|
Macquarie Triple Junction
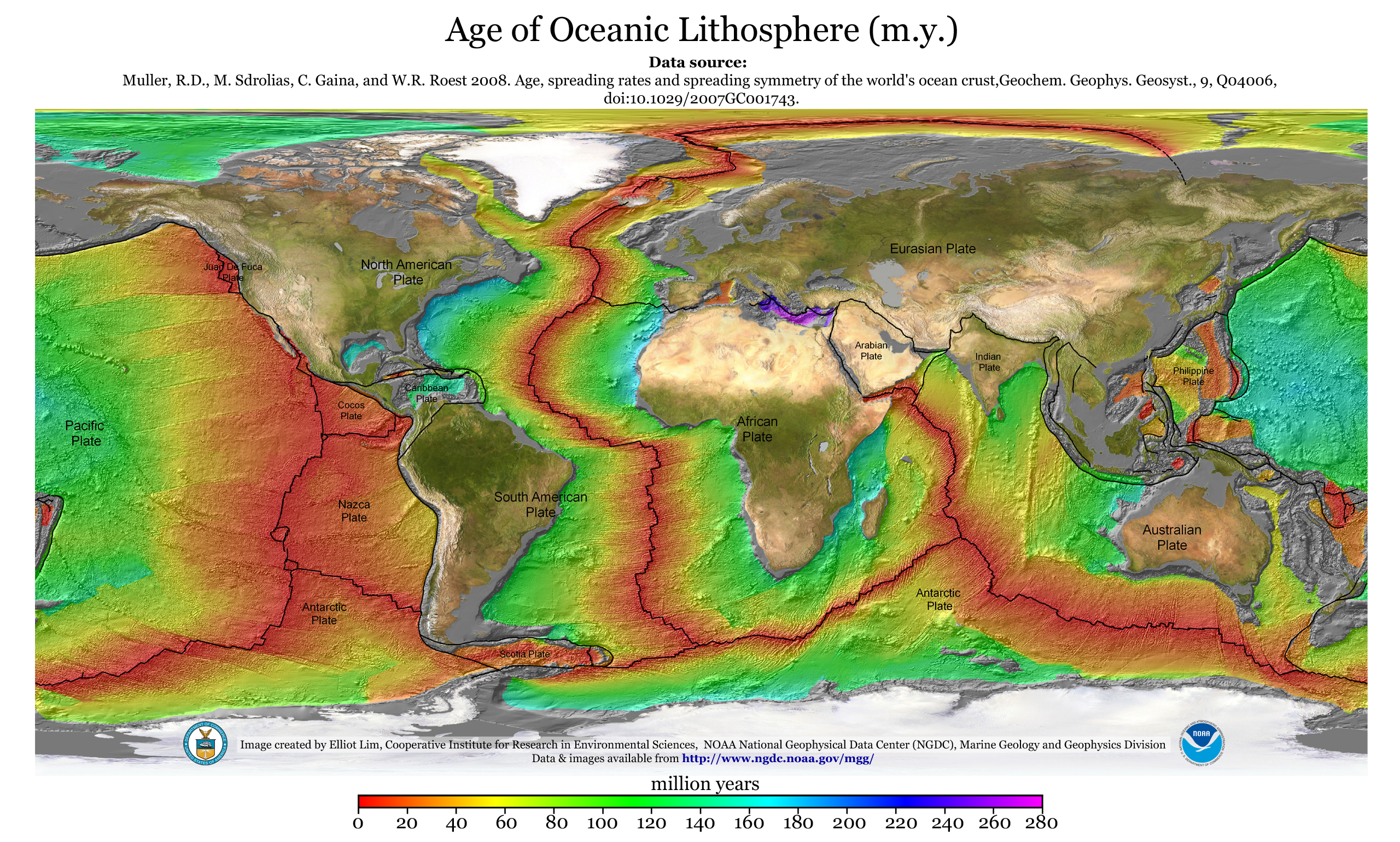
The Macquarie Triple Junction is a geologically active tectonic boundary located at at which the Indo-Australian Plate, Pacific Plate, and Antarctic Plate collide and interact. The term Triple Junction is given to particular tectonic boundaries at which three separate tectonic plates meet at a specific, singular location. The Macquarie Triple Junction is located on the seafloor of the southern region of the Pacific Ocean, just south of New Zealand. This tectonic boundary was named in respect to the nearby Macquarie Island, which is located southeast of New Zealand. Evolution, stability, and migration Our understanding of the evolution of the Macquarie Triple Junction was made possible due to extensive research of the regions tectonic magnetic anomalies as well as local fractures reconstruction. The origin of the Macquarie Triple Junction has been interpreted to have occurred 47.91 Mya (million years ago), based on Anomaly 21. Thorough reconstruction of the Macquarie Trip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macquarie Triple Junction
The Macquarie Triple Junction is a geologically active tectonic boundary located at at which the Indo-Australian Plate, Pacific Plate, and Antarctic Plate collide and interact. The term Triple Junction is given to particular tectonic boundaries at which three separate tectonic plates meet at a specific, singular location. The Macquarie Triple Junction is located on the seafloor of the southern region of the Pacific Ocean, just south of New Zealand. This tectonic boundary was named in respect to the nearby Macquarie Island, which is located southeast of New Zealand. Evolution, stability, and migration Our understanding of the evolution of the Macquarie Triple Junction was made possible due to extensive research of the regions tectonic magnetic anomalies as well as local fractures reconstruction. The origin of the Macquarie Triple Junction has been interpreted to have occurred 47.91 Mya (million years ago), based on Anomaly 21. Thorough reconstruction of the Macquarie Trip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transtension
Transtension is the state in which a rock mass or area of the Earth's crust experiences both ''extensive'' and ''transtensive'' shear. As such, transtensional regions are characterised by both extensional structures ( normal faults, grabens) and wrench structures (strike-slip faults). In general, many tectonic regimes that were previously defined as simple strike-slip shear zones are actually transtensional. It is unlikely that a deforming body will experience 'pure' extension or 'pure' strike-slip. Transtensional shear zones are characterized by the co-existence of different structures, related to both strike-slip shear and extension. End member structures include pure strike-slip faults and purely extensional ("normal") dip-slip faults. Faults which have components of both (termed 'oblique' slip faults) are abundant. Releasing bend ''Releasing bends'' are transtensional structures that form where the orientation of a strike-slip fault becomes oblique to the regional slip vector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine Fault
The Alpine Fault is a geological fault that runs almost the entire length of New Zealand's South Island (c. 480 km) and forms the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate. The Southern Alps have been uplifted on the fault over the last 12 million years in a series of earthquakes. However, most of the motion on the fault is strike-slip (side to side), with the Tasman district and West Coast moving North and Canterbury and Otago moving South. The average slip rates in the fault's central region are about 38 mm a year, very fast by global standards. The last major earthquake on the Alpine Fault was in c. 1717 AD, and the probability of another one occurring within the next 50 years is estimated at about 75 percent. Geographic extent and plate motion ThPacific Plate and Indo-Australian Plate boundaryforms the Macquarie Fault Zone in the Puysegur Trench off the southwestern corner of the South Island and comes onshore as the Alpine Fault just nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macquarie Fault Zone
The Macquarie Fault Zone is a major right lateral-moving transform fault along the seafloor of the south Pacific Ocean which runs from New Zealand southwestward to the Macquarie Triple Junction. It is also the tectonic plate boundary between the Indo-Australian Plate to the northwest and the Pacific Plate to the southeast. The Macquarie Fault Zone includes a component of convergence which increases as it approaches the South Island of New Zealand. Many researchers conclude that the fault zone here is an incipient subduction zone, with oblique motion corresponding to the transition from lateral (strike-slip) motion. In the area known as the Puysegur Trench, the Indo-Australian Plate appears to be starting to sink beneath the Pacific Plate, the reverse of what is occurring off of New Zealand's North Island (see Kermadec-Tonga Subduction Zone). A major geographic feature which runs along the Macquarie Fault Zone is known as the Macquarie Ridge. This ridge represents both the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puysegur Trench
The deepStern, Robert J. (2004)Subduction initiation: spontaneous and induced Earth and Planetary Science Letters 226, 275–292. . Puysegur Trench is a deep cleft in the floor of the south Tasman Sea formed by the subduction of the Indo-Australian Plate under the Pacific Plate to the south of New Zealand. Immediately to its east lies a ridge, a northern extension of the Macquarie Ridge, which separates the Puysegur Trench from the Solander Trough. To the west is the expanse of the Tasman Basin, which stretches most of the distance to Australia. To the north of the trench lies the Fiordland Basin, which can be considered an extension of the trench. The Puysegur Trench mirrors the Kermadec Trench and Tonga Trench north of New Zealand. The Puysegur Trench stretches for over 800 kilometres south from the southwesternmost point of the South Island's coast, its southernmost extent being 400 kilometres due west of the Auckland Islands. It is named after Puysegur Point. Earthqua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle Plumes
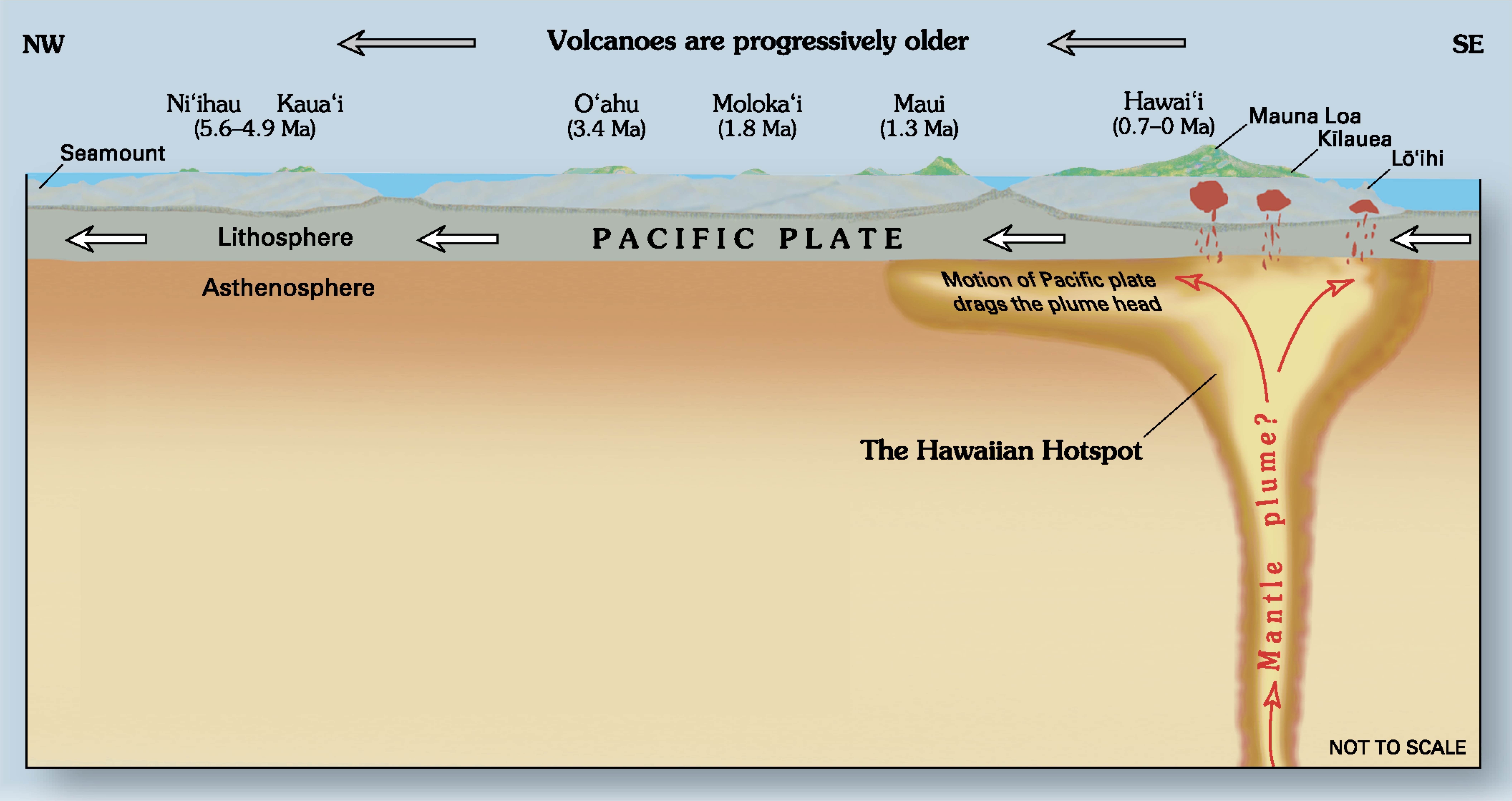
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hotspot (geology), hotspots, such as Hawaii hotspot, Hawaii or Iceland hotspot, Iceland, and large igneous provinces such as the Deccan Traps, Deccan and Siberian Traps. Some such volcanic regions lie far from Plate tectonics#Types of plate boundaries, tectonic plate boundaries, while others represent unusually large-volume volcanism near plate boundaries. Concepts Mantle plumes were first proposed by J. Tuzo Wilson in 1963 and further developed by W. Jason Morgan in 1971 and 1972. A mantle plume is posited to exist where super-heated material forms (nucleation, nucleates) at the core-mantle boundary and rises through the Earth's mantle. Rather than a continuous stream, plumes should be viewed as a series of hot bubbles of material. Reaching ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Pacific Rise
The East Pacific Rise is a mid-ocean rise (termed an oceanic rise and not a mid-ocean ridge due to its higher rate of spreading that results in less elevation increase and more regular terrain), a divergent tectonic plate boundary located along the floor of the Pacific Ocean. It separates the Pacific Plate to the west from (north to south) the North American Plate, the Rivera Plate, the Cocos Plate, the Nazca Plate, and the Antarctic Plate. It runs south from the Gulf of California in the Salton Sea basin in Southern California to a point near 55° S, 130° W, where it joins the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge trending west-southwest towards Antarctica, near New Zealand (though in some uses the PAR is regarded as the southern section of the EPR). Much of the rise lies about 3200 km (2000 mi) off the South American coast and rises about 1,800–2,700 m (6,000–9,000 ft) above the surrounding seafloor. Overview The oceanic crust is moving away from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific-Antarctic Ridge
The Pacific-Antarctic Ridge (PAR) is a Divergent boundary, divergent tectonic plate boundary located on the seafloor of the South Pacific Ocean, separating the Pacific Plate from the Antarctic Plate. It is regarded as the southern section of the East Pacific Rise in some usages, generally south of the Challenger Fracture Zone and stretching to the Macquarie Triple Junction south of New Zealand. The Louisville Ridge Stretching for 4,300 km north-west from the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge to the Osbourn Seamount at Tonga and Kermadec Junction is a long line of seamounts called the Louisville Ridge – the longest such chain in the Pacific – thought to have formed from the Pacific Plate sliding over a long-lived center of upwelling magma called the Louisville hotspot. See also * Hollister Ridge * Oceanic ridge * List of tectonic plate interactions References Further reading * {{Coord, -61.999555, -157.000165, display=title Underwater ridges of the Pacific Ocean Und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic cumulates. The crust overlies the rigid uppermost layer of the mantle. The crust and the rigid upper mantle layer together constitute oceanic lithosphere. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium. It is thinner than continental crust, or sial, generally less than 10 kilometers thick; however, it is denser, having a mean density of about 3.0 grams per cubic centimeter as opposed to continental crust which has a density of about 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter. The crust uppermost is the result of the cooling of magma derived from mantle material below the plate. The magma is injected into the spreading center, which consists mainly of a partly solidified crystal mush derived from earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-oceanic Ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting ocean basis but regardless, are traditionally called mid-ocean rid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotspot (geology)
In geology, hotspots (or hot spots) are volcanic locales thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Examples include the Hawaii, Iceland, and Yellowstone hotspots. A hotspot's position on the Earth's surface is independent of tectonic plate boundaries, and so hotspots may create a chain of volcanoes as the plates move above them. There are two hypotheses that attempt to explain their origins. One suggests that hotspots are due to mantle plumes that rise as thermal diapirs from the core–mantle boundary. The alternative plate theory is that the mantle source beneath a hotspot is not anomalously hot, rather the crust above is unusually weak or thin, so that lithospheric extension permits the passive rising of melt from shallow depths. Origin The origins of the concept of hotspots lie in the work of J. Tuzo Wilson, who postulated in 1963 that the formation of the Hawaiian Islands resulted from the slow movement of a tecton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after Indian subcontinent, India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' (Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic) before the Pacific Ocean, Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Ming treasure voyages, Chinese explorers in the Indian Oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |