|
M864
The M864 is an American made 155 mm calibre, 155 mm artillery shell. It carries a dual-purpose Improved Conventional Munition, ICM submunition warhead and incorporates base bleed technology to increase its range. The projectile is capable of delivering 24 M46 and 48 M42 dual-purpose anti-materiel/anti-personnel sub-munitions at ranges out to 29 kilometers. Base bleed technology was developed to reduce the amount of base drag on a projectile, thereby increasing the achieved range. The drag is reduced by a gas generator located on the base of the projectile. Once ignited, the gas generator bleeds hot gas into the projectiles wake which causes the flow of air at the base to be less turbulent. The decrease in turbulence, reduces base drag, which typically accounts for 50 percent of total drag. The amount of thrust produced by the base burner unit is negligible and does not serve the same function as the rocket motor on a rocket-assisted projectile (RAP). The M864 projectile is not ballis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
155 Mm Calibre
155 mm (6.1 in) is a common, NATO-standard, artillery caliber. It is defined in AOP-29 part 1 with reference to STANAG 4425. It is commonly used in field guns, howitzers, and gun-howitzers. Land warfare The caliber originated in France after its defeat in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871, when an artillery committee met on 2 February 1874 to discuss new models for the French fortress and siege artillery, among which there was a piece in the caliber range (later on it became known as the De Bange 155 mm cannon). After several meetings, on 16 April 1874 the committee settled on the 15.5 cm caliber (in the subsequent program-letter of the committee, dating from 21 April 1874, the caliber was for the first time expressed as 155 mm). Since the early 21st century, most NATO armies have adopted 155 mm weapons as an all-purpose standard. They are seen as striking a good compromise between range and power, while only using a single caliber greatly simplifies the logi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Bleed
Base bleed is a system used on some artillery shells to increase range, typically by about 20–35%. It expels gas into the low pressure area behind the shell to reduce base drag (it does not produce thrust). Since base bleed extends the range by a percentage, it is more useful on longer range artillery where an increase of approximately can be achieved. Until the late 1980s the small gains in range were not considered worthwhile for field artillery. Base bleed shells are becoming more common in units equipped with modern artillery with far greater range than older guns, but are usually only used when the longer range is required, due to their higher cost. Function Most (50–60%) of the drag on an artillery shell comes from the nose of the shell, as it pushes the air out of its way at supersonic speeds. Shaping the shell properly can reduce this drag. However, another powerful source of drag is the low-pressure area left behind the shell due to its blunt base. Base blee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket-assisted Projectile
A rocket-assisted projectile (RAP) is a cannon, howitzer, Mortar (weapon), mortar, or recoilless rifle round incorporating a rocket motor for independent propulsion. This gives the projectile greater speed and range than a non-assisted Ballistics, ballistic shell, which is propelled only by the gun's exploding charge. Some forms of rocket-assisted projectiles can be outfitted with a laser-guide for greater accuracy. The German Sturmtiger (1944) used a 380 mm Rocket Propelled Round as its main projectile. These rounds were high explosive shells or shaped charges with a maximum range of 6,000 m. The gun first accelerated the projectile to 45 m/s (150 ft/s), the 40 kg (88 lb) rocket charge then boosted this to about 250 m/s (820 ft/s). Also the German Krupp K5 railway gun of World War 2 used rocket assisted projectiles in the later stages of the war, although it also used conventional artillery projectiles. The North Korean Koksan (artillery), M-1978 / M1989 (KOKSAN) 170mm self ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
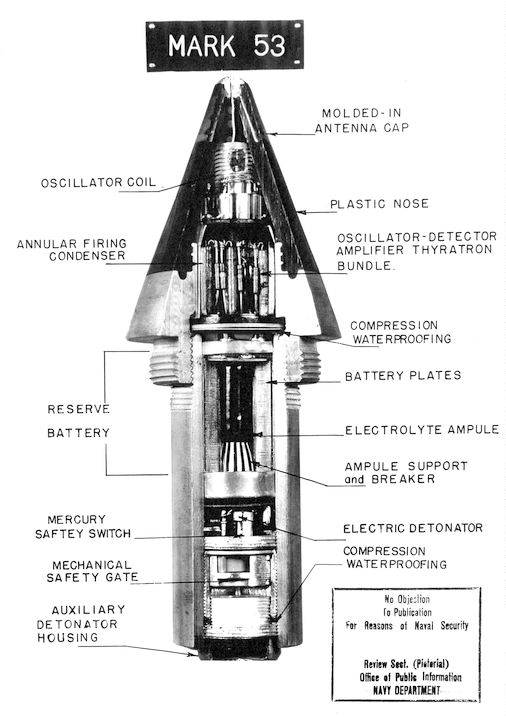
Fuze
In military munitions, a fuze (sometimes fuse) is the part of the device that initiates function. In some applications, such as torpedoes, a fuze may be identified by function as the exploder. The relative complexity of even the earliest fuze designs can be seen in cutaway diagrams. A fuze is a device that detonates a munition's explosive material under specified conditions. In addition, a fuze will have safety and arming mechanisms that protect users from premature or accidental detonation. For example, an artillery fuze's battery is activated by the high acceleration of cannon launch, and the fuze must be spinning rapidly before it will function. "Complete bore safety" can be achieved with mechanical shutters that isolate the detonator from the main charge until the shell is fired. A fuze may contain only the electronic or mechanical elements necessary to signal or actuate the detonator, but some fuzes contain a small amount of primary explosive to initiate the detonation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Artillery
Artillery has been one of primary weapons of war since before the Napoleonic Era. Several countries have developed and built artillery systems, while artillery itself has been continually improved and redesigned to meet the evolving needs of the battlefield. This has led to a multitude of different types and designs which have played a role in the history of warfare and continue to be a significant factor in modern combat. For the most part, the following lists of artillery cover guns, howitzers, mortars, and other large projectile weapons. Small arms and missiles are not generally included, though rockets and other bombardment weapons may be. For a more complete listing of various weapons, see list of weapons. __NOTOC__ By name : ''See list of artillery by name'' By type : ''See full list of artillery by type or jump to a specific type from the list below:'' By caliber List of the largest cannon by caliber By country : ''See full list of artillery by country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Crew Served Weapons Of The US Armed Forces
This list contains weapons that are classified as crew-served, as the term is used in the United States military. While the general understanding is that crew-served weapons require more than one person to operate them, there are important exceptions in the case of both squad automatic weapons (SAW) and sniper rifles. Within the table of organization and equipment for both the United States Army and the U.S. Marine Corps, these two classes of weapons are understood to be crew-served, as the operator of the weapon (identified as a marksman or as a SAW gunner) has an assistant, who carries additional ammunition and associated equipment, acts as a spotter, and is also fully qualified in the operation of the weapon. Light and medium machine guns In active service Light machine guns * M249 SAW (Squad Automatic Weapon) (5.56×45mm NATO) General purpose machine guns * M240B/M240E4 (7.62×51mm NATO) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery Shells
A shell, in a military context, is a projectile whose payload contains an explosive, incendiary, or other chemical filling. Originally it was called a bombshell, but "shell" has come to be unambiguous in a military context. Modern usage sometimes includes large solid kinetic projectiles that is properly termed shot. Solid shot may contain a pyrotechnic compound if a tracer or spotting charge is used. All explosive- and incendiary-filled projectiles, particularly for mortars, were originally called ''grenades'', derived from the French word for pomegranate, so called because of the similarity of shape and that the multi-seeded fruit resembles the powder-filled, fragmentizing bomb. Words cognate with ''grenade'' are still used for an artillery or mortar projectile in some European languages. Shells are usually large-caliber projectiles fired by artillery, armored fighting vehicles (e.g. tanks, assault guns, and mortar carriers), warships, and autocannons. The shape is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold War Artillery Of The United States
Cold is the presence of low temperature, especially in the atmosphere. In common usage, cold is often a subjective perception. A lower bound to temperature is absolute zero, defined as 0.00K on the Kelvin scale, an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. This corresponds to on the Celsius scale, on the Fahrenheit scale, and on the Rankine scale. Since temperature relates to the thermal energy held by an object or a sample of matter, which is the kinetic energy of the random motion of the particle constituents of matter, an object will have less thermal energy when it is colder and more when it is hotter. If it were possible to cool a system to absolute zero, all motion of the particles in a sample of matter would cease and they would be at complete rest in the classical sense. The object could be described as having zero thermal energy. Microscopically in the description of quantum mechanics, however, matter still has zero-point energy even at absolute zero, because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |