|
Macroeconomic Indicators
Macroeconomic indicators are aggregated statistics for a geography, population, or political jurisdiction gathered by agencies and bureaus of various government statistical organization, and sometimes by private organizations using similar techniques. List of macroeconomic indicators * Aggregate demand * Aggregate supply * External debt indicators * GDP deflator * Green gross domestic product * Gross domestic product * Gross national product * Gross National Happiness * Jobless claims * Monetary conditions index * Net foreign assets * Nominal GDP * Nonfarm payrolls * Real gross domestic product * Social Progress Index See also * :Macroeconomic indicators * Economic indicators An economic indicator is a statistic about an economic activity. Economic indicators allow analysis of economic performance and predictions of future performance. One application of economic indicators is the study of business cycles. Economic in ... References {{Reflist Macroeconomic indicators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurisdiction
Jurisdiction (from Latin 'law' + 'declaration') is the legal term for the legal authority granted to a legal entity to enact justice. In federations like the United States, areas of jurisdiction apply to local, state, and federal levels. Jurisdiction draws its substance from international law, conflict of laws, constitutional law, and the powers of the executive and legislative branches of government to allocate resources to best serve the needs of society. International dimension Generally, international laws and treaties provide agreements which nations agree to be bound to. Such agreements are not always established or maintained. The exercise of extraterritorial jurisdiction by three principles outlined in the UN charter. These are equality of states, territorial sovereignty and non-intervention. This raises the question of when can many states prescribe or enforce jurisdiction. The ''Lotus'' case establishes two key rules to the prescription and enforcement of jurisdi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monetary Conditions Index
In macroeconomics, a monetary conditions index (MCI) is an index number calculated from a linear combination of a small number of economy-wide financial variables deemed relevant for monetary policy. These variables always include a short-run interest rate and an exchange rate. An MCI may also serve as a day-to-day operating target for the conduct of monetary policy, especially in small open economies. Central banks compute MCIs, with the Bank of Canada being the first to do so, beginning in the early 1990s. The MCI begins with a simple model of the determinants of aggregate demand in an open economy, which include variables such as the real exchange rate as well as the real interest rate. Moreover, monetary policy is assumed to have a significant effect on these variables, especially in the short run. Hence a linear combination of these variables can measure the effect of monetary policy on aggregate demand. Since the MCI is a function of the real exchange rate, the MCI is in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Macroeconomic Indicators ...
{{Commons Economic indicators Indicators Indicator may refer to: Biology * Environmental indicator of environmental health (pressures, conditions and responses) * Ecological indicator of ecosystem health (ecological processes) * Health indicator, which is used to describe the health o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Progress Index
The Social Progress Index (SPI) measures the extent to which countries provide for the social and environmental needs of their citizens. Fifty-four indicators in the areas of basic human needs, foundations of well-being, and opportunity to progress show the relative performance of nations. The index is published by the nonprofit Social Progress Imperative, and is based on the writings of Amartya Sen, Douglass North, and Joseph Stiglitz. The SPI measures the well-being of a society by observing social and environmental outcomes directly rather than the economic factors. The social and environmental factors include wellness (including health, shelter and sanitation), equality, inclusion, sustainability and personal freedom and safety. Introduction and methodology The index combines three dimensions # Basic human needs # Foundations of well-being # Opportunity Each dimension includes four components, which are each composed of between three and five specific outcome indicators. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Gross Domestic Product
Real gross domestic product (real GDP) is a macroeconomics, macroeconomic measure of the value of economic output (economics), output adjusted for price changes (i.e. inflation (economics), inflation or deflation). This adjustment transforms the money-value measure, Gross domestic product#Nominal GDP and adjustments to GDP, nominal GDP, into an Index (economics), index for quantity of total output. Although GDP is total output, it is primarily useful because it closely approximates the total spending: the sum of consumer spending, investment made by industry, excess of exports over imports, and government spending. Due to inflation, GDP increases and does not actually reflect the true growth in an economy. That is why the GDP must be divided by the inflation rate (raised to the power of units of time in which the rate is measured) to get the growth of the real GDP. Different organizations use different types of 'Real GDP' measures, for example, the United Nations Conference on Tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominal GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is often revised before being considered a reliable indicator. GDP (nominal) per capita does not, however, reflect differences in the cost of living and the inflation rates of the countries; therefore, using a basis of GDP per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP) may be more useful when comparing living standards between nations, while nominal GDP is more useful comparing national economies on the international market. Total GDP can also be broken down into the contribution of each industry or sector of the economy. The ratio of GDP to the total population of the region is the per capita GDP (also called the Mean Standard of Living). GDP definitions are maintained by a number of national and international economic organizations. The Organisa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Net Foreign Assets
In economics, the concept of net foreign assets relates to balance of payments identity. The net foreign asset (NFA) position of a country is the value of the assets that country owns abroad, minus the value of the domestic assets owned by foreigners. The net foreign asset position of a country reflects the indebtedness of that country. The traditional balance of payments identity Traditional balance-of-payments accounting is that the change in the net foreign asset position equals the current account balance. In other words, if a country runs a $700 billion current account deficit, it has to borrow exactly $700 billion from abroad to finance the deficit and therefore, the country's net foreign asset position falls by $700 billion. \begin \mbox & = \mbox \\ \end The augmented balance of payments identity The traditional balance of payments identity does not take into account changes in asset prices and exchange rates. For example, the value of external assets or liabiliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
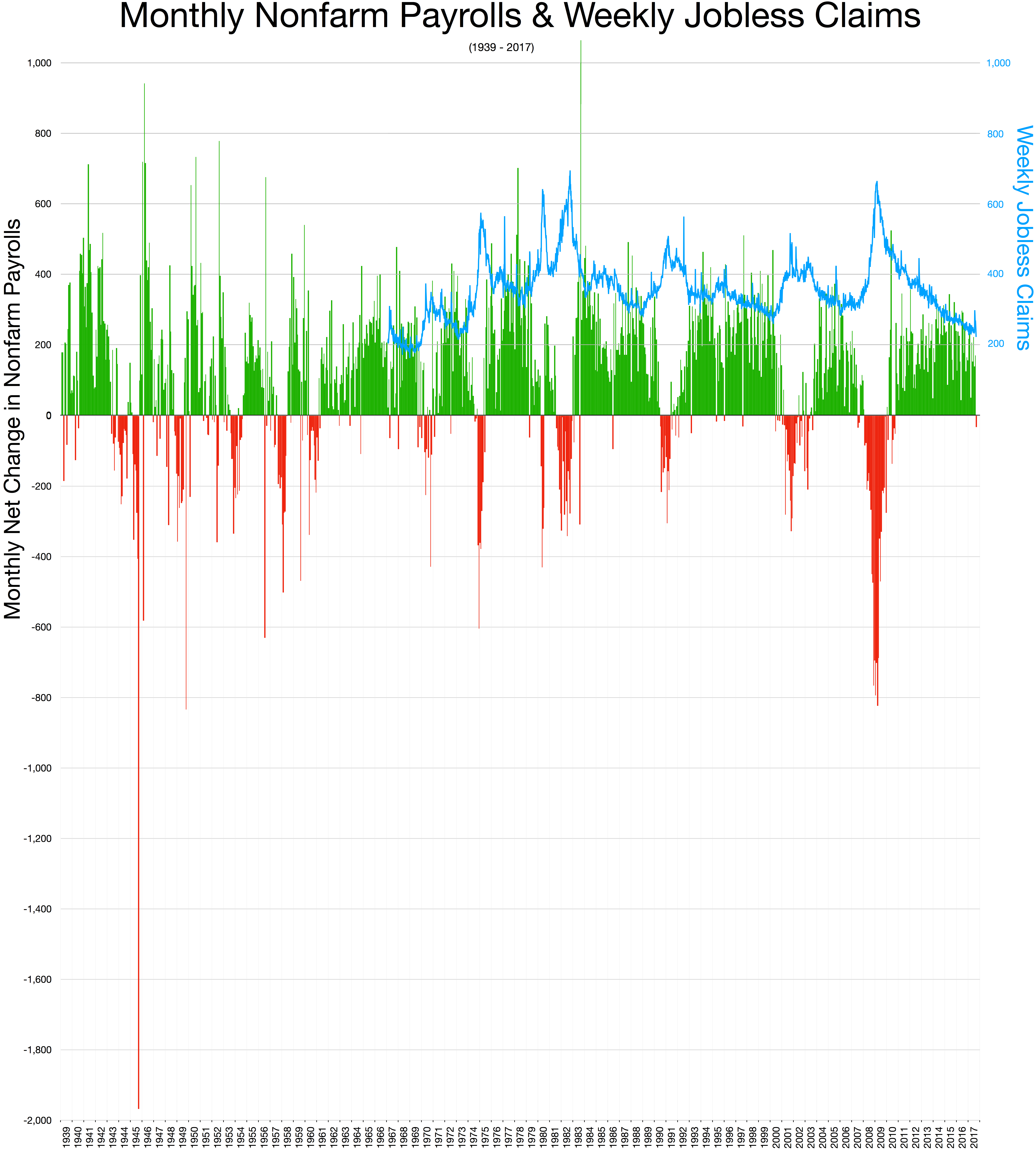
Jobless Claims
Initial jobless claims are a data point issued by the U.S. Department of Labor as part of its weekly Unemployment Insurance Weekly Claims Report. Initial jobless claims refer to claims for unemployment benefits filed by unemployed individuals with state unemployment agencies. Initial claims should not be confused with the number of people who actually receive unemployment benefits. For one, initial claims don't include continued claims—individuals who claim benefits for additional weeks of unemployment beyond their initial claim. Additionally, not all claimants will actually receive unemployment benefits. The report is released weekly at 08:30 Eastern Time on Thursdays. The data in the report is collected from state unemployment agencies who report the information to the Department of Labor's Office of Unemployment Insurance. Market impact The weekly release of the report can be a market moving event. The employment situation is extremely important for a macroeconomic analy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggregate Demand
In macroeconomics, aggregate demand (AD) or domestic final demand (DFD) is the total demand for final goods and services in an economy at a given time. It is often called effective demand, though at other times this term is distinguished. This is the demand for the gross domestic product of a country. It specifies the amount of goods and services that will be purchased at all possible price levels. Consumer spending, investment, corporate and government expenditure, and net exports make up the aggregate demand. The aggregate demand curve is plotted with real output on the horizontal axis and the price level on the vertical axis. While it is theorized to be downward sloping, the Sonnenschein–Mantel–Debreu results show that the slope of the curve cannot be mathematically derived from assumptions about individual rational behavior. Instead, the downward sloping aggregate demand curve is derived with the help of three macroeconomic assumptions about the functioning of markets: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross National Happiness
Gross National Happiness (GNH), sometimes called Gross Domestic Happiness (GDH), is a philosophy that guides the government of Bhutan. It includes an index which is used to measure the collective happiness and well-being of a population. Gross National Happiness Index is instituted as the goal of the government of Bhutan in the Constitution of Bhutan, enacted on 18 July 2008. History The advent and concept of "Gross National Happiness" (GNH) germinated in the mind of Bodhisattva Druk Gyelpo, the 4th King of Bhutan, Jigme Singye Wangchuk, groomed with the evolution of "Gaki Phuensum" (Peace and Prosperity) and the modernization period of Bhutan during the reign of Druk Gyelpo, the 3rd King of Bhutan, Jigme Dorji Wangchuk. The term "Gross National Happiness" as conceptualized by the 4th King of Bhutan, Jigme Singye Wangchuck, in 1972 was declared as, "more important than Gross Domestic Product." The concept implies that sustainable development should take a holistic approach toward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross National Product
The gross national income (GNI), previously known as gross national product (GNP), is the total domestic and foreign output claimed by residents of a country, consisting of gross domestic product (GDP), plus factor incomes earned by foreign residents, minus income earned in the domestic economy by nonresidents. Comparing GNI to GDP shows the degree to which a nation's GDP represents domestic or international activity. GNI has gradually replaced GNP in international statistics. While being conceptually identical, it is calculated differently. GNI is the basis of calculation of the largest part of contributions to the budget of the European Union. In February 2017, Ireland's GDP became so distorted from the base erosion and profit shifting ("BEPS") tax planning tools of U.S. multinationals, that the Central Bank of Ireland replaced Irish GDP with a new metric, Irish Modified GNI (or "GNI*"). In 2017, Irish GDP was 162% of Irish Modified GNI. Comparison of GNI and GDP \mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |