|
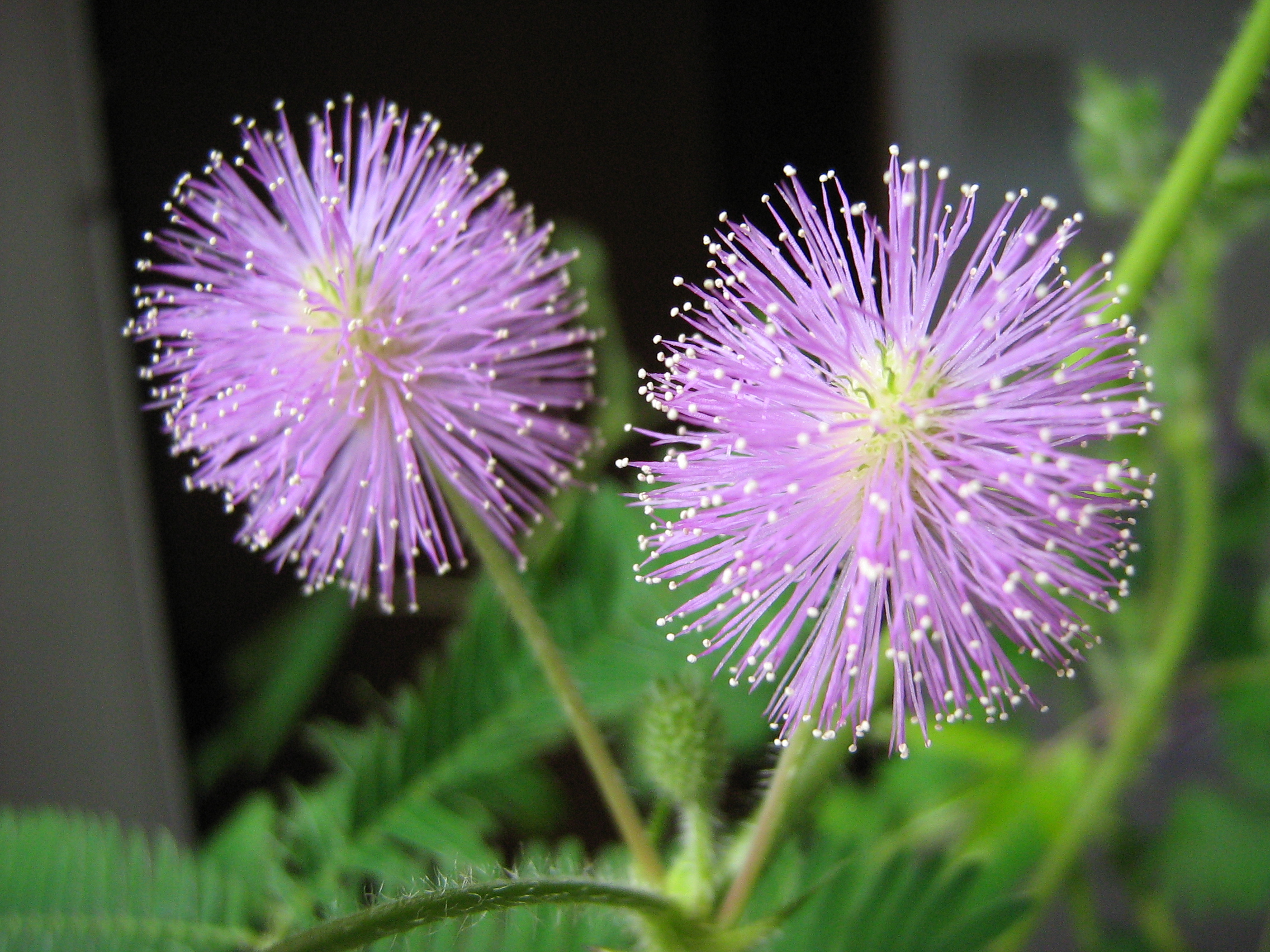
Mimosa
''Mimosa'' is a genus of about 600 species of herbs and shrubs, in the mimosoid clade of the legume family Fabaceae. Species are native to the Americas, from North Dakota to northern Argentina, and to eastern Africa (Tanzania, Mozambique, and Madagascar) as well as the Indian subcontinent and Indochina. The generic name is derived from the Greek word (''mimos''), 'actor' or 'mime', and the feminine suffix -''osa'', 'resembling', suggesting its 'sensitive leaves' which seem to 'mimic conscious life'. Two species in the genus are especially notable. One is '' Mimosa pudica'', commonly known as touch-me-not, which folds its leaves when touched or exposed to heat. It is native to southern Central and South America but is widely cultivated elsewhere for its curiosity value, both as a houseplant in temperate areas, and outdoors in the tropics. Outdoor cultivation has led to weedy invasion in some areas, notably Hawaii. The other is '' Mimosa tenuiflora'', which is best known for i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mimosa Species
The following species in the flowering plant genus ''Mimosa'' are accepted by Plants of the World Online. About 90% of its hundreds of species are found in the Neotropics. *''Mimosa acantholoba'' *''Mimosa acapulcensis'' *''Mimosa accedens'' *''Mimosa acroconica'' *''Mimosa aculeaticarpa'' *''Mimosa acutistipula'' *''Mimosa adamantina'' *''Mimosa adenantheroides'' *''Mimosa adenocarpa'' *''Mimosa adenotricha'' *''Mimosa adpressa'' *''Mimosa affinis'' *''Mimosa aguapeia'' *''Mimosa albida'' *''Mimosa albolanata'' *''Mimosa alleniana'' *''Mimosa altoparanensis'' *''Mimosa amambayensis'' *''Mimosa amnis-atri'' *''Mimosa andina'' *''Mimosa andringitrensis'' *''Mimosa annularis'' *''Mimosa antioquensis'' *''Mimosa antrorsa'' *''Mimosa apodocarpa'' *''Mimosa arenosa'' *''Mimosa arturoana'' *''Mimosa aspera'' *''Mimosa asperoides'' *''Mimosa atlantica'' *''Mimosa aureliana'' *''Mimosa auriberbis'' *''Mimosa auriculata'' *''Mimosa aurivillus'' *''Mimosa au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimosa Pudica Leaves Folding When Touched 2
''Mimosa'' is a genus of about 600 species of herbs and shrubs, in the Mimosoideae, mimosoid clade of the legume family Fabaceae. Species are native to the Americas, from North Dakota to northern Argentina, and to eastern Africa (Tanzania, Mozambique, and Madagascar) as well as the Indian subcontinent and Indochina. The generic name is derived from the Greek language, Greek word (''mimos''), 'actor' or 'mime', and the feminine suffix -''osa'', 'resembling', suggesting its 'sensitive leaves' which seem to 'mimic conscious life'. Two species in the genus are especially notable. One is ''Mimosa pudica'', commonly known as touch-me-not, which folds its leaves when touched or exposed to heat. It is native to southern Central America, Central and South America, South America but is widely cultivated elsewhere for its curiosity value, both as a houseplant in temperate areas, and outdoors in the tropics. Outdoor cultivation has led to weedy invasive species, invasion in some areas, not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimosa Pudica
''Mimosa pudica'' (also called sensitive plant, sleepy grass, sleepy plant, action plant, humble plant, touch-me-not, touch-and-die, or shameplant) is a creeping annual or perennial flowering plant of the pea/legume family Fabaceae. It is often grown for its curiosity value: the sensitive compound leaves quickly fold inward and droop when touched or shaken and re-open a few minutes later. For this reason, this species is commonly cited as an example of rapid plant movement. Like a number of other plant species, it undergoes changes in leaf orientation termed "sleep" or nyctinastic movement. The foliage closes during darkness and reopens in light. This was first studied by French scientist Jean-Jacques d'Ortous. In the UK it has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit. The species is native to the Caribbean and South and Central America, but is now a pantropical weed, and can now be found in the Southern United States, South Asia, East Asia, Micronesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimosa Tenuiflora
''Mimosa tenuiflora'', syn. ''Mimosa hostilis'', also known as jurema preta, calumbi (Brazil), tepezcohuite (México), carbonal, cabrera, jurema, black jurema, and binho de jurema, is a perennial tree or shrub native to the northeastern region of Brazil (Paraíba, Rio Grande do Norte, Ceará, Pernambuco, Bahia) and found as far north as southern Mexico (Oaxaca and coast of Chiapas), and the following countries: El Salvador, Honduras, Panama, Colombia and Venezuela. It is most often found in lower altitudes, but it can be found as high as . Description The fern-like branches have leaves that are ''Mimosa'' like, finely pinnate, growing to long. Each compound leaf contains 15–33 pairs of bright green leaflets long. The tree itself grows up to tall and it can reach tall in less than 5 years. The white, fragrant flowers occur in loosely cylindrical spikes long. In the Northern Hemisphere it blossoms and produces fruit from November to June or July. In the Southern Hemisph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Plant Movement
Rapid plant movement encompasses movement in plant structures occurring over a very short period, usually under one second. For example, the Venus flytrap closes its trap in about 100 milliseconds. The traps of Utricularia are much faster, closing in about 0.5 milliseconds. The dogwood bunchberry's flower opens its petals and fires pollen in less than 0.5 milliseconds. The record is currently held by the white mulberry tree, with flower movement taking 25 microseconds, as pollen is catapulted from the stamens at velocities in excess of half the speed of sound—near the theoretical physical limits for movements in plants.Taylor, P.E., G. Card, J. House, M. H. Dickinson & R.C. Flagan 2006. High-speed pollen release in the white mulberry tree, ''Morus alba'' L.. ''Sexual Plant Reproduction'' 19(1): 19–24. These rapid plant movements differ from the more common, but much slower "growth-movements" of plants, called tropisms. Tropisms encompass movements that lead to physical, per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acacia Dealbata
''Acacia dealbata'', the silver wattle, blue wattle or mimosa, is a species of flowering plant in the legume family, Fabaceae. It is native to southeastern Australia and widely introduced in other warm climates. Description It is a fast-growing evergreen tree or shrub growing up to tall, typically a pioneer species after fire. The leaves are bipinnate, glaucous blue-green to silvery grey, and the leaves resemble those of a fern. They are , occasionally up to 17 cm, in length and 1–11 cm broad, with 6–30 pairs of pinnae. Each pinna is divided into 10–68 pairs of leaflets, which are 0.7–6 mm long and 0.4–1 mm broad. The flowers are produced in large racemose inflorescences made up of numerous smaller globose bright yellow flowerheads of 13–42 individual flowers. The fruit is a flattened pod 2–11.5 cm long and 6–14 mm broad, containing several seeds.Flora of Australia Online''Acacia dealbata'' Trees generally do not live longer th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyltryptamine
Dimethyltryptamine (DMT), also known as ''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine (''N'',''N''-DMT), is a Psychedelic drug, serotonergic hallucinogen and Investigational New Drug, investigational drug of the substituted tryptamine, tryptamine family that natural product, occurs naturally in many plants and animals, including humans. DMT is used as a psychedelic drug and prepared by various cultures for ritual purposes as an entheogen. DMT has a rapid onset of action, onset, intense effects, and a relatively short duration of action. For those reasons, DMT was known as the "businessman's trip" during the 1960s in the United States, as a user could access the full depth of a psychedelic experience in considerably less time than with other substances such as Lysergic acid diethylamide, LSD or psilocybin mushrooms. DMT can be inhaled or injected and its effects depend on the dose, as well as the mode of administration. When inhaled or injected, the effects last about five to fifteen minutes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albizia Julibrissin
''Albizia julibrissin'', the Persian silk tree, pink silk tree, or mimosa tree, is a species of tree in the Fabaceae family, native to Western Asia, southwestern and East Asia, eastern Asia. Taxonomy It was introduced to Europe in the mid-18th century by Italian nobleman Filippo degli Albizzi, and the name of its entire genus Albizzia is given after him. The specific name (botany), specific epithet ''julibrissin'' is a corruption of the Persian language, Persian word (), which means "silk flower" (from "flower" + "silk"). ''Albizia julibrissin'' was described by species:Antonio Durazzini, Antonio Durazzini. John Gilbert Baker used the same scientific name to refer to ''Albizia kalkora'' written by David Prain, the ''Mimosa kalkora'' of William Roxburgh. Names ''Albizia julibrissin'' is known by a wide variety of common names, such as Persian silk tree and pink siris. It is also called Lankaran acacia or bastard tamarind, though it is not too closely related to either ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimosoideae
The Mimosoideae are a traditional subfamily of trees, herbs, lianas, and shrubs in the pea family (Fabaceae) that mostly grow in tropical and subtropical climates. They are typically characterized by having radially symmetric flowers, with petals that are twice divided (valvate) in bud and with numerous showy, prominent stamens. Recent work on phylogenetic relationships has found that the Mimosoideae form a clade nested with subfamily Caesalpinioideae and the most recent classification by ''The Legume Phylogeny Working Group'' refer to them as the Mimosoid clade within subfamily Caesalpinioideae. The group includes about 40 genera and 2,500 species. Taxonomy Some classification systems, for example the Cronquist system, treat the Fabaceae in a narrow sense, raising the Mimisoideae to the rank of family as Mimosaceae. The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group treats Fabaceae in the broad sense. The Mimosoideae were historically subdivided into four tribes (Acacieae, Ingeae, Mimoseae, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabaceae
Fabaceae () or Leguminosae,International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants. Article 18.5 states: "The following names, of long usage, are treated as validly published: ....Leguminosae (nom. alt.: Fabaceae; type: Faba Mill. Vicia L.; ... When the Papilionaceae are regarded as a family distinct from the remainder of the Leguminosae, the name Papilionaceae is conserved against Leguminosae." English pronunciations are as follows: , and . commonly known as the legume, pea, or bean family, is a large and agriculturally important family of |
Ayahuasca
AyahuascaPronounced as in the UK and in the US. Also occasionally known in English as ''ayaguasca'' (Spanish-derived), ''aioasca'' (Brazilian Portuguese-derived), or as ''yagé'', pronounced or . Etymologically, all forms but ''yagé'' descend from the compound Quechua word ''ayawaska'', from ''aya'' () and ''waska'' (). For more names for ayahuasca, see § Etymology. is a South American psychoactive decoction prepared from '' Banisteriopsis caapi'' vine and a dimethyltryptamine (DMT)-containing plant, used by Indigenous cultures in the Amazon and Orinoco basins as part of traditional medicine and shamanism. The word ayahuasca, originating from Quechuan languages spoken in the Andes, refers both to the ''B. caapi'' vine and the psychoactive brew made from it, with its name meaning “spirit rope” or “liana of the soul.” The specific ritual use of ayahuasca was widespread among Indigenous groups by the 19th century, though its precise origin is uncertain. Ayahuasca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Jacques D'Ortous De Mairan
Jean-Jacques d'Ortous de Mairan (26 November 1678 – 20 February 1771) was a French natural philosopher (physicist), born in the town of Béziers on 26 November 1678. De Mairan lost his father, François d'Ortous, at age four and his mother twelve years later at age sixteen. Over the course of his life, de Mairan was elected into numerous scientific societies and made key discoveries in a variety of fields including ancient texts and astronomy. His observations and experiments also inspired the beginning of what is now known as the study of biological circadian rhythms. At the age of 92, de Mairan died of pneumonia in Paris on 20 February 1771. Biography De Mairan attended college in Toulouse from 1694–1697 with a focus on ancient Greek. In 1698 he went to Paris to study mathematics and physics under the teachings of Nicolas Malebranche. In 1702, he returned home to Béziers and began his lifelong study of several fields, most notably astronomy and plant rhythms. Further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |