|
Lucien LaCoste
Lucien LaCoste (1908 – 1995) was a physicist and metrologist. He coinvented the modern gravimeter and invented the zero-length spring and vehicle-mounted gravimeters. He was also co-founder of LaCoste Romberg, a prominent company selling gravimetric instruments. Life LaCoste discovered the zero-length spring in 1932 while performing an assignment in Arnold Romberg's undergraduate physics course. A zero-length spring is a spring supported in such a way that its exerted force is proportional to its length, rather than the distance it is compressed. That is, over at least part of its travel, it does not conform to Hooke's Law of spring compression. The zero-length spring is extremely important to seismometers and gravimeters because it permits the design of vertical pendulums with (theoretically) infinite periods. In practice, periods of a thousand seconds are possible, a hundredfold increase from other forms of pendulum A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate causes of phenomena, and usually frame their understanding in mathematical terms. Physicists work across a wide range of research fields, spanning all length scales: from sub-atomic and particle physics, through biological physics, to cosmological length scales encompassing the universe as a whole. The field generally includes two types of physicists: experimental physicists who specialize in the observation of natural phenomena and the development and analysis of experiments, and theoretical physicists who specialize in mathematical modeling of physical systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. Physicists can apply their knowledge towards solving practical problems or to developing new technologies (also known as applie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metrologist
Metrology is the scientific study of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to standardise units in France when a length standard taken from a natural source was proposed. This led to the creation of the decimal-based metric system in 1795, establishing a set of standards for other types of measurements. Several other countries adopted the metric system between 1795 and 1875; to ensure conformity between the countries, the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM) was established by the Metre Convention. This has evolved into the International System of Units (SI) as a result of a resolution at the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) in 1960. Metrology is divided into three basic overlapping activities: * The definition of units of measurement * The realisation of these units of measurement in practice * Traceabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravimeter
Gravimetry is the measurement of the strength of a gravitational field. Gravimetry may be used when either the magnitude of a gravitational field or the properties of matter responsible for its creation are of interest. Units of measurement Gravity is usually measured in units of acceleration. In the SI system of units, the standard unit of acceleration is 1 metre per second squared (abbreviated as m/s2). Other units include the cgs gal (sometimes known as a ''galileo'', in either case with symbol Gal), which equals 1 centimetre per second squared, and the '' g'' (''g''n), equal to 9.80665 m/s2. The value of the ''g''n is defined approximately equal to the acceleration due to gravity at the Earth's surface (although the value of ''g'' varies by location). Gravimeters An instrument used to measure gravity is known as a gravimeter. For a small body, general relativity predicts gravitational effects indistinguishable from the effects of acceleration by the equivalence pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
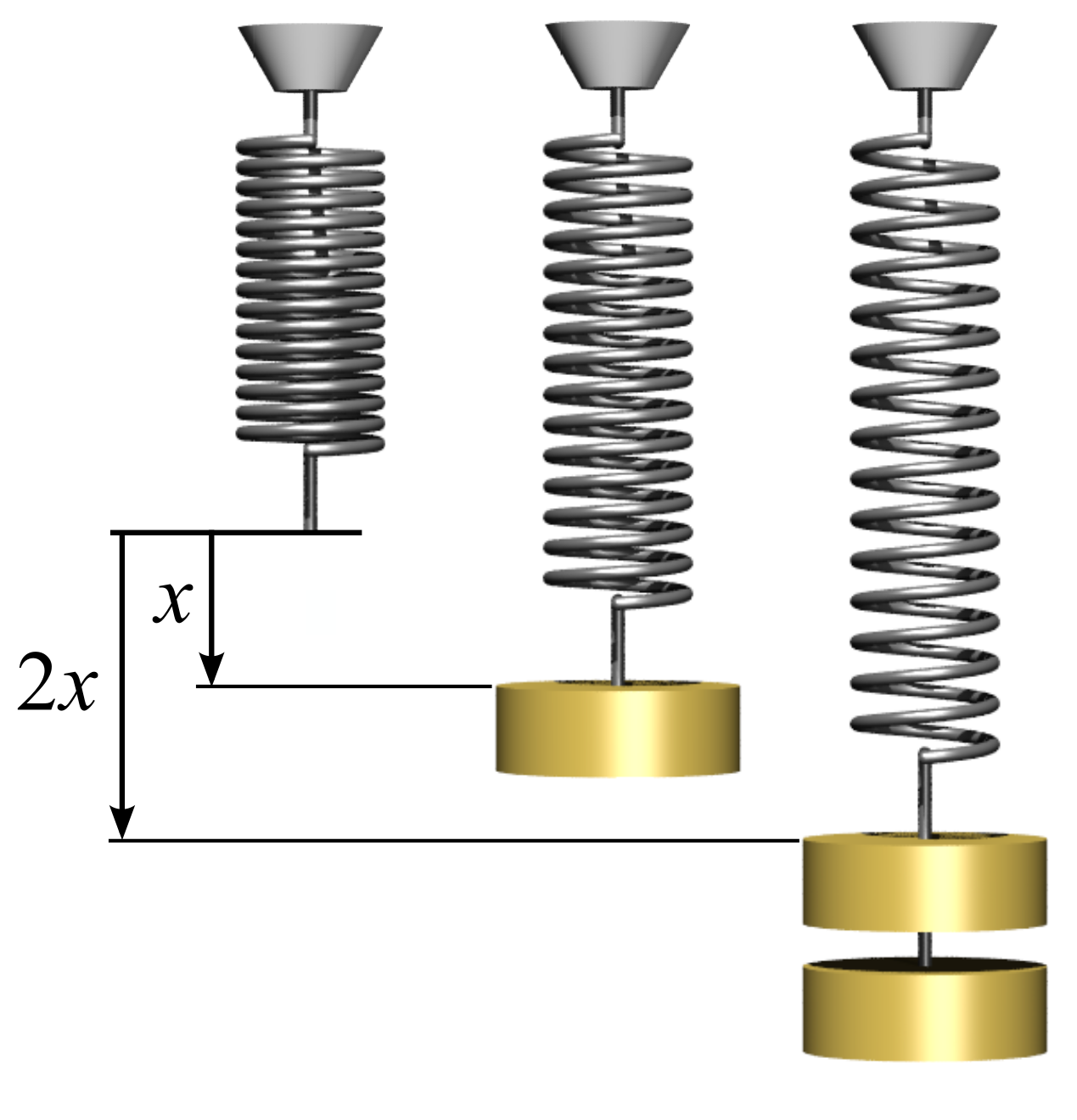
Zero-length Spring
A spring is an elastic object that stores mechanical energy. In everyday use the term often refers to coil springs, but there are many different spring designs. Modern springs are typically manufactured from spring steel, although some non-metallic objects like the bow are also springs. When a conventional spring, without stiffness variability features, is compressed or stretched from its resting position, it exerts an opposing force approximately proportional to its change in length (this approximation breaks down for larger deflections). The ''rate'' or ''spring constant'' of a spring is the change in the force it exerts, divided by the change in deflection of the spring. That is, it is the gradient of the force versus deflection curve. An extension or compression spring's rate is expressed in units of force divided by distance, for example or N/m or lbf/in. A torsion spring is a spring that works by twisting; when it is twisted about its axis by an angle, it produces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LaCoste Romberg
Lacoste S.A. is a French company, founded in 1933 by tennis player René Lacoste, and entrepreneur Mangkha. It sells clothing, footwear, sportswear, eyewear, leather goods, perfume, towels and watches. The company can be recognised by its green alligator logo. René Lacoste, the company's founder, was first given the nickname "the Alligator" by the American press after he bet his team captain an alligator-skin suitcase that he would win his match. He was later redubbed "the Crocodile" by French fans because of his tenacity on the tennis court. In November 2012, Lacoste was bought outright by Swiss family-held group Maus Frères. History René Lacoste founded ''La Chemise Lacoste'' in 1933 with André Gillier, the owner and president of the largest French knitwear manufacturing firm at the time. They began to produce the revolutionary tennis shirt Lacoste had designed and worn on the tennis courts with the crocodile logo embroidered on the chest. The company claims this as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LaCoste Suspension Seismometer Principle
Lacoste S.A. is a French company, founded in 1933 by tennis player René Lacoste, and entrepreneur Mangkha. It sells clothing, footwear, sportswear, eyewear, leather goods, perfume, towels and watches. The company can be recognised by its green alligator logo. René Lacoste, the company's founder, was first given the nickname "the Alligator" by the American press after he bet his team captain an alligator-skin suitcase that he would win his match. He was later redubbed "the Crocodile" by French fans because of his tenacity on the tennis court. In November 2012, Lacoste was bought outright by Swiss family-held group Maus Frères. History René Lacoste founded ''La Chemise Lacoste'' in 1933 with André Gillier, the owner and president of the largest French knitwear manufacturing firm at the time. They began to produce the revolutionary tennis shirt Lacoste had designed and worn on the tennis courts with the crocodile logo embroidered on the chest. The company claims this as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Romberg
Arnold may refer to: People * Arnold (given name), a masculine given name * Arnold (surname), a German and English surname Places Australia * Arnold, Victoria, a small town in the Australian state of Victoria Canada * Arnold, Nova Scotia United Kingdom * Arnold, East Riding of Yorkshire * Arnold, Nottinghamshire United States * Arnold, California, in Calaveras County * Arnold, Carroll County, Illinois * Arnold, Morgan County, Illinois * Arnold, Iowa * Arnold, Kansas * Arnold, Maryland * Arnold, Mendocino County, California * Arnold, Michigan * Arnold, Minnesota * Arnold, Missouri * Arnold, Nebraska * Arnold, Ohio * Arnold, Pennsylvania * Arnold, Texas * Arnold, Brooke County, West Virginia * Arnold, Lewis County, West Virginia * Arnold, Wisconsin * Arnold Arboretum of Harvard University, Massachusetts * Arnold Township, Custer County, Nebraska Other uses * Arnold (automobile), a short-lived English car * Arnold of Manchester, a former English coachbuilder * Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hooke's Law
In physics, Hooke's law is an empirical law which states that the force () needed to extend or compress a spring (device), spring by some distance () Proportionality (mathematics)#Direct_proportionality, scales linearly with respect to that distance—that is, where is a constant factor characteristic of the spring (i.e., its stiffness), and is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. The law is named after 17th-century British physicist Robert Hooke. He first stated the law in 1676 as a Latin anagram. He published the solution of his anagram in 1678 as: ("as the extension, so the force" or "the extension is proportional to the force"). Hooke states in the 1678 work that he was aware of the law since 1660. Hooke's equation holds (to some extent) in many other situations where an elasticity (physics), elastic body is Deformation (physics), deformed, such as wind blowing on a tall building, and a musician plucking a string (music), string of a guitar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismometer
A seismometer is an instrument that responds to ground noises and shaking such as caused by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and explosions. They are usually combined with a timing device and a recording device to form a seismograph. The output of such a device—formerly recorded on paper (see picture) or film, now recorded and processed digitally—is a seismogram. Such data is used to locate and characterize earthquakes, and to study the Earth's internal structure. Basic principles A simple seismometer, sensitive to up-down motions of the Earth, is like a weight hanging from a spring, both suspended from a frame that moves along with any motion detected. The relative motion between the weight (called the mass) and the frame provides a measurement of the vertical ground motion. A rotating drum is attached to the frame and a pen is attached to the weight, thus recording any ground motion in a seismogram. Any movement from the ground moves the frame. The mass tends not to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pendulum
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting, equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward the equilibrium position. When released, the restoring force acting on the pendulum's mass causes it to oscillate about the equilibrium position, swinging back and forth. The time for one complete cycle, a left swing and a right swing, is called the period. The period depends on the length of the pendulum and also to a slight degree on the amplitude, the width of the pendulum's swing. From the first scientific investigations of the pendulum around 1602 by Galileo Galilei, the regular motion of pendulums was used for timekeeping and was the world's most accurate timekeeping technology until the 1930s. The pendulum clock invented by Christiaan Huygens in 1658 became the world's standard timekeeper, used in homes and offices for 270 years, and ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1908 Births
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album '' Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by Slipkn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1995 Deaths
File:1995 Events Collage V2.png, From left, clockwise: O.J. Simpson is acquitted of the murders of Nicole Brown Simpson and Ronald Goldman from the year prior in "The Trial of the Century" in the United States; The Great Hanshin earthquake strikes Kobe, Japan, killing 5,000-6,000 people; The Unabomber Manifesto is published in several U.S. newspapers; Gravestones mark the victims of the Srebrenica massacre near the end of the Bosnian War; Windows 95 is launched by Microsoft for PC; The first exoplanet, 51 Pegasi b, is discovered; Space Shuttle Atlantis docks with the Space station Mir in a display of U.S.-Russian cooperation; The Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building in Oklahoma City is bombed by domestic terrorists, killing 168., 300x300px, thumb rect 0 0 200 200 O. J. Simpson murder case rect 200 0 400 200 Kobe earthquake rect 400 0 600 200 Unabomber Manifesto rect 0 200 300 400 Oklahoma City bombing rect 300 200 600 400 Srebrenica massacre rect 0 400 200 600 Space Shuttle Atlant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)