|
Lübeck–Hamburg Railway
The Hamburg–Lübeck railway is one of the most important mainline railways of the German states of Schleswig-Holstein and Hamburg. It connects the two Hanseatic cities of Hamburg and Lübeck, and is part of the line to Denmark. The line was opened in 1865. Route The line runs the south-west from Lübeck through mostly agricultural, undulating land. The Trave river is crossed three times. The most important intermediate stop is Bad Oldesloe, where the line connects with hourly services on the line to Bad Segeberg and Neumünster, operated by Nordbahn. Between Ahrensburg and Hamburg-Rahlstedt the line runs along the Stellmoor tunnel valley. In the city of Hamburg the line crosses the rail freight bypass and then runs parallel to the S-Bahn line until Hamburg Hauptbahnhof is reached from the east. History The first plans to build a direct rail link between Hamburg and Lübeck were put forward in 1831. Because of the refusal of the Danish authorities to allow a direct line to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15 KV AC Railway Electrification
Railway electrification systems using at are used on transport railways in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Sweden, and Norway. The high voltage enables high power transmission with the lower frequency reducing the losses of the traction motors that were available at the beginning of the 20th century. Railway electrification in late 20th century tends to use AC systems which has become the preferred standard for new railway electrifications but extensions of the existing networks are not completely unlikely. In particular, the Gotthard Base Tunnel (opened on 1 June 2016) still uses 15 kV, 16.7 Hz electrification. Due to high conversion costs, it is unlikely that existing systems will be converted to despite the fact that this would reduce the weight of the on-board step-down transformers to one third that of the present devices. History The first electrified railways used series-wound DC motors, first at 600 V and then 1,500 V. Areas with 3 kV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hagenow Land–Bad Oldesloe Railway
The Hagenow Land–Bad Oldesloe railway (also known in German as the ''Kaiserbahn'' or ''Kaiserstrecke''—"Emperor Railway") was a railway line in the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Schleswig-Holstein. It linked the towns of Hagenow, Ratzeburg and Bad Oldesloe with each other and formed with lines continuing via Bad Segeberg and Neumünster the shortest rail link between Berlin and Kiel, the difference with the other two routes is about 55 kilometres in each case. Today, only the short section between the stations of Hagenow Land and Hagenow Stadt (called just Hagenow until 2010) is regularly served by passenger services, although the Hollenbek–Ratzeburg section is used for draisine rides. The Hagenow–Zarrentin section is served occasionally. The other sections are closed and dismantled. Its alternative name ''Kaiserbahn'' refers to Emperor Wilhelm II, who often used it. History Before the construction of the line there were already two rail connections between B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berliner Tor Station
Berliner Tor (; literally "Berlin Gate") is a transport hub in Hamburg, Germany, served by the Hamburg U-Bahn (underground railway) and the Hamburg S-Bahn (suburban railway). The station is located in St. Georg, part of the borough of Hamburg-Mitte. The railway station is listed by the German railway company, because S-Bahn call at this station, and the S-Bahn part of it is managed by DB Station&Service. History Berliner Tor S-Bahn station opened in 1906. The original Berliner Tor U-Bahn station was designed by the architect, Erich Elingius, and built between 1908 and 1910, opening on 1 March 1912. It had a brick wall on the North, and some glass walls on the South. During the British Operation Gomorrah (air raids) in 1943, the damage to the station was so severe that the U-Bahn was no longer able to serve the line. On 19 January 1948, the station re-opened as a terminus for trains to Barmbek via Schlump, and from 1 July 1949, trains continued again to Mundsburg. From 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg Hasselbrook Station
Hasselbrook station is a railway station of the Hamburg S-Bahn and a mainline station on the Lübeck-Hamburg railway in the area of Hasselbrook, Eilbek quarter in the German city of Hamburg. History The heritage-listed entrance building was built from 1905 to 1907 as a castle-like brick building of the Gründerzeit-like style of the Hanover school of architecture by its important representative in Hamburg, the civil engineer Franz Andreas Meyer. The station is one of the last stations in Hamburg built in the style and was opened to traffic on 12 August 1907. It served as an interchange point between the ''Hamburg-Altonaer Stadt- und Vorortbahn'' (Hamburg-Altona City and Suburban railway, the predecessor of the S-Bahn) and the Lübeck-Hamburg railway. The station building, designed by the architect Eugene Goebel, was restored in the mid-1990s and is now used as a restaurant. Layout The bridge next to the station was renovated in 2007 and the side walls of the station had to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg-Altona Link Line
The Hamburg-Altona link line (german: Hamburg-Altonaer Verbindungsbahn) is a railway line in Hamburg, Germany. It now connects the lines from the north and west of Hamburg and Altona station with Hamburg Hauptbahnhof and the lines to the south and east. It was initially designed as a freight line only but is it now one of the busiest lines in Germany. It includes the suburban tracks of the Hamburg ''Stadtbahn'', originally the core of the Hamburg S-Bahn. History The first railway connection In 1842 the Hamburg-Bergedorf Railway Company opened a 16.5 km line from Hamburg to Bergedorf. In 1846 this line was extended to Berlin. Two years later, the Altona-Kiel Railway Company opened a line to Kiel. There was originally no link between Altona and Hamburg, so freight moving from one line to the other had to be reloaded several times, which was time-consuming and expensive. A two-track link line was therefore built between the stations. The route of the line is affected st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
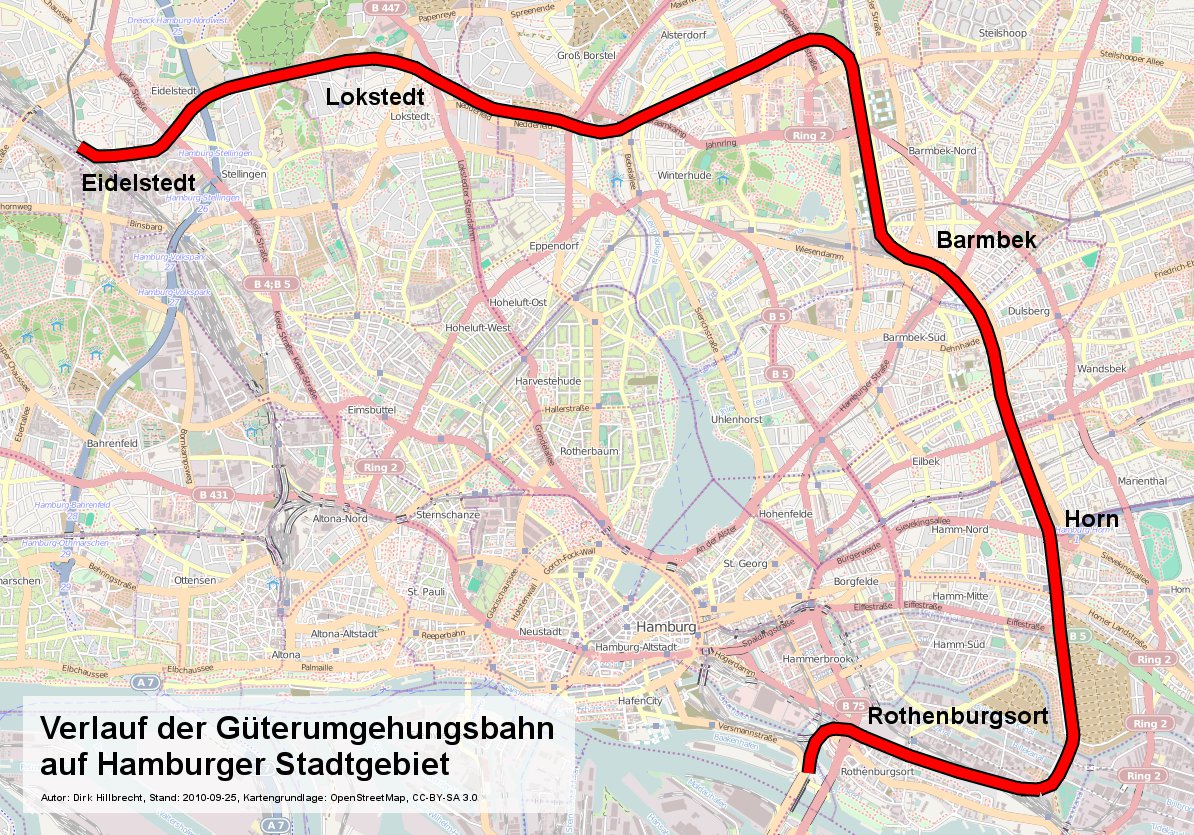
Hamburg Freight Bypass
The Hamburg freight rail bypass (german: Güterumgehungsbahn) is a railway line in the German city of Hamburg. It runs from Hamburg-Eidelstedt via Hamburg-Rothenburgsort to Hamburg-Harburg and connects the long-distance railways approaching Hamburg, bypassing the link line and the railway junctions on the approaches to Hamburg-Altona station and Hamburg Hauptbahnhof. The line is mainly used for rail freight. History The first part of the freight bypass was opened in 1902 by the Lübeck-Büchen Railway Company (''Lübeck-Büchener Eisenbahn'') as a link connecting Wandsbek station on the Lübeck–Hamburg railway and Rothenburgsort station on the Berlin–Hamburg railway. On 21 February 1903, the bypass was connected to Hamburg Hauptbahnhof via the main freight yard (''Hauptgüterbahnhof'') at the former ''Hannoverscher Bahnhof'' (the original terminal station on the line to Hanover). An extension to Ohlsdorf was completed from the link line before the First World War, alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg-Wandsbek Station
Wandsbek station was a station in the German city of Hamburg. It was built during the construction of the Lübeck–Hamburg railway by the Lübeck-Büchen Railway Company (''Lübeck-Büchener Eisenbahn''). The railway line cuts through the ''Wandsbeker Gehölz'' (Wandsbek wood) here. Former station building The three-part building was opened in 1865. The single-storey middle section was originally decorated with gables and a clock. Two-storey wings were added on its sides, which served as entrance and exit halls. The eastern wing was modified after damage during the Second World War. Despite the changes, the stucco building with its neoclassical forms, which were usual at the time, has heritage protection. The building is now used as a restaurant called the ''Hofbräu-Wirtshaus Wandsbek''. The platform was renewed in 2003 and received a new roof, a lift, new signs and new lighting. File:Hh-wandsbek-bhf2.jpg, Former station building, street side File:Hh-wandsbek-gbf.jpg, Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg-Tonndorf Station
Hamburg-Tonndorf station (german: Haltepunkt Hamburg-Tonndorf) is a railway station in the Tonndorf district in the city of Hamburg, Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe .... References {{Authority control Tonndorf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg-Rahlstedt Station ...
Hamburg-Rahlstedt station (german: Bahnhof Hamburg-Rahlstedt) is a railway station in the Rahlstedt district in the city of Hamburg, Germany. References {{Portal bar, Transport, Hamburg Rahlstedt Rahlstedt () is a quarter (''Stadtteil'') in the Wandsbek borough (''Bezirk'') of the Free and Hanseatic city of Hamburg in northern Germany. In 2020, the population was 92,511. History The quarter was first mentioned in 1248 with the name of "''R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahrensburg West (Hamburg U-Bahn Station)
Ahrensburg West is a station on the Großhansdorf branch of Hamburg U-Bahn line U1, located in the southwestern part of the town of Ahrensburg in Schleswig-Holstein. History The station was built based on schematics by Eugen Göbel, and was opened on November 5, 1921, under the name "Ahrensburg" with only one track. The second track at the station was added in 1957. When the next stop on the line, "Hopfenbach," was renamed to Ahrensburg Ost in 1952, "Ahrensburg" station was renamed to Ahrensburg West to avoid confusion between the two stations. Services Ahrensburg West is served by Hamburg U-Bahn The Hamburg U-Bahn is a rapid transit system serving the cities of Hamburg, Norderstedt and Ahrensburg in Germany. Although referred to by the term U-Bahn (the "U" commonly being understood as standing for "underground"), most of the system's ... line U1. References U-Bahn West U1 (Hamburg U-Bahn) stations Hamburg U-Bahn stations in Schleswig-Holstein Buildings and struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahrensburg
Ahrensburg () is a town in the district of Stormarn, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is located northeast of Hamburg and is part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region. Its population is around 31,000. ''Schloss Ahrensburg'', the town's symbol, is a Renaissance castle dating from 1595. Geography Ahrensburg is situated in the ''Tunneltal'', in which Alfred Rust excavated many items dating back to the ice age. Ahrensburg is situated next to the Autobahn ''A1'' and on the railway route between the Hanseatic cities of Hamburg and Lübeck. History Early history The Ahrensburger ''Tunneltal'' is a place of numerous excavations from the Upper Paleolithic culture. The culture is called Ahrensburg culture by archaeologists. Middle Ages The town dates back to the 13th Century, when the Counts of Schauenburg and Holstein, Counts of Schauenburg founded the village of Woldenhorn (which later became the town of Ahrensburg) and the neighbouring villages Ahrensfelde, Meilsdorf and Beimoor. Wol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bargteheide
Bargteheide (West Low German: ''Bartheil'') is a town in the district of Stormarn, Schleswig-Holstein state, Germany. It is situated between the cities of Ahrensburg and Bad Oldesloe, on the Hamburg to Lübeck rail line and is part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region. The population of Bargteheide was 16,045 at the end of 2017. Mayors * 1946–1957: Julius Gerken * 1957–1962: Enno Wilkens * 1962–1971: Karl Eduard Claussen ( CDU) * 1971–1984: Erich Reincke * 1985–1996: Frank Pries * 1996–2008: Werner Mitsch * 2008–2016: Henning Görtz (CDU) * since 2016: Birte Kruse-Gobrecht (independent) Population development *1840: ca. 1.000 *1905: 1.980 *1914: 2.300 *1949: 6.900 *1970: 7.374 *2002: 13.820 *2008: 14.902 *2009: 15.306 *2012: 15.528 *2013: 16.000 *2015: 16.292 Notable people * Luise Zietz (1865-1922), socialist politician * Katharina Fegebank (born 1977), German politician (The Greens) * David Kross (born 1990), German actor * Axel Fischer (born 1981), German pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |