|
M4 (computer Language)
m4 is a general-purpose macro processor included in most Unix-like operating systems, and is a component of the POSIX standard. The language was designed by Brian Kernighan and Dennis Ritchie for the original versions of UNIX. It is an extension of an earlier macro processor, m3, written by Ritchie for an unknown AP-3 minicomputer.Brian W. Kernighan and Dennis M. Ritchie. The m4 macro processor. Technical report, Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, New Jersey, USA, 1977pdf/ref> The macro preprocessor operates as a text-replacement tool. It is employed to re-use text templates, typically in computer programming applications, but also in text editing and text-processing applications. Most users require m4 as a dependency of GNU autoconf and GNU Bison. History Macro processors became popular when programmers commonly used assembly language. In those early days of programming, programmers noted that much of their programs consisted of repeated text, and they invented simple means fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macro (computer Science)
In computer programming, a macro (short for "macro instruction"; ) is a rule or pattern that specifies how a certain input should be mapped to a replacement output. Applying a macro to an input is known as macro expansion. The input and output may be a sequence of lexical tokens or characters, or a syntax tree. Character macros are supported in software applications to make it easy to invoke common command sequences. Token and tree macros are supported in some programming languages to enable code reuse or to extend the language, sometimes for domain-specific languages. Macros are used to make a sequence of computing instructions available to the programmer as a single program statement, making the programming task less tedious and less error-prone. Thus, they are called "macros" because a "big" block of code can be expanded from a "small" sequence of characters. Macros often allow positional or keyword parameters that dictate what the conditional assembler program gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Strachey
Christopher S. Strachey (; 16 November 1916 – 18 May 1975) was a British computer scientist. He was one of the founders of denotational semantics, and a pioneer in programming language design and computer time-sharing.F. J. Corbató, et al., The Compatible Time-Sharing System A Programmer's Guide' (MIT Press, 1963) . "the first paper on time-shared computers by C. Strachey at the June 1959 UNESCO Information Processing conference" He has also been credited as possibly being the first developer of a video game and for coining terms such as polymorphism and referential transparency that are still widely used by developers today. He was a member of the Strachey family, prominent in government, arts, administration, and academia. Early life and education Christopher Strachey was born on 16 November 1916 to Oliver Strachey and Rachel (Ray) Costelloe in Hampstead, England. Oliver Strachey was the son of Richard Strachey and the great-grandson of Sir Henry Strachey, 1st Baronet. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delimiter
A delimiter is a sequence of one or more Character (computing), characters for specifying the boundary between separate, independent regions in plain text, Expression (mathematics), mathematical expressions or other Data stream, data streams. An example of a delimiter is the comma character, which acts as a ''field delimiter'' in a sequence of comma-separated values. Another example of a delimiter is the time gap used to separate letters and words in the transmission of Morse code. In mathematics, delimiters are often used to specify the scope of an Operation (mathematics), operation, and can occur both as isolated symbols (e.g., Colon (punctuation), colon in "1 : 4") and as a pair of opposing-looking symbols (e.g., Angled bracket, angled brackets in \langle a, b \rangle). Delimiters represent one of various means of specifying boundaries in a data stream. String literal#Declarative notation, Declarative notation, for example, is an alternate method (without the use of delimiter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backtick
The backtick is a typographical mark used mainly in computing. It is also known as backquote, grave, or grave accent. The character was designed for typewriters to add a grave accent to a (lower-case) base letter, by overtyping it atop that letter. On early computer systems, however, this physical dead key+overtype function was rarely supported, being functionally replaced by precomposed characters. Consequently, this ASCII symbol was rarely (if ever) used in computer systems for its original aim and became repurposed for many unrelated uses in computer programming. The sign is located on the left-top of a US or UK layout keyboard, next to the key. Provision (if any) of the backtick on other keyboards varies by national keyboard layout and keyboard mapping. History Typewriters On typewriters designed for languages that routinely use diacritics (accent marks), there are two possible solutions. Keys can be dedicated to pre-composed characters or alternatively a dead key mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turing-complete
In computability theory, a system of data-manipulation rules (such as a model of computation, a computer's instruction set, a programming language, or a cellular automaton) is said to be Turing-complete or computationally universal if it can be used to simulate any Turing machine (devised by English mathematician and computer scientist Alan Turing). This means that this system is able to recognize or decode other data-manipulation rule sets. Turing completeness is used as a way to express the power of such a data-manipulation rule set. Virtually all programming languages today are Turing-complete. A related concept is that of Turing equivalence two computers P and Q are called equivalent if P can simulate Q and Q can simulate P. The Church–Turing thesis conjectures that any function whose values can be computed by an algorithm can be computed by a Turing machine, and therefore that if any real-world computer can simulate a Turing machine, it is Turing equivalent to a Turing ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free-form Language
In computer programming, a free-form language is a programming language in which the positioning of characters on the page in program text is insignificant. Program text does not need to be placed in specific columns as on old punched card systems, and frequently ends of lines are insignificant. Whitespace characters are used only to delimit tokens, and have no other significance. Free-form languages allow a greater degree of flexibility and have fewer syntactic rules to learn, which could lower the entry barrier for beginners. Most free-form languages descend from ALGOL, including C, Pascal, and Perl. Lisp languages are free-form, although they do not descend from ALGOL. Rexx and its dialects ooRexx and NetRexx are mostly free-form, though in some cases whitespace characters are concatenation operators. SQL, though not a full programming language, is also free-form. Most free-form languages are also structured programming languages, which is sometimes thought to go along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Programming
In computer science, automatic programming is a type of computer programming in which some mechanism generates a computer program, to allow human programmers to write the code at a higher abstraction level. There has been little agreement on the precise definition of automatic programming, mostly because its meaning has changed over time. David Parnas, tracing the history of "automatic programming" in published research, noted that in the 1940s it described automation of the manual process of punching paper tape. Later it referred to translation of high-level programming languages like Fortran and ALGOL. In fact, one of the earliest programs identifiable as a compiler was called Autocode. David Parnas, Parnas concluded that "automatic programming has always been a euphemism for programming in a higher-level language than was then available to the programmer." Program synthesis is one type of automatic programming where a procedure is created from scratch, based on mathematical req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
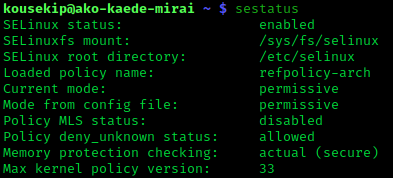
SELinux
Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) is a Linux kernel security module that provides a mechanism for supporting access control security policies, including mandatory access controls (MAC). SELinux is a set of kernel modifications and user-space tools that have been added to various Linux distributions. Its architecture strives to separate enforcement of security decisions from the security policy, and streamlines the amount of software involved with security policy enforcement. The key concepts underlying SELinux can be traced to several earlier projects by the United States National Security Agency (NSA). Overview The NSA Security-enhanced Linux Team describes NSA SELinux as a set of patches to the Linux kernel and utilities to provide a strong, flexible, mandatory access control (MAC) architecture into the major subsystems of the kernel. It provides an enhanced mechanism to enforce the separation of information based on confidentiality and integrity requirements, which allows th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GEDA
The term gEDA refers to two things: # A set of software applications ( CAD tools) used for electronic design released under the GPL. As such, gEDA is an ECAD (electronic CAD) or EDA (electronic design automation) application suite. gEDA is mostly oriented towards printed circuit board design (as opposed to integrated circuit design). The gEDA applications are often referred to collectively as "the gEDA Suite". # The collaboration of free software/open-source developers who work to develop and maintain the gEDA toolkit. The developers communicate via gEDA mailing lists, and have participated in the annual " Google Summer of Code" event as a single project. This collaboration is often referred to as "the gEDA Project". The word "gEDA" is a conjunction of " GPL" and "EDA". The names of some of the individual tools in the gEDA Suite are prefixed with the letter "g" to emphasize that they are released under the GNU General Public License. History The gEDA project was sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mail Transfer Agent
Within the Internet email system, a message transfer agent (MTA), mail transfer agent, or mail relay is software that transfers electronic mail messages from one computer to another using the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. In some contexts, the alternative names mail server, mail exchanger, or MX host are used to describe an MTA. Messages exchanged across networks are passed between mail servers, including any attached data files (such as images, multimedia, or documents). These servers often keep mailboxes for email. Access to this email by end users is typically either by webmail or an email client. Operation A message transfer agent receives mail from either another MTA, a mail submission agent (MSA), or a mail user agent (MUA). The transmission details are specified by the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). When a recipient mailbox of a message is not hosted locally, the message is relayed, that is, forwarded to another MTA. Every time an MTA receives an email message, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |