|
MLC Building, Sydney
The MLC Building is a heritage-listed office building located at 42-46 Martin Place in the Sydney central business district, in the City of Sydney local government area of New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Bates Smart & McCutcheon and built from 1936 to 1938 by Concrete Constructions Limited. It is also known as Mutual Life & Assurance Building. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999. From the time of its construction and for many years thereafter, the building served as the offices for Australian life insurance company, Mutual Life & Citizens Assurance Company Limited. the anchor tenant was Norton Rose Fulbright, formerly Henry Davis York, an international law firm. History Major insurance companies were formed in Victorian Australia, often with British assets, to cover the problems of world trade, internal communication, retirement and the constant hazard of fire. The Mutual Life and Citizens Assurance Company, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Mutual Life Assurance Building
The City Mutual Life Assurance Building is a heritage-listed commercial building located at 60-66 Hunter Street, Sydney, Hunter Street, in the Sydney central business district, in the City of Sydney local government area of New South Wales, Australia. It was built during 1936. It is also known as CML Building and 10 Bligh Street. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999. History The Head Office of the City Mutual Life Assurance Society Limited has been associated with the eastern corner of Hunter and Bligh Streets since 1891. On 16 February 1891, part of the present corner site was purchased by the Society for . The site had approximately equal frontage to both street. At the time of acquisition the site was occupied by a plumber's shop at the corner of the two streets, along with several other buildings dating to the middle of the nineteenth century. Five leading Sydney architects were invited to submit designs for the Society's new head ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lighting
Lighting or illumination is the deliberate use of light to achieve practical or aesthetic effects. Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources like lamps and light fixtures, as well as natural illumination by capturing daylight. Daylighting (using windows, skylights, or light shelves) is sometimes used as the main source of light during daytime in buildings. This can save energy in place of using artificial lighting, which represents a major component of energy consumption in buildings. Proper lighting can enhance task performance, improve the appearance of an area, or have positive psychological effects on occupants. Indoor lighting is usually accomplished using light fixtures, and is a key part of interior design. Lighting can also be an intrinsic component of landscape projects. History With the discovery of fire, the earliest form of artificial lighting used to illuminate an area were campfires or torches. As early as 400,000 years ago, fire was kindl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
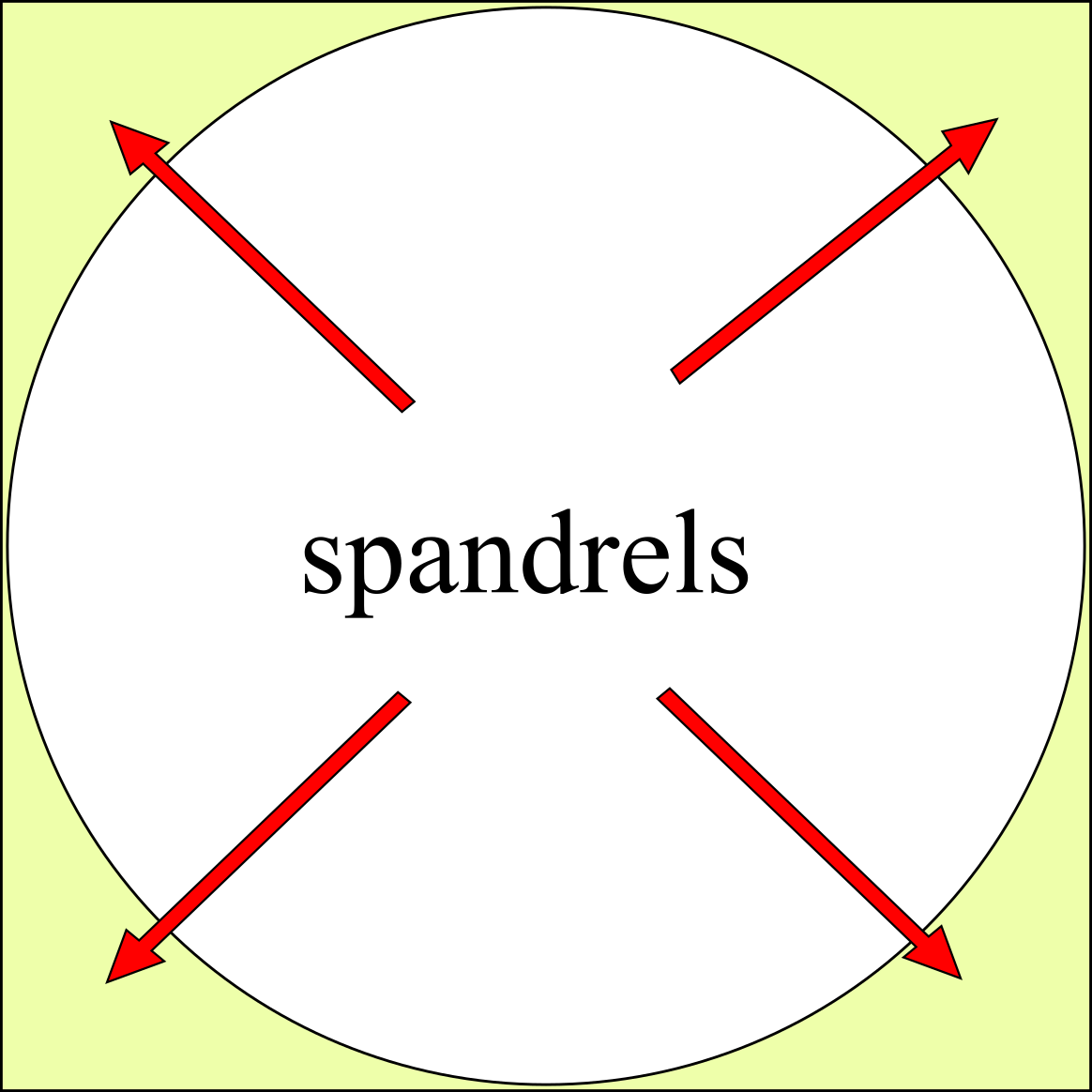
Spandrel
A spandrel is a roughly triangular space, usually found in pairs, between the top of an arch and a rectangular frame; between the tops of two adjacent arches or one of the four spaces between a circle within a square. They are frequently filled with decorative elements. Meaning There are four or five accepted and cognate meanings of the term ''spandrel'' in architectural and art history, mostly relating to the space between a curved figure and a rectangular boundary – such as the space between the curve of an arch and a rectilinear bounding moulding, or the wallspace bounded by adjacent arches in an arcade and the stringcourse or moulding above them, or the space between the central medallion of a carpet and its rectangular corners, or the space between the circular face of a clock and the corners of the square revealed by its hood. Also included is the space under a flight of stairs, if it is not occupied by another flight of stairs. In a building with more than one floor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pier (architecture)
A pier, in architecture, is an upright support for a structure or superstructure such as an arch or bridge. Sections of structural walls between openings (bays) can function as piers. External or free-standing walls may have piers at the ends or on corners. Description The simplest cross section of the pier is square, or rectangular, but other shapes are also common. In medieval architecture, massive circular supports called drum piers, cruciform (cross-shaped) piers, and compound piers are common architectural elements. Columns are a similar upright support, but stand on a round base. In buildings with a sequence of bays between piers, each opening (window or door) between two piers is considered a single bay. Bridge piers Single-span bridges have abutments at each end that support the weight of the bridge and serve as retaining walls to resist lateral movement of the earthen fill of the bridge approach. Multi-span bridges require piers to support the ends of spans betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plinth
A pedestal (from French ''piédestal'', Italian ''piedistallo'' 'foot of a stall') or plinth is a support at the bottom of a statue, vase, column, or certain altars. Smaller pedestals, especially if round in shape, may be called socles. In civil engineering, it is also called ''basement''. The minimum height of the plinth is usually kept as 45 cm (for buildings). It transmits loads from superstructure to the substructure and acts as the retaining wall for the filling inside the plinth or raised floor. In sculpting, the terms base, plinth, and pedestal are defined according to their subtle differences. A base is defined as a large mass that supports the sculpture from below. A plinth is defined as a flat and planar support which separates the sculpture from the environment. A pedestal, on the other hand, is defined as a shaft-like form that raises the sculpture and separates it from the base. An elevated pedestal or plinth that bears a statue, and which is raised from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is nearly alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mullion
A mullion is a vertical element that forms a division between units of a window or screen, or is used decoratively. It is also often used as a division between double doors. When dividing adjacent window units its primary purpose is a rigid support to the glazing of the window. Its secondary purpose is to provide structural support to an arch or lintel above the window opening. Horizontal elements separating the head of a door from a window above are called transoms. History Stone mullions were used in Armenian, Saxon and Islamic architecture prior to the 10th century. They became a common and fashionable architectural feature across Europe in Romanesque architecture, with paired windows divided by a mullion, set beneath a single arch. The same structural form was used for open arcades as well as windows, and is found in galleries and cloisters. In Gothic architecture windows became larger and arrangements of multiple mullions and openings were used, both for structure and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydney Sandstone
Sydney sandstone is the common name for Sydney Basin Hawkesbury Sandstone, one variety of which is historically known as Yellowblock, and also as "yellow gold" a sedimentary rock named after the Hawkesbury River north of Sydney, where this sandstone is particularly common. It forms the bedrock for much of the region of Sydney, Australia. Well known for its durable quality, it is the reason many Aboriginal rock carvings and drawings in the area still exist. As a highly favoured building material, especially preferred during the city's early years—from the late 1790s to the 1890s—its use, particularly in public buildings, gives the city its distinctive appearance. The stone is notable for its geological characteristics; its relationship to Sydney's vegetation and topography; the history of the quarries that worked it; and the quality of the buildings and sculptures constructed from it. This bedrock gives the city some of its "personality" by dint of its meteorologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APA Building, Sydney
The APA Building is a heritage-listed office building located at 53-63 Martin Place in the Sydney central business district, in the City of Sydney local government area of New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by David W. King and built in 1936 by Kell & Rigby. From 2004 to October 2021, the building most notably housed a Lindt chocolate café on the eastern side of the ground floor. The (now-closed) café came to international attention during the 2014 Sydney hostage crisis, thus being commonly referred to as the Lindt café siege. The building was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999. History The development of a new headquarters building for the Australian Provincial Assurance Association Ltd in Martin Place was intrinsically connected to the development of Martin Place itself. When on 8 April 1936, the extension of Martin Place to Macquarie Street was opened, a series of development sites along each side of the new thoroughfare were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Bank
The Commonwealth Bank of Australia (CBA), or CommBank, is an Australian multinational bank with businesses across New Zealand, Asia, the United States and the United Kingdom. It provides a variety of financial services including retail, business and institutional banking, funds management, superannuation, insurance, investment and broking services. The Commonwealth Bank is the largest Australian listed company on the Australian Securities Exchange as of August 2015 with brands including Bankwest, Colonial First State Investments, ASB Bank (New Zealand), Commonwealth Securities (CommSec) and Commonwealth Insurance (CommInsure). Its former constituent parts were the Commonwealth Trading Bank of Australia, the Commonwealth Savings Bank of Australia, and the Commonwealth Development Bank. Founded in 1911 by the Australian Government and fully privatised in 1996, the Commonwealth Bank is one of the " big four" Australian banks, with the National Australia Bank (NAB), ANZ and Wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MLC_building_Sydney.jpg)


.jpg)


