|
Lužnica, Croatia
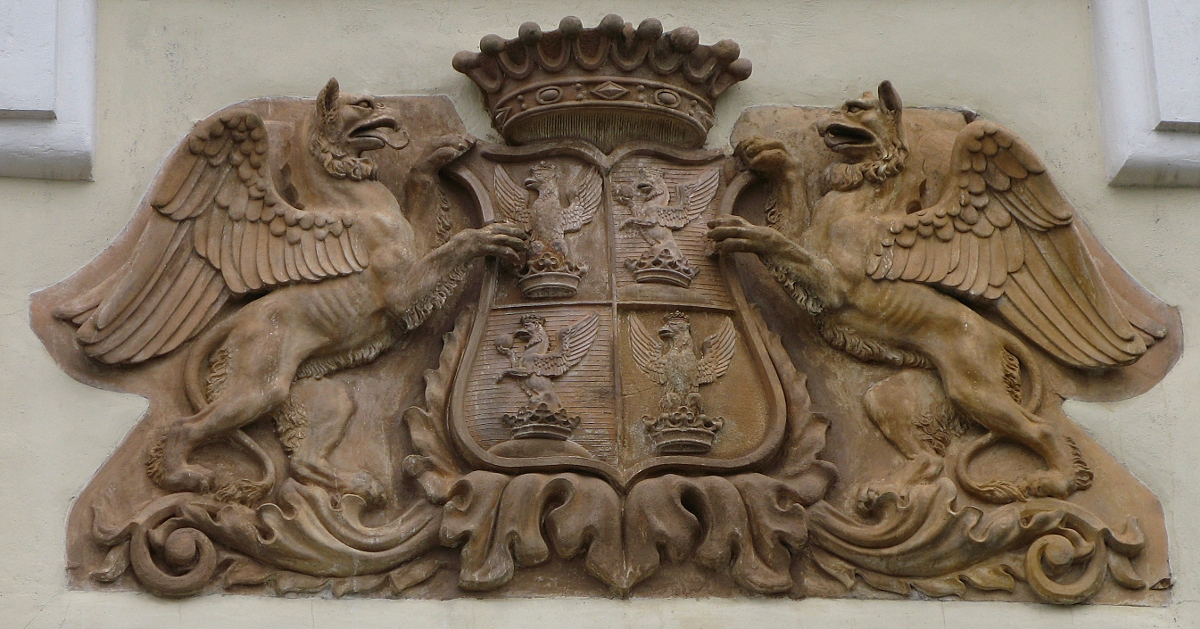
Lužnica is a settlement (naselje) in the town of Zaprešić, Zagreb County, Croatia. According to the 2001 census, it had 62 inhabitants, spread over an area of . It is thus the smallest settlement by population in Zaprešić. Lužnica is the location of the Lužnica Castle, a baroque castle and touristic point of interest built in 1791 and owned by the Convent of St. Vincent de Paul. The nuns operate nursing home for the elderly. The castle was previously owned by Croatian nobility Croatian nobility ( hr, plemstvo, lit=vlastelin; french: la noblesse) was a privileged social class in Croatia during the Antiquity and Medieval periods of the country's history. Noble families in the Kingdom of Croatia included high ranking popu ..., namely the Čikulin, Moscon and Rauch families. References External links Convent of St. Vincent de Paul website Populated places in Zagreb County Zaprešić {{ZagrebCounty-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naselje
The territory of Croatia is divided by the Croatian Bureau of Statistics into small settlements, in Croatian ''naselje'' (singular, pl. ''naselja''). They indicate existing or former human settlement (similar to the United States census designated places or the UK census output areas - OA) and are not necessarily incorporated places. Rather, the administrative units (local authorities) are cities (''grad'', pl. ''gradovi'') and municipalities (''općina'', pl. ''općine''), which are composed of one or more settlements. , there are 6,749 settlements in Croatia. Rural individual settlements are usually referred to as '' selo'' (village; pl. ''sela''). Municipalities (or communes) in Croatia comprise one or more, usually, rural settlements. A city usually includes an eponymous large settlement which in turn consists of several urban and suburban settlements. The Constitution of Croatia allows a ''naselje'' or a part thereof to form some form of local government. This form of local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naselje
The territory of Croatia is divided by the Croatian Bureau of Statistics into small settlements, in Croatian ''naselje'' (singular, pl. ''naselja''). They indicate existing or former human settlement (similar to the United States census designated places or the UK census output areas - OA) and are not necessarily incorporated places. Rather, the administrative units (local authorities) are cities (''grad'', pl. ''gradovi'') and municipalities (''općina'', pl. ''općine''), which are composed of one or more settlements. , there are 6,749 settlements in Croatia. Rural individual settlements are usually referred to as '' selo'' (village; pl. ''sela''). Municipalities (or communes) in Croatia comprise one or more, usually, rural settlements. A city usually includes an eponymous large settlement which in turn consists of several urban and suburban settlements. The Constitution of Croatia allows a ''naselje'' or a part thereof to form some form of local government. This form of local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatian Nobility
Croatian nobility ( hr, plemstvo, lit=vlastelin; french: la noblesse) was a privileged social class in Croatia during the Antiquity and Medieval periods of the country's history. Noble families in the Kingdom of Croatia included high ranking populates from Slavonia, Dalmatia, Istria, and Republic of Ragusa. Members belonged to an elite social hierarchy, normally placed immediately behind blood royalty, that possessed considerably more privileges or eminence than most other classes in a society. Membership thereof typically was often hereditary. Historically, membership in the nobility and the prerogatives thereof have been regulated or acknowledged by the monarch. Acquisition of sufficient power, wealth, military prowess or royal favour enabled commoners to ascend into the nobility. The country's royalty was heavily influenced by France's nobility resulting members of the Royal Courts to assume French titles and practices during French occupation. The controversial assumption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nursing Home
A nursing home is a facility for the residential care of elderly or disabled people. Nursing homes may also be referred to as skilled nursing facility (SNF) or long-term care facilities. Often, these terms have slightly different meanings to indicate whether the institutions are public or private, and whether they provide mostly assisted living, or nursing care and emergency medical care. Nursing homes are used by people who do not need to be in a hospital, but cannot be cared for at home. The nursing home facility nurses have the responsibilities of caring for the patients' medical needs and also the responsibility of being in charge of other employees, depending on their ranks. Most nursing homes have nursing aides and skilled nurses on hand 24 hours a day. In the United States, while nearly 1 in 10 residents age 75 to 84 stays in a nursing home for five or more years, nearly 3 in 10 residents in that age group stay less than 100 days, the maximum duration covered by Medicare, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vincent De Paul
Vincent de Paul, CM (24 April 1581 – 27 September 1660), commonly known as Saint Vincent de Paul, was a Occitan French Catholic priest who dedicated himself to serving the poor. In 1622 Vincent was appointed a chaplain to the galleys. After working for some time in Paris among imprisoned galley slaves, he returned to be the superior of what is now known as the Congregation of the Mission, or the "Vincentians" (in France known as "Lazaristes"). These priests, with vows of poverty, chastity, obedience, and stability, were to devote themselves entirely to the people in smaller towns and villages. Vincent was zealous in conducting retreats for clergy at a time when the local clergy's morals were flagging. He was a pioneer in seminary education and founded the Congregation of the Mission and the Daughters of Charity of Saint Vincent de Paul. He was renowned for his compassion, humility, and generosity. Vincent was canonized in 1737 and is venerated as a saint in the Catholic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point Of Interest
A point of interest (POI) is a specific point location that someone may find useful or interesting. An example is a point on the Earth representing the location of the Eiffel Tower, or a point on Mars representing the location of its highest mountain, Olympus Mons. Most consumers use the term when referring to hotels, campsites, fuel stations or any other categories used in modern automotive navigation systems. Users of a mobile device can be provided with geolocation and time aware POI service that recommends geolocations nearby and with a temporal relevance (e.g. POI to special services in a ski resort are available only in winter). The term is widely used in cartography, especially in electronic variants including GIS, and GPS navigation software. In this context the synonym waypoint is common. A GPS point of interest specifies, at minimum, the latitude and longitude of the POI, assuming a certain map datum. A name or description for the POI is usually included, and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including the Iberian Peninsula it continued, together with new styles, until the first decade of the 19th century. It followed Renaissance art and Mannerism and preceded the Rococo (in the past often referred to as "late Baroque") and Neoclassical styles. It was encouraged by the Catholic Church as a means to counter the simplicity and austerity of Protestant architecture, art, and music, though Lutheran Baroque art developed in parts of Europe as well. The Baroque style used contrast, movement, exuberant detail, deep colour, grandeur, and surprise to achieve a sense of awe. The style began at the start of the 17th century in Rome, then spread rapidly to France, northern Italy, Spain, and Portugal, then to Austria, southern Germany, and Russia. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central European Summer Time
Central European Summer Time (CEST), sometimes referred to as Central European Daylight Time (CEDT), is the standard clock time observed during the period of summer daylight-saving in those European countries which observe Central European Time (CET; UTC+01:00) during the other part of the year. It corresponds to UTC+02:00, which makes it the same as Eastern European Time, Central Africa Time, South African Standard Time, Egypt Standard Time and Kaliningrad Time in Russia. Names Other names which have been applied to Central European Summer Time are Middle European Summer Time (MEST), Central European Daylight Saving Time (CEDT), and Bravo Time (after the second letter of the NATO phonetic alphabet). Period of observation Since 1996, European Summer Time has been observed between 01:00 UTC (02:00 CET and 03:00 CEST) on the last Sunday of March, and 01:00 UTC on the last Sunday of October; previously the rules were not uniform across the European Union. There were proposals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Countries
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concernin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central European Time
Central European Time (CET) is a standard time which is 1 hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The time offset from UTC can be written as UTC+01:00. It is used in most parts of Europe and in a few North African countries. CET is also known as Middle European Time (MET, German: MEZ) and by colloquial names such as Amsterdam Time, Berlin Time, Brussels Time, Madrid Time, Paris Time, Rome Time, Warsaw Time or even Romance Standard Time (RST). The 15th meridian east is the central axis for UTC+01:00 in the world system of time zones. As of 2011, all member states of the European Union observe summer time (daylight saving time), from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. States within the CET area switch to Central European Summer Time (CEST, UTC+02:00) for the summer. In Africa, UTC+01:00 is called West Africa Time (WAT), where it is used by several countries, year round. Algeria, Morocco, and Tunisia also refer to it as ''Central European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |