|
Lu Mao
Lu Mao (died 239), courtesy name Zizhang, was a Chinese politician of the state of Eastern Wu during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He was a younger brother of Lu Xun, a prominent politician and general who served as the third Imperial Chancellor of Eastern Wu. Life Lu Mao was a younger brother of Lu Xun. His ancestral home was in Wu County, Wu Commandery, which is in present-day Suzhou, Jiangsu. At a young age, he was already known for being a keen learner and for valuing righteousness. Some of his friends – Chen Rong (), Puyang Yi, Jiang Zuan () and Yuan Di () – were from humble backgrounds but had great ambitions. Lu Mao, who was from a more affluent family, often shared his wealth with them. Xu Yuan (), who was also from Wu Commandery, moved to Kuaiji Commandery. He had never met Lu Mao before, but before his death, he wrote to Lu Mao and requested Lu to help him take care of his young son. Lu Mao obliged, had a proper tomb constructed for Xu Yuan, and adopted Xu Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Quan
Sun Quan (, Chinese: 孫權) (183 – 21 May 252), courtesy name Zhongmou (), posthumously known as Emperor Da of Wu, was the founder of the Eastern Wu dynasty, one of the Three Kingdoms of China. He inherited control of the warlord regime established by his elder brother, Sun Ce, in 200. He declared formal independence and ruled from 222 to 229 as the King of Wu and from 229 to 252 as the Emperor of Wu. Unlike his rivals Cao Cao and Liu Bei, Sun Quan was much younger than they were and governed his state mostly separate of politics and ideology. He is sometimes portrayed as neutral considering he adopted a flexible foreign policy between his two rivals with the goal of pursuing the greatest interests for the country. Sun Quan was born while his father Sun Jian served as the adjutant of Xiapi County. After Sun Jian's death in the early 190s, he and his family lived at various cities on the lower Yangtze River, until Sun Ce carved out a warlord regime in the Jiangdong region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
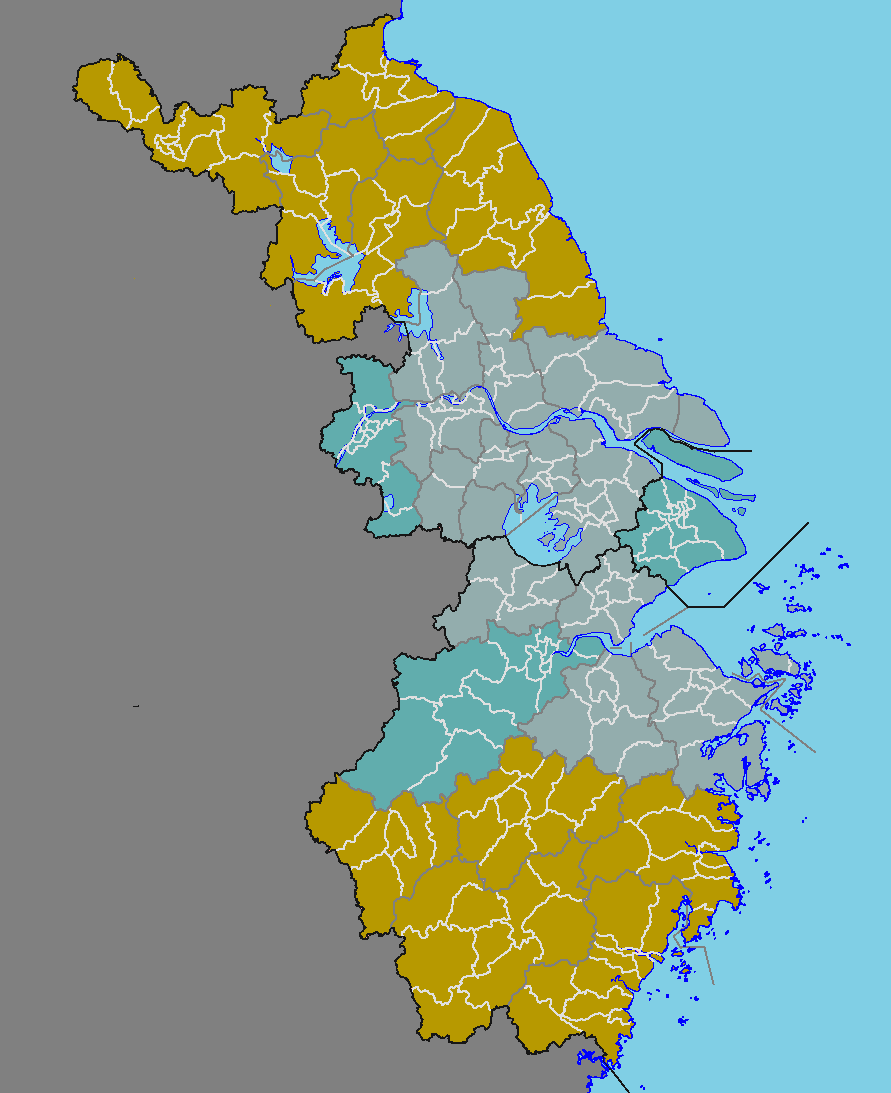
Wu Commandery
Wu Commandery was a commandery of imperial China. It covers parts of the contemporary Northern Zhejiang and Southern Jiangsu. The capital of Wu commandery was Wu (today's Suzhou). Major counties of Wu commandery include Wu (county), Yuhang county, and Huating county which later became known as Suzhou, Hangzhou and Shanghai. History During its existence, Wu commandery was ruled by various dynasties and regimes. Chronologically, Han dynasty, Eastern Wu, Jin dynasty, Liu Song dynasty, Southern Qi dynasty, Liang dynasty, Chen dynasty, Sui dynasty and Tang dynasty governed Wu commandery in sequence. In the year of 129, Wu commandery was established during the reign of emperor Shun of Han. When Kuaiji Commandery was divided, lands west of Qiantang river in Kuaiji commandery formed the new Wu commandery. After the division of Kuaiji, Wu constitutes one of the commanderies of Yang Province. In 195, local strongman of Fuchun county Sun Ce acquired the entire Wu commandery without the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Departments And Six Ministries
The Three Departments and Six Ministries () system was the primary administrative structure in imperial China from the Sui dynasty (581–618) to the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368). It was also used by Balhae (698–926) and Goryeo (918–1392) and various other kingdoms in Manchuria, Korea and Vietnam. The Three Departments were three top-level administrative structures in imperial China. They were the Central Secretariat, responsible for drafting policy, the Chancellery, responsible for reviewing policy and advising the emperor, and the Department of State Affairs, responsible for implementing policy. The former two were loosely joined as the Secretariat-Chancellery during the late Tang dynasty, Song dynasty and in the Korean kingdom of Goryeo. The Six Ministries (also translated as Six Boards) were direct administrative organs of the state under the authority of the Department of State Affairs. They were the Ministries of Personnel, Rites, War, Justice, Works, and Revenue. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Twenty-four Filial Exemplars
''The Twenty-four Filial Exemplars'', also translated as ''The Twenty-four Paragons of Filial Piety'' (), is a classic text of Confucian filial piety written by Guo Jujing ()() Wang, Qi (). ''Xu Wenxian Tongkao'' () vol. 71. during the Yuan dynasty (1260–1368). The text was extremely influential in the medieval Far East and was used to teach Confucian moral values. Authorship The text is generally attributed to Guo Jujing () but other sources suggested two other possible authors or editors: Guo Shouzheng () and Guo Juye (). History Some of the stories in ''The Twenty-four Filial Exemplars'' were taken from other texts such as the ''Xiaozi Zhuan'' (), ''Yiwen Leiju'', ''Imperial Readings of the Taiping Era'' and ''In Search of the Supernatural''. There were earlier precedents of ''The Twenty-four Filial Exemplars''. A Buddhist ''bianwen'' titled ''Ershisi Xiao Yazuowen'' (), which was among the manuscripts discovered in Dunhuang's Mogao Caves, is the oldest extant text rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the ChuHan contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) and the Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history, and it has influenced the identity of the Chinese civilization ever since. Modern China's majority ethnic group refers to themselves as the "Han people", the Sinitic language is known as "Han language", and the written Chinese is referred to as "Han characters". The emperor was at the pinnacle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li (Confucianism)
''Li'' () is a classical Chinese word which is commonly used in Chinese philosophy, particularly within Confucianism. ''Li'' does not encompass a definitive object but rather a somewhat abstract idea and, as such, is translated in a number of different ways. Wing-tsit Chan explains that ''li'' originally meant "a religious sacrifice, but has come to mean ceremony, ritual, decorum, rules of propriety, good form, good custom, etc., and has even been equated with natural law." In Chinese cosmology, human agency participates in the ordering of the universe by ''Li'' ('rites'). There are several Chinese definitions of a rite. One of the most common definitions is that it transforms the invisible to visible; through the performance of rites at appropriate occasions, humans make visible the underlying order. Performing the correct ritual focuses, links, orders, and moves the social, which is the human realm, in correspondence with the terrestrial and celestial realms to keep all three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanyue
The Shanyue (山越) were an ancient conglomeration of upland Yue hill tribes living in what is today the mountainous regions of Southern China and Northern Vietnam during the Han dynasty. Since the Southern part of China was not yet controlled by the Han Empire (the Han court only claimed ownership of the lands, but lacked the power to control them in reality), the Shanyue people would perform regular rebellions against Han citizens to gather living essentials. The tribe became powerful during the Eastern Han and the period of the end of the Eastern Han, the Shanyue were absorbed into Han Empire after the Sun family established a strong local government on Jiangdong. The Kingdom of Wu, founded by Sun Quan, launched numerous campaigns against the Shanyue, but to no avail because the tribesmen of Shanyue had lived in the hills for generations and knew the area well, and would go into hiding once they lost a battle. However, one of the Wu generals, Ling Tong, attempted a diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memorial To The Throne
A memorial to the throne () was an official communication to the Emperor of China. They were generally careful essays in Classical Chinese and their presentation was a formal affair directed by government officials. Submission of a memorial was a right theoretically available to everyone from the Crown Prince to a common farmer, but the court secretaries would read them aloud to the emperor and exercised considerable control over what was considered worthy of his time. They were used in imperial China as a means of regulating corrupt local officials who might otherwise have escaped oversight.Brook33 Han dynasty Under the Han dynasty, generally, the reception of memorials was the responsibility of the Imperial Secretary tasked with overseeing provincial administration. He was generally required to present any formal memorials, but could reject them for improper formatting.Wang (1949), 148–149. Masters of Writing under the Minister Steward then copied and processed these pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Wei
Wei ( Hanzi: 魏; pinyin: ''Wèi'' < : *''ŋjweiC'' < : *''ŋuiC'') (220–266), known as Cao Wei or Former Wei in historiography, was one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the period (220–280). With its capital initially located at , and thereafter |
Gongsun Yuan
Gongsun Yuan () (died September 238Cao Rui's biography in ''Sanguozhi'' indicated that Sima Yi laid siege to Xiangping on the ''bingyin'' day of the 8th month of the 2nd year of the ''Jing'chu'' era. However, there is no ''bingyin'' day in that month; the next ''bingyin'' day is in the 9th month of that year and corresponds to 3 Sep 238 in the Julian calendar. Volume 74 of ''Zizhi Tongjian'' placed the fall of Xiangping on the ''renwu'' day of the 8th month of that year. However, there is also no ''renwu'' day in that month; the next ''renwu'' day is also in the 9th month and corresponds to 19 Sep 238 in the Julian calendar.), courtesy name Wenyi, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He rebelled against Wei in 237 and declared himself "King of Yan" (). In 238, the Cao Wei general Sima Yi led forces to Liaodong and successfully conquered Yan. Life Gongsun Yuan was a son of Gongsun Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Resources
Human resources (HR) is the set of people who make up the workforce of an organization, business sector, industry, or economy. A narrower concept is human capital, the knowledge and skills which the individuals command. Similar terms include manpower, Labour (human activity), labor, personnel, associates or simply: people. The Human Resources department (HR department) of an organization performs human resource management, overseeing various aspects of employment, such as compliance with labor law and employment standards, job interview, interviewing and selection, performance management, administration of Employee benefits, organizing of employee files with the required documents for future reference, and some aspects of recruitment (also known as talent acquisition) and employee offboarding. They serve as the link between an organization's management and its employees. The duties include planning, recruitment and selection process, posting job ads, evaluating the performance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ji Yan (Three Kingdoms)
Ji Yan (died 224), courtesy name Zixiu, was an official of the state of Eastern Wu during the Three Kingdoms period of China. An impulsive and impetuous man, he thought highly of himself and liked to assume the moral high ground to criticise and disparage others. While serving in the selection bureau (the equivalent of a present-day human resources department), he came up with radical ideas to reform the bureaucracy by demoting or dismissing officials based on assessments of their moral character. His ideas proved to be highly unpopular as he incurred much resentment from his colleagues, who accused him of being unprofessional and biased. When his colleagues Lu Xun, Lu Mao and Zhu Ju advised him to change his offensive behaviour, he ignored their well-meaning advice. In 224, he committed suicide after he was removed from office on allegations of unprofessional conduct. Life Ji Yan was from Wu Commandery, which is around present-day Suzhou, Jiangsu. Through the recommendation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)