzyme capable of cleaving the phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides of nucleic acids. Nucleases variously effect single and double stranded breaks in their target molecules. In living organisms, they are essential machinery for many aspects of DNA repair. Defects in certain nucleases can cause genetic instability or immunodeficiency. Nucleases are also extensively used in molecular cloning. There are two primary classifications based on the locus of activity. Exonucleases digest nucleic acids from the ends. Endonucleases act on regions in the ''middle'' of target molecules. They are further subcategorized as deoxyribonucleases and ribonucleases. The former acts on DNA, the latter on RNA. History In the late 1960s, scientists Stuart Linn and Werner Arber isolated examples of the two types of enzymes responsible for phage growth restriction in Escherichia coli ( E. coli) bacteria. One of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |