|
Luis Berríos-Negrón
Luis Berríos-Negrón (born 15 May 1971 in San Juan, Puerto Rico) is a Puerto Rican artist working with sculpture and installation, in public and environmental art. He has an independent practice, as well as is the founder of the Anxious Prop art collective and the Paramodular environmental design group. Berríos-Negrón lives and works in Berlin since 2006. Education He currently is candidate for doctor of philosophy at the Konstfack College of the Arts and the Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) in Stockholm. He holds a Master of Architecture from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and a Bachelor of Fine Arts from the Parsons New School for Design. While at the New School, he was teaching assistant to urban ecologist Jean Gardner, assistant editor/curator to conceptual artist Silvia Kolbowski, and studio assistant to photographer Larry Clark. While at M.I.T., he was teaching assistant to Joan Jonas, Antoni Muntadas and Krzysztof Wodiczko. His master's thesis was co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Juan, Puerto Rico
San Juan (, , ; Spanish for "Saint John") is the capital city and most populous municipality in the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, an unincorporated territory of the United States. As of the 2020 census, it is the 57th-largest city under the jurisdiction of the United States, with a population of 342,259. San Juan was founded by Spanish colonists in 1521, who called it Ciudad de Puerto Rico ("City of Puerto Rico", Spanish for ''rich port city''). Puerto Rico's capital is the third oldest European-established capital city in the Americas, after Santo Domingo, in the Dominican Republic, founded in 1496, and Panama City, in Panama, founded in 1521, and is the oldest European-established city under United States sovereignty. Several historical buildings are located in San Juan; among the most notable are the city's former defensive forts, Fort San Felipe del Morro and Fort San Cristóbal, and La Fortaleza, the oldest executive mansion in continuous use in the Americas. Today, Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ute Meta Bauer
Ute Meta Bauer (born 1958). She is an international curator, professor of contemporary art and the director of the Centre for Contemporary Art (CCA) in Singapore. Early life and education Bauer was born in 1958 in Stuttgart, Germany. She studied at the Hochschule der Bildenden Künste, Hamburg, Germany, between 1980-1989. Her diplomas focus on art theory, visual communication and stage design. She has worked as a free-lance curator since 1985. Career From 1990 to 1994, Bauer was Artistic Director of the Künstlerhaus Stuttgart, where she programmed several exhibitions and conferences on contemporary art, such as ''Radical Chic'' (1993) and ''A New Spirit in Curating'' (1992). From 1996-2006, Bauer held an appointment at the Academy of Fine Arts Vienna in Austria, as a professor of theory and practice of contemporary art. Bauer served as the Founding Director of the Office for Contemporary Art in Norway from 2002 to 2005. Afterwards, she moved onto Massachusetts Institute of Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
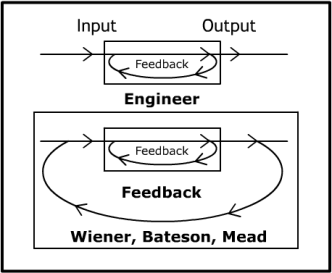
Second-order Cybernetics
Second-order cybernetics, also known as the cybernetics of cybernetics, is the recursive application of cybernetics to itself and the reflexive practice of cybernetics according to such a critique. It is cybernetics where "the role of the observer is appreciated and acknowledged rather than disguised, as had become traditional in western science". Glanville, R. (2002). "Second order cybernetics." In F. Parra-Luna (ed.), Systems science and cybernetics. In ''Encyclopaedia of Life Support Systems'' (EOLSS). OxfordEoLSS Second-order cybernetics was developed between the late 1960s and mid 1970s by Heinz von Foerster and others, with key inspiration coming from Margaret Mead. Foerster referred to it as "the control of control and the communication of communication" and differentiated first order cybernetics as "the cybernetics of observed systems" and second-order cybernetics as "the cybernetics of observing systems". Foerster, Heinz von, ed. ''Cybernetics of Cybernetics: Or, the Contro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transculturation
Transculturation is a term coined by Cuban anthropologist Fernando Ortiz in 1940 (from the article Our America by José Martí) to describe the phenomenon of merging and converging cultures. Transculturation encompasses more than transition from one culture to another; it does not consist merely of acquiring another culture (acculturation) or of losing or uprooting a previous culture (deculturation). Rather, it merges these concepts and instead carries the idea of the consequent creation of new cultural phenomena ( neoculturation) in which the blending of cultures is understood as producing something entirely new. Although transculturation is somewhat inevitable, cultural hegemony has historically shaped this process. Particularly, Ortiz referred to the devastating effects of Spanish colonialism on Cuba's indigenous peoples as a "failed transculturation". Further, he affirmed "that when cultures encounter each other, each of the parties invariably exerts a strong influence on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Concrete Movement
The Neo-Concrete Movement (1959–61) was a Brazilian art movement, a group that splintered off from the larger Concrete Art movement prevalent in Latin America and in other parts of the world. The Neo-Concretes emerged from Rio de Janeiro’s Grupo Frente. They rejected the pure rationalist approach of concrete art and embraced a more phenomenological and less scientific art. Ferreira Gullar inspired Neo-Concrete philosophy through his essay “Theory of the Non-Object” (1959) and wrote the “Neo-Concrete Manifesto” (1959) which outlines what Neo-Concrete art should be. Lygia Clark, Hélio Oiticica, and Lygia Pape were among the primary leaders of this movement. Background After World War I, Europe witnessed a boom of art movements based upon rationalism such as De Stijl and Bauhaus. Artists believed humanity would be able to achieve progress through its ability to reason. In Latin America, ideas of rationalist and non-objective art took root in the early 1950s in reaction t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Leckey
Mark Leckey (born 1964) is a British contemporary artist. His found object art and video pieces, which incorporate themes of nostalgia and anxiety, and draw on elements of pop culture, span several works and exhibitions. In particular, he is known for '' Fiorucci Made Me Hardcore'' (1999) and ''Industrial Light and Magic'' (2008), for which he won the 2008 Turner Prize. His work has been widely exhibited internationally, including solo exhibitions at Kölnischer Kunstverein, Cologne, in 2008 and at Le Consortium, Dijon, in 2007. His performances have been presented in New York City at the Museum of Modern Art, Abrons Arts Center; at the Institute of Contemporary Arts, London, both in 2009; and at the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum, New York City, in 2008. His works are held in the collections of the Tate and the Centre Pompidou. Life and career Leckey was born in Birkenhead, Wirral, near Liverpool, in 1964. In a 2008 interview in ''The Guardian'', he described how he grew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans-Jörg Rheinberger
Hans-Jörg Rheinberger (born 12 January 1946) is an historian of science who comes from Liechtenstein. He was director of the Max Planck Institute for the History of Science in Berlin from 1997 to 2014. His focus areas within the history of science are the history and epistemology of the experiment, and further the history of molecular biology and protein biosynthesis. Additionally he writes and publicizes essays and poems. Life Hans-Jörg Rheinberger was born in Grabs, Switzerland on 12 January 1946. He is the great-grandnephew of the composer Josef Rheinberger and grandchild of the artist and architect . He studied philosophy, linguistics and biology at the University of Tübingen, the Free University of Berlin and the Technical University of Berlin. After completing his magister degree in philosophy (1973) he earned his doctorate (Dr. rer. nat.) in 1982 with a dissertation concerned with protein biosynthesis and habilitated 1987 in molecular biology at the FU Berlin. From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental System
In scientific research, an experimental system is the physical, technical and procedural basis for an experiment or series of experiments. Historian of science Hans-Jörg Rheinberger defines an experimental system as: "A basic unit of experimental activity combining local, technical, instrumental, institutional, social, and epistemic aspects." Scientists (particularly laboratory biologists) and historians and philosophers of biology have pointed to the development and spread of successful experimental systems, such as those based on popular model organism or scientific apparatus, as key elements in the history of science, particularly since the early 20th century. The choice of an appropriate experimental system is often seen as critical for a scientist's long-term success, as experimental systems can be very productive for some kinds of questions and less productive for others, acquiring a sort of momentum that takes research in unpredicted directions. A successful experimental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James R
James is a common English language surname and given name: *James (name), the typically masculine first name James * James (surname), various people with the last name James James or James City may also refer to: People * King James (other), various kings named James * Saint James (other) * James (musician) * James, brother of Jesus Places Canada * James Bay, a large body of water * James, Ontario United Kingdom * James College, a college of the University of York United States * James, Georgia, an unincorporated community * James, Iowa, an unincorporated community * James City, North Carolina * James City County, Virginia ** James City (Virginia Company) ** James City Shire * James City, Pennsylvania * St. James City, Florida Arts, entertainment, and media * ''James'' (2005 film), a Bollywood film * ''James'' (2008 film), an Irish short film * ''James'' (2022 film), an Indian Kannada-language film * James the Red Engine, a character in ''Thomas the Tank En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susan Leigh Star
Susan Leigh Star (1954–2010) was an American sociologist. She specialized in the study of information in modern society; information worlds; information infrastructure; classification and standardization; sociology of science; sociology of work and the history of science, medicine, technology, and communication/information systems. She commonly used the qualitative methods methodology and feminist theory approach. She was also known for developing the concept of boundary objects and for contributions to computer-supported cooperative work. Biography Life and education Star grew up in a rural working class area of Rhode Island. Her family was of Jewish, English, and Scottish descent and she describes herself as "half-Jewish". Starved for philosophy she befriended an ex-nun during high school and eventually obtained a scholarship to Radcliffe College where she began taking philosophy classes. Not fitting in and deterred from taking a Religion degree, Star dropped out, mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary Object
In sociology and science and technology studies, a boundary object is information, such as specimens, field notes, and maps, used in different ways by different communities ''for collaborative work through scales''. Boundary objects are plastic, interpreted differently across communities but with enough immutable content (i.e., common identity across social words and contexts) to maintain integrity. The concept was introduced by Susan Leigh Star and James R. Griesemer in a 1989 publication (p. 393): In their article, Star and Griesemer describe the importance of boundary objects and methods standardization in the development of the Berkeley Museum of Vertebrate Zoology. Boundary objects can be abstract or concrete (e.g., digital technologies or abstract ideas); so in this case some of the boundary objects that they list include specimens, field notes, and maps of particular territories. These objects interact with members of various social groups (including amateur collect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |