|
Luo Shixin
Luo Shixin (c. 600–622) was a general during the transitional period between the Sui and Tang dynasties of China. History Luo Shixin was originally a young soldier under Zhang Xutuo, one of top generals of the Sui Dynasty during Emperor Yang's reign. In 613, when he was only 14 years old, Luo Shixin fought in various battles against peasant uprisings in the Shandong region. His bravery left a deep impression on Zhang Xutuo. Afterwards, Luo Shixin continued serving in Zhang Xutuo's army. He gradually became famous within Sui armies in which he served as well as within many rebellious forces. Because he was strong and brave in the battle, it was commonly believed that his enemies would be scared after hearing his name. Even Emperor Yang knew him by name and commended him, which was rare for a soldier of his rank. In 614, Luo Shixin and Qin Shubao played key roles in defeating the peasant army led by Lu Mingyue. In 616, Zhang Xutuo was killed in battle. Luo Shixin thus becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jinan
Jinan (), Postal Map Romanization, alternately romanization of Chinese, romanized as Tsinan, is the Capital (political), capital of Shandong province in East China, Eastern China. With a population of 9.2 million, it is the second-largest city in Shandong. The area of present-day Jinan has played an important role in the history of the region from the earliest beginnings of civilization and has evolved into a major national administrative, economic, and transportation hub. The city has held Sub-provincial city, sub-provincial administrative status since 1994. Jinan is often called the "City of Springs" for its famous 72 Artesian aquifer, artesian springs. Jinan is one of the top List of cities by scientific output, 40 cities in the world for scientific research as tracked by the Nature Index according to the Nature Index 2022 Science Cities. The city is home to List of universities and colleges in Shandong, several major universities, including Shandong University, Shangdong, Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
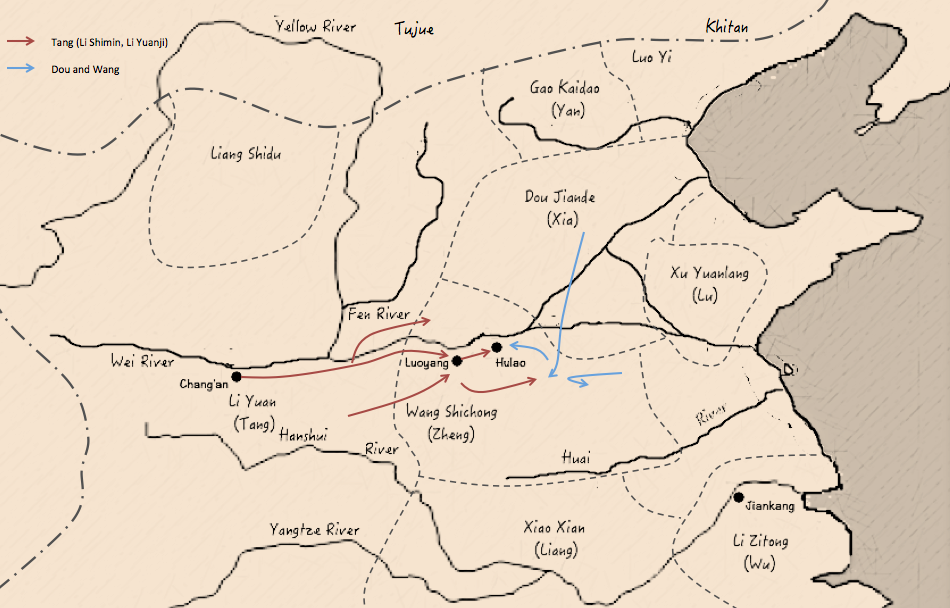
Wang Shichong
Wang Shichong (; 567– August 621), courtesy name Xingman (行滿), was a Chinese military general, monarch, and politician during the Sui dynasty who deposed Sui's last emperor Yang Tong and briefly ruled as the emperor of a succeeding state of Zheng. He first became prominent during the reign of Emperor Yang of Sui as one of the few Sui generals having success against rebel generals, and during Yang Tong's brief reign, he was able to defeat the rebel general Li Mi and seize Li Mi's territory. After becoming emperor, however, he was unable to withstand military pressure from Tang dynasty forces, forcing him to seek aid from Dou Jiande the Prince of Xia. After Dou was defeated and captured by the Tang general Li Shimin (the later Emperor Taizong), Wang surrendered. Emperor Gaozu of Tang spared him, but the Tang official Dugu Xiude (獨孤修德), whose father Dugu Ji (獨孤機) had been executed by Wang, assassinated him. Early career Wang Shichong's ancestors were su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty People
Tang or TANG most often refers to: * Tang dynasty * Tang (drink mix) Tang or TANG may also refer to: Chinese states and dynasties * Jin (Chinese state) (11th century – 376 BC), a state during the Spring and Autumn period, called Tang (唐) before 8th century BC * Tang dynasty (唐; 618–907), a major Chinese dynasty * Later Tang (唐; 923–937), a state during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period * Southern Tang (唐; 937–975), a state during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period Food * Tang (drink mix), a brand name of instant fruit flavored drinks, produced by Mondelēz International * Guk, soup or stew in Korean cuisine, sometimes known as "tang" Places Europe * Tang, County Westmeath, a village in Ireland * Tang, North Yorkshire, a settlement in England Asia * Tang, Ardabil, a village in Ardabil Province, Iran * Tang, Badakhshan, a village in Afghanistan * Tang, a village in Bumthang District, Bhutan * Tang (唐镇), a town in Pudong, Shanghai, China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luo Yi
Luo Yi () (died 627), known during service to Tang Dynasty as Li Yi (), courtesy name Ziyan (子延) or Ziting (子廷), was a Sui Dynasty official who rose against the rule of Emperor Yang of Sui and occupied the modern Beijing region. He subsequently submitted to Emperor Gaozu of Tang and was created the Prince of Yan and granted the imperial surname of Li. He subsequently, in the struggle between Emperor Gaozu's sons Li Jiancheng the Crown Prince and Li Shimin the Prince of Qin, joined Li Jiancheng's faction. After Li Shimin killed Li Jiancheng in 626 and forced Emperor Gaozu to yield the throne to him (as Emperor Taizong), Li Yi was fearful, and he rebelled against Emperor Taizong in 627. He was soon defeated and killed. Initial uprising Luo Yi's clan was originally from Xiangyang (襄陽, in modern Xiangfan, Hubei), but moved from there to the Sui capital Chang'an. Luo Yi's father Luo Rong (羅榮) was a minor general during Sui. Luo Yi was said to be intelligent, self- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luo Cheng
18 Warriors of Sui-Tang Period (隋唐十八条好汉) are 18 legendary and fictional heroes living in Sui Dynasty and early Tang Dynasty. The concept of 18 Warriors was first mentioned in the traditional historical novel ''Shuo Tang''. The ranking of those 18 warriors was based on their skills in martial arts as well as their physical strength. Some of them somehow have historical archetypes such as Qin Shubao and Shan Xiongxin while others are created by authors of folk stories such as Luo Cheng and Yuwen Chengdu. The ranking The ranking itself is disputed, largely because the novel ''Shuo Tang'' only defined 13 out of all 18 warriors. Those 13 defined by the book Shuo Tang were generally accepted: # Li Yuanba (李元霸) # Yuwen Chengdu (宇文成都) # Pei Yuanqing (裴元庆) # Xiong Kuohai (熊阔海) # Wu Yunzhao (伍云召) # Wu Tianxi (伍天锡) # Luo Cheng (罗成) # Yang Lin (杨林) # Wei Wentong (魏文通) # Shang Shitu (尚师徒) # Xin Wenli (新文理) # ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zizhi Tongjian
''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song (960–1127), Northern Song dynasty in the form of a chronicle recording Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynasties and spanning almost 1400 years. The main text is arranged into 294 scrolls (''juan'' , equivalent to a chapter) totaling about 3 million Chinese characters. In 1065 AD, Emperor Yingzong of Song commissioned his official Sima Guang (1019–1086 AD) to lead a project to compile a universal history of China, and granted him funding and the authority to appoint his own staff. His team took 19 years to complete the work and in 1084 AD it was presented to Emperor Yingzong's successor Emperor Shenzong of Song. It was well-received and has proved to be immensely influential among both scholars and the general public. Endymion Wilkinson regards it as reference quality: "It had an enormous influence on la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Shimin
Emperor Taizong of Tang (28January 59810July 649), previously Prince of Qin, personal name Li Shimin, was the second emperor of the Tang dynasty of China, ruling from 626 to 649. He is traditionally regarded as a co-founder of the dynasty for his role in encouraging Li Yuan, his father, to rebel against the Sui dynasty at Jinyang in 617. Taizong subsequently played a pivotal role in defeating several of the dynasty's most dangerous opponents and solidifying its rule over China. Taizong is considered to be one of the greatest emperors in China's history and henceforth, his reign became regarded as the exemplary model against which all future emperors were measured. His era, the "Reign of Zhenguan ()" is considered a golden age in ancient Chinese history and was treated as required studying material for future crown princes. Taizong continued to develop imperial examination systems. He asked his officers to become loyal to the policies not people, in order to eliminate corr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahe, Hebei
Shahe () is a county-level city in the prefecture-level city of Xingtai, in the southern part of Hebei province, China. Shahe has been called China's "glass capital." Its glass factories manufacture about ten percent of the world supply of flat glass. About 50,000 of Shahe's 480,000 residents work in the glass industry. Smog in Shahe has become a serious problem, with some factories preferring to pay fines rather than comply with air pollution enforcement requirements. Administrative divisions Subdistricts: * Dalian Subdistrict (), Qiaodong Subdistrict (), Qiaoxi Subdistrict Qiaoxi District (桥西区) may refer to the following locations in Hebei, China: * Qiaoxi District, Shijiazhuang *Qiaoxi District, Xingtai *Qiaoxi District, Zhangjiakou Qiaoxi District () is a district of the city of Zhangjiakou, Hebei H ... (), Zanshan Subdistrict (), Zhouzhuang Subdistrict () Towns: * Shahecheng (), Xincheng (), Baita (), Shiliting (), Qicun (綦村镇 Townships: * Liuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Junkuo
Wang may refer to: Names * Wang (surname) (王), a common Chinese surname * Wāng (汪), a less common Chinese surname * Titles in Chinese nobility The nobility of China was an important feature of the traditional social structure of Ancient China and Imperial China. While the concepts of hereditary sovereign and peerage titles and noble families were featured as early as the semi-mythic ... * A title in Korean nobility * A title in Mongolian nobility Places * Wang River in Thailand * Wang Township, Minnesota, a township in the United States * Wang, Bavaria, a town in the district of Freising, Bavaria, Germany * Wang, Austria, a town in the district of Scheibbs in Lower Austria * An abbreviation for the town of Wangaratta, Australia * Wang Theatre, in Boston, Massacheussetts * Charles B. Wang Center, an Asian American center at Stony Brook University Other * Wang (Tibetan Buddhism), a form of empowerment or initiation * Wang tile, in mathematics, are a class of form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Heita
Liu Heita () (died 623) was an agrarian rebel leader during China's transition period from Sui Dynasty to Tang Dynasty, who initially successively served under Hao Xiaode (), Li Mi, and Wang Shichong. He eventually followed Dou Jiande the Prince of Xia. After Dou was killed by Emperor Gaozu of Tang in 621 and his territory was taken by Tang, Liu rose to avenge Dou, and briefly recaptured Dou's territory, north of the Yellow River. He was then defeated, first by the Tang general Li Shimin (the eventual Emperor Taizong) and then Li Shimin's brother Li Jiancheng the Crown Prince, and in 623, he was captured by his one-time subordinate Zhuge Dewei () and executed. Service under Hao Xiaode, Li Mi, Wang Shichong, and Dou Jiande Little is known about Liu Heita's background, and it is not known when he was born. He was from Zhangnan (漳南, in modern Handan, Hebei)—the same county as Dou Jiande—and was said to be brave and quick in reaction from his youth. He was also said ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hulao
The Battle of Hulao () or Battle of Sishui (汜水之戰, Wade–Giles: Ssŭ Shui), on 28 May 621 was the main and final battle of the Luoyang–Hulao campaign between the rival Tang, Zheng, and Xia regimes during the transition from Sui to Tang. It was a decisive victory for the Tang prince Li Shimin, through which he was able to subdue two rival warlords, Dou Jiande who headed the Xia regime in Hebei, and Wang Shichong, the self-declared emperor of the Zheng dynasty. The battle was fought at the strategically important Hulao Pass, east of Luoyang. Following victories in the west that had established his credentials as a general, in August 620 Li Shimin marched against Wang Shichong. Tang troops blockaded Wang in his capital of Luoyang, while seizing the rest of Henan province. After failing in his efforts to break through the Tang siege, and suffering from ever greater privations, Wang solicited help from Dou Jiande. In April 621, Dou Jiande led a 100,000–120,000 strong a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dou Jiande
Dou Jiande (; 573 – 3 August 621) was a leader of the agrarian rebels who rose against the rule of Emperor Yang of Sui near the end of the Chinese Sui dynasty. Generally considered the kindest and most able of the agrarian rebel leaders of the time, he was eventually able to capture the modern Hebei region and declare himself initially the Prince of Changle, and then the Prince of Xia. In 621, when the Tang dynasty general Li Shimin (later Emperor Taizong) attacked Wang Shichong the Emperor of Zheng, who ruled the modern Henan region, Dou believed that if Tang were able to destroy Zheng, his own Xia state would suffer the same fate, and therefore went to Wang's aid, against the advice of his strategist Ling Jing () and his wife Empress Cao. Li defeated him at the Battle of Hulao, capturing him. Li's father Emperor Gaozu of Tang subsequently put Dou to death. Xia territory was briefly seized by Tang, but soon Dou's general Liu Heita rose against Tang rule, recaptur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |