|
Lyapunov Optimization
This article describes Lyapunov optimization for dynamical systems. It gives an example application to optimal control in queueing networks. Introduction Lyapunov optimization refers to the use of a Lyapunov function to optimally control a dynamical system. Lyapunov functions are used extensively in control theory to ensure different forms of system stability. The state of a system at a particular time is often described by a multi-dimensional vector. A Lyapunov function is a nonnegative scalar measure of this multi-dimensional state. Typically, the function is defined to grow large when the system moves towards undesirable states. System stability is achieved by taking control actions that make the Lyapunov function drift in the negative direction towards zero. Lyapunov drift is central to the study of optimal control in queueing networks. A typical goal is to stabilize all network queues while optimizing some performance objective, such as minimizing average energy or maximizing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamical System
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a Function (mathematics), function describes the time dependence of a Point (geometry), point in an ambient space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, fluid dynamics, the flow of water in a pipe, the Brownian motion, random motion of particles in the air, and population dynamics, the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real number, real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a Set (mathematics), set, without the need of a Differentiability, smooth space-time structure defined on it. At any given time, a dynamical system has a State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optimal Control
Optimal control theory is a branch of mathematical optimization that deals with finding a control for a dynamical system over a period of time such that an objective function is optimized. It has numerous applications in science, engineering and operations research. For example, the dynamical system might be a spacecraft with controls corresponding to rocket thrusters, and the objective might be to reach the moon with minimum fuel expenditure. Or the dynamical system could be a nation's economy, with the objective to minimize unemployment; the controls in this case could be fiscal and monetary policy. A dynamical system may also be introduced to embed operations research problems within the framework of optimal control theory. Optimal control is an extension of the calculus of variations, and is a mathematical optimization method for deriving control policies. The method is largely due to the work of Lev Pontryagin and Richard Bellman in the 1950s, after contributions to calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
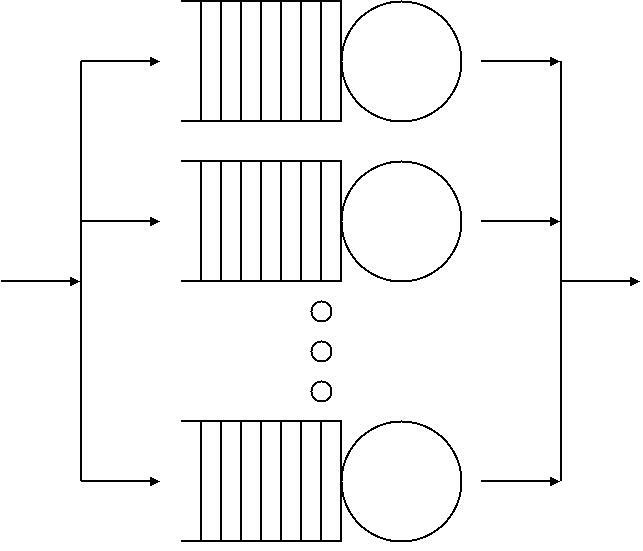
Queueing Theory
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of waiting lines, or queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operations research because the results are often used when making business decisions about the resources needed to provide a service. Queueing theory has its origins in research by Agner Krarup Erlang when he created models to describe the system of Copenhagen Telephone Exchange company, a Danish company. The ideas have since seen applications including telecommunication, traffic engineering, computing and, particularly in industrial engineering, in the design of factories, shops, offices and hospitals, as well as in project management. Spelling The spelling "queueing" over "queuing" is typically encountered in the academic research field. In fact, one of the flagship journals of the field is ''Queueing Systems''. Single queueing nodes A queue, or queueing node ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyapunov Function
In the theory of ordinary differential equations (ODEs), Lyapunov functions, named after Aleksandr Lyapunov, are scalar functions that may be used to prove the stability of an equilibrium of an ODE. Lyapunov functions (also called Lyapunov’s second method for stability) are important to stability theory of dynamical systems and control theory. A similar concept appears in the theory of general state space Markov chains, usually under the name Foster–Lyapunov functions. For certain classes of ODEs, the existence of Lyapunov functions is a necessary and sufficient condition for stability. Whereas there is no general technique for constructing Lyapunov functions for ODEs, in many specific cases the construction of Lyapunov functions is known. For instance, quadratic functions suffice for systems with one state; the solution of a particular linear matrix inequality provides Lyapunov functions for linear systems; and conservation laws can often be used to construct Lyapunov funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backpressure Routing
In queueing theory, a discipline within the mathematical theory of probability, the backpressure routing algorithm is a method for directing traffic around a queueing network that achieves maximum network throughput, which is established using concepts of Lyapunov drift. Backpressure routing considers the situation where each job can visit multiple service nodes in the network. It is an extension of max-weight scheduling where each job visits only a single service node. Introduction Backpressure routing is an algorithm for dynamically routing traffic over a multi-hop network by using congestion gradients. The algorithm can be applied to wireless communication networks, including sensor networks, mobile ad hoc networks ( MANETS), and heterogeneous networks with wireless and wireline components.L. Tassiulas and A. Ephremides, "Stability Properties of Constrained Queueing Systems and Scheduling Policies for Maximum Throughput in Multihop Radio Networks, ''IEEE Transactions on Aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drift Plus Penalty
In the mathematical theory of probability, the drift-plus-penalty method is used for optimization of queueing networks and other stochastic systems. The technique is for stabilizing a queueing network while also minimizing the time average of a network penalty function. It can be used to optimize performance objectives such as time average power, throughput, and throughput utility. M. J. Neely,Energy Optimal Control for Time Varying Wireless Networks" IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, vol. 52, no. 7, pp. 2915–2934, July 2006. M. J. Neely, E. Modiano, and C. Li,Fairness and Optimal Stochastic Control for Heterogeneous Networks" Proc. IEEE INFOCOM, March 2005. In the special case when there is no penalty to be minimized, and when the goal is to design a stable routing policy in a multi-hop network, the method reduces to backpressure routing. L. Tassiulas and A. Ephremides, "Stability Properties of Constrained Queueing Systems and Scheduling Policies for Maximum Throughput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
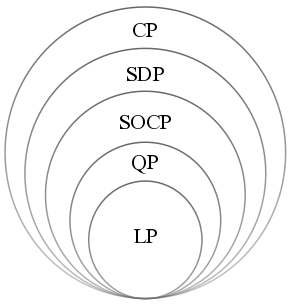
Convex Optimization
Convex optimization is a subfield of mathematical optimization that studies the problem of minimizing convex functions over convex sets (or, equivalently, maximizing concave functions over convex sets). Many classes of convex optimization problems admit polynomial-time algorithms, whereas mathematical optimization is in general NP-hard. Convex optimization has applications in a wide range of disciplines, such as automatic control systems, estimation and signal processing, communications and networks, electronic circuit design, data analysis and modeling, finance, statistics ( optimal experimental design), and structural optimization, where the approximation concept has proven to be efficient. With recent advancements in computing and optimization algorithms, convex programming is nearly as straightforward as linear programming. Definition A convex optimization problem is an optimization problem in which the objective function is a convex function and the feasible set is a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Programming
Linear programming (LP), also called linear optimization, is a method to achieve the best outcome (such as maximum profit or lowest cost) in a mathematical model whose requirements are represented by linear function#As a polynomial function, linear relationships. Linear programming is a special case of mathematical programming (also known as mathematical optimization). More formally, linear programming is a technique for the mathematical optimization, optimization of a linear objective function, subject to linear equality and linear inequality Constraint (mathematics), constraints. Its feasible region is a convex polytope, which is a set defined as the intersection (mathematics), intersection of finitely many Half-space (geometry), half spaces, each of which is defined by a linear inequality. Its objective function is a real number, real-valued affine function, affine (linear) function defined on this polyhedron. A linear programming algorithm finds a point in the polytope where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foster's Theorem
In probability theory, Foster's theorem, named after Gordon Foster, is used to draw conclusions about the positive recurrence of Markov chains with countable state spaces. It uses the fact that positive recurrent Markov chains exhibit a notion of "Lyapunov stability" in terms of returning to any state while starting from it within a finite time interval. Theorem Consider an irreducible discrete-time Markov chain on a countable state space ''S'' having a transition probability matrix P with elements ''p''''ij'' for pairs ''i'', ''j'' in ''S''. Foster's theorem states that the Markov chain is positive recurrent if and only if there exists a Lyapunov function V: S \to \mathbb, such that V(i) \geq 0 \text \forall \text i \in S and # \sum_p_V(j) < for # for all for some finite set ''F'' and strictly positive ''ε''. Related links * |
Markov Chains
A Markov chain or Markov process is a stochastic process, stochastic model describing a sequence of possible events in which the probability of each event depends only on the state attained in the previous event. Informally, this may be thought of as, "What happens next depends only on the state of affairs ''now''." A countably infinite sequence, in which the chain moves state at discrete time steps, gives a discrete-time Markov chain (DTMC). A continuous-time process is called a continuous-time Markov chain (CTMC). It is named after the Russian mathematician Andrey Markov. Markov chains have many applications as statistical models of real-world processes, such as studying cruise control, cruise control systems in motor vehicles, queues or lines of customers arriving at an airport, currency exchange rates and animal population dynamics. Markov processes are the basis for general stochastic simulation methods known as Markov chain Monte Carlo, which are used for simulating sampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backpressure Routing
In queueing theory, a discipline within the mathematical theory of probability, the backpressure routing algorithm is a method for directing traffic around a queueing network that achieves maximum network throughput, which is established using concepts of Lyapunov drift. Backpressure routing considers the situation where each job can visit multiple service nodes in the network. It is an extension of max-weight scheduling where each job visits only a single service node. Introduction Backpressure routing is an algorithm for dynamically routing traffic over a multi-hop network by using congestion gradients. The algorithm can be applied to wireless communication networks, including sensor networks, mobile ad hoc networks ( MANETS), and heterogeneous networks with wireless and wireline components.L. Tassiulas and A. Ephremides, "Stability Properties of Constrained Queueing Systems and Scheduling Policies for Maximum Throughput in Multihop Radio Networks, ''IEEE Transactions on Aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control-Lyapunov Function
In control theory, a control-Lyapunov function (CLF) is an extension of the idea of Lyapunov function V(x) to systems with control inputs. The ordinary Lyapunov function is used to test whether a dynamical system is ''(Lyapunov) stable'' or (more restrictively) ''asymptotically stable''. Lyapunov stability means that if the system starts in a state x \ne 0 in some domain ''D'', then the state will remain in ''D'' for all time. For ''asymptotic stability'', the state is also required to converge to x = 0. A control-Lyapunov function is used to test whether a system is ''asymptotically stabilizable'', that is whether for any state ''x'' there exists a control u(x,t) such that the system can be brought to the zero state asymptotically by applying the control ''u''. The theory and application of control-Lyapunov functions were developed by Zvi Artstein and Eduardo D. Sontag in the 1980s and 1990s. Definition Consider an autonomous dynamical system with inputs where x\in\mathbb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |