|
MFI BA-12 Sländan
The MFI BA-12 Sländan is a single seat ultralight of pod and high boom configuration and with a butterfly tail. It was designed and built in Sweden in the 1980s and led to a two-seat, slightly larger, development called the BA-14. Design and development The Sländan ( en, Dragonfly) was the first Swedish microlight apart from glider based types. It is built from composite materials, with a square section beam formed in two halves supporting the engine well ahead of the wing leading edge and extending aft continuously to the tail. The wings, rectangular in plan and with a high aspect ratio (10:1), are attached to the beam with dihedral of 1.5°. Ailerons cover 30% of the trailing edge. The wing has two pressed spars, foam filled glass fibre ribs and Kevlar filled glass fibre sandwich skins. The butterfly tail surfaces are also rectangular and assisted by a short ventral fin with the same chord as the tailplane. The round nosed, single seat cabin is formed from six bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kevlar
Kevlar (para-aramid) is a strong, heat-resistant synthetic fiber, related to other aramids such as Nomex and Technora. Developed by Stephanie Kwolek at DuPont in 1965, the high-strength material was first used commercially in the early 1970s as a replacement for steel in racing tires. It is typically spun into ropes or fabric sheets that can be used as such, or as an ingredient in composite material components. Kevlar has many applications, ranging from bicycle tires and racing sails to bulletproof vests, all due to its high tensile strength-to-weight ratio; by this measure it is five times stronger than steel. It is also used to make modern marching drumheads that withstand high impact; and for mooring lines and other underwater applications. A similar fiber called Twaron with the same chemical structure was developed by Akzo in the 1970s; commercial production started in 1986, and Twaron is now manufactured by Teijin. History Poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide (K2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FFK Aerotech , a Norwegian football club
{{disambiguation ...
FFK may refer to: * Curaçao Football Federation (Papiamento: ') * Faye Fang Kaew, a Thai pop trio * Falköpings FK, a Swedish football club * Finnmark, a county of Norway * Football Federation of Kazakhstan * Football Federation of Kosovo * Fredrikstad FK Fredrikstad Fotballklubb (also known as Fredrikstad or FFK) is a Norwegian association football, football club from the town of Fredrikstad. With nine league championships and eleven Norwegian Football Cup, Norwegian Cup wins, FFK is one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Swedish Aero Club
Royal Swedish Aero Club ( sv, Kungliga Svenska Aeroklubben, abbreviated KSAK, previously ''Svenska Aeronautiska Sällskapet'', abbreviated SAS), established in 1900, is today the national organization for Sweden's over 150 flying clubs and have by the Swedish Transport Agency been authorized to administer the ultralight aviation in Sweden. The Royal Swedish Aero Club has a wholly owned service company, located at Bromma Airport, which sells aeronautical maps and other aviation accessories. History When the Swedish Aeronautical Society (''Svenska Aeronautiska Sällskapet'', SAS) was established in Stockholm on 15 December 1900, there were only one predecessor in the world, the Aéro-Club de France. The purpose of the society was "to its ability encourage the art of ballooning in Sweden in all its branches", and the first years until about 1910 was mostly about aerostats (balloons) and was later transformed into aerodynes (aircraft). At the Society's initiatives a large number of ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
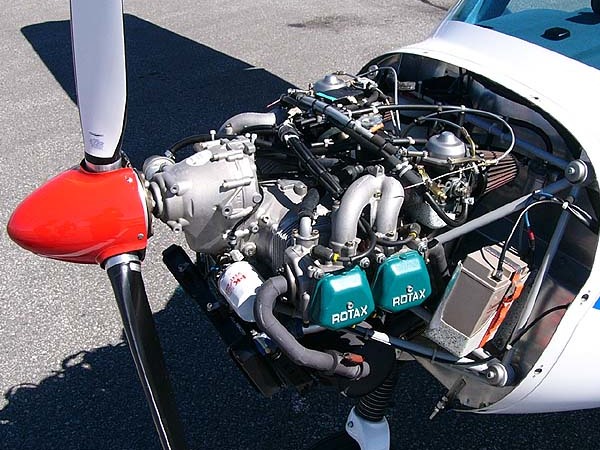
Rotax
Rotax is the brand name for a range of internal combustion engines developed and manufactured by the Austrian company BRP-Rotax GmbH & Co KG (until 2016 BRP-Powertrain GmbH & Co. KG), in turn owned by the Canadian Bombardier Recreational Products. Rotax four-stroke and advanced two-stroke engines are used in a wide variety of small land, sea and airborne vehicles. Bombardier Recreational Products (BRP) use them in their own range of such vehicles. In the light aircraft class, in 1998 Rotax outsold all other aero engine manufacturers combined.Gunston, W.; "''World Encyclopaedia of Aero Engines''", 4th Edition, Patrick Stephens Ltd, 1998, Page 170. History The company was founded in 1920 in Dresden, Germany, as ROTAX-WERK AG. In 1930, it was taken over by Fichtel & Sachs and transferred its operations to Schweinfurt, Germany. Operations were moved to Wels, Austria, in 1943 and finally to Gunskirchen, Austria, in 1947. In 1959, the majority of Rotax shares were taken over by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lotus Magnum 2
Lotus may refer to: Plants * Lotus (plant), various botanical taxa commonly known as lotus, particularly: ** ''Lotus'' (genus), a genus of terrestrial plants in the family Fabaceae ** Lotus flower, a symbolically important aquatic Asian plant also known as Indian or sacred lotus * Lotus tree, a plant in Greek and Roman mythology Places * Lotus, California, an unincorporated community in El Dorado County, California, United States *Lotus, Indiana, an unincorporated community in Union County, Indiana, United States *Lotus, Florida, a former village in Brevard County, Florida, United States *Lotus, Kentucky, an unincorporated community in Bullitt County, Kentucky, United States Brands *Lotus Cars, a British motor vehicle manufacturer ** Lotus F1 Team, a British Formula One team that started competing in the 2012 season ** Team Lotus, a British Formula One racing team that competed between 1954 and 1994 **Pacific Team Lotus, the successor team that resulted from a merger with Pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-stroke Engine
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of the crankshaft. A four-stroke engine requires four strokes of the piston to complete a power cycle during two crankshaft revolutions. In a two-stroke engine, the end of the combustion stroke and the beginning of the compression stroke happen simultaneously, with the intake and exhaust (or scavenging) functions occurring at the same time. Two-stroke engines often have a high power-to-weight ratio, power being available in a narrow range of rotational speeds called the power band. Two-stroke engines have fewer moving parts than four-stroke engines. History The first commercial two-stroke engine involving cylinder compression is attributed to Scottish engineer Dugald Clerk, who patented his design in 1881. However, unlike most later two-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
König SD 570
The König SD 570 is a four-cylinder, two-stroke, single ignition radial aircraft engine designed for powered paragliders, powered parachutes and single place ultralight trikes.Cliche, Andre: ''Ultralight Aircraft Shopper's Guide'' 8th Edition, page G-6 Cybair Limited Publishing, 2001. The engine was originally designed and produced by Dieter König of Berlin, Germany. The design was sold to Zanzottera Technologies of Italy and then sold again, along with the rest of Zanzottera's two-stroke ultralight aircraft engine line to Compact Radial Engines of Surrey, British Columbia, Canada. Compact Radial Engines was then in turn acquired by Fiate Aviation Co., Ltd. of Hefei, Anhui, China in August 2017. Fiate Aviation did not advertise the engine as available in 2021. Development The SD 570 is an unusual four-cylinder radial engine that is very compact and light weight at only . The engine features single capacitor discharge ignition, a single Bing 49 diaphragm-type carburetor an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tailskid
Conventional landing gear, or tailwheel-type landing gear, is an aircraft undercarriage consisting of two main wheels forward of the center of gravity and a small wheel or skid to support the tail.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 133. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. From the Ground Up, 27th edition, page 11 The term taildragger is also used, although some argue it should apply only to those aircraft with a tailskid rather than a wheel. The term "conventional" persists for historical reasons, but all modern jet aircraft and most modern propeller aircraft use tricycle gear. History In early aircraft, a tailskid made of metal or wood was used to support the tail on the ground. In most modern aircraft with conventional landing gear, a small articulated wheel assembly is attached to the rearmost part of the airframe in place of the skid. This wheel may be steered by the pilot through a connection to the rudder pedals, allowing the rudder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantilever
A cantilever is a rigid structural element that extends horizontally and is supported at only one end. Typically it extends from a flat vertical surface such as a wall, to which it must be firmly attached. Like other structural elements, a cantilever can be formed as a beam, plate, truss, or slab. When subjected to a structural load at its far, unsupported end, the cantilever carries the load to the support where it applies a shear stress and a bending moment. Cantilever construction allows overhanging structures without additional support. In bridges, towers, and buildings Cantilevers are widely found in construction, notably in cantilever bridges and balconies (see corbel). In cantilever bridges, the cantilevers are usually built as pairs, with each cantilever used to support one end of a central section. The Forth Bridge in Scotland is an example of a cantilever truss bridge. A cantilever in a traditionally timber framed building is called a jetty or forebay. In the southe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricycle Undercarriage
Tricycle gear is a type of aircraft undercarriage, or ''landing gear'', arranged in a tricycle fashion. The tricycle arrangement has a single nose wheel in the front, and two or more main wheels slightly aft of the center of gravity. Tricycle gear aircraft are the easiest for takeoff, landing and taxiing, and consequently the configuration is the most widely used on aircraft.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 524. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. Aviation Publishers Co. Limited, ''From the Ground Up'', page 11 (27th revised edition) History Several early aircraft had primitive tricycle gear, notably very early Antoinette planes and the Curtiss Pushers of the pre-World War I Pioneer Era of aviation. Waldo Waterman's 1929 tailless '' Whatsit'' was one of the first to have a steerable nose wheel. In 1956, Cessna introduced sprung-steel tricycle landing gear on the Cessna 172. Their marketing department described this as "Land-O-Matic" to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strut
A strut is a structural component commonly found in engineering, aeronautics, architecture and anatomy. Struts generally work by resisting longitudinal compression, but they may also serve in tension. Human anatomy Part of the functionality of the clavicle is to serve as a strut between the scapula and sternum, resisting forces that would otherwise bring the upper limb close to the thorax. Keeping the upper limb away from the thorax is vital for its range of motion. Complete lack of clavicles may be seen in cleidocranial dysostosis, and the abnormal proximity of the shoulders to the median plane exemplifies the clavicle's importance as a strut. Architecture and construction Strut is a common name in timber framing for a support or brace of scantlings lighter than a post. Frequently struts are found in roof framing from either a tie beam or a king post to a principal rafter. Struts may be vertically plumb or leaning (then called canted, raking, or angled) and may be straight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |