|
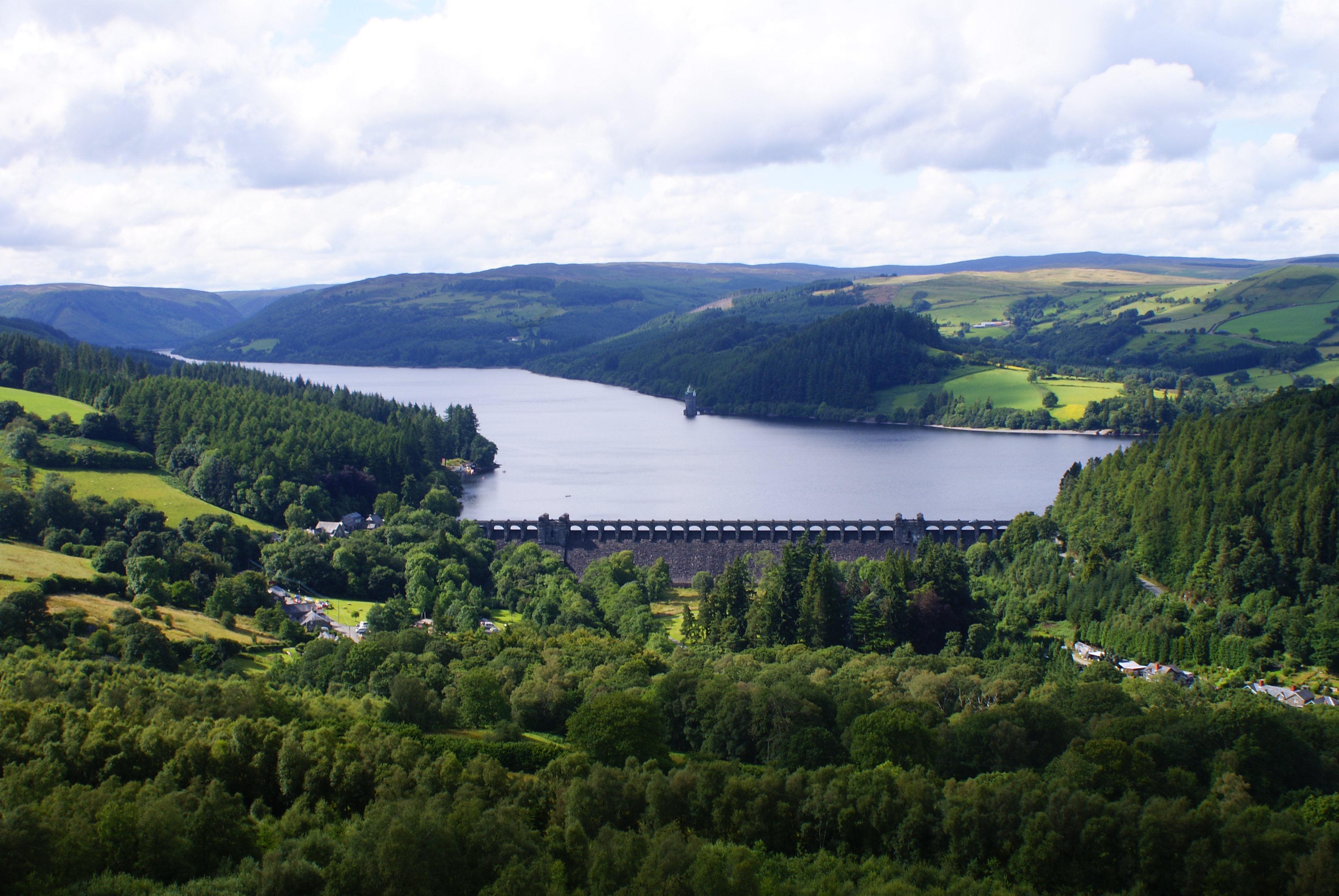
Lower Rivington Reservoir
Lower Rivington Reservoir is at the end of the Rivington chain of reservoirs in Lancashire, England, with Upper Rivington Reservoir to the north, and Rivington Water Treatment Works to the south. The Rivington chain primarily supplies 70,000 households in the Wigan area. The chain was built to supply Liverpool. The engineer for the Rivington reservoirs was Thomas Hawksley and construction for the Liverpool Corporation Waterworks took place between 1852 and 1857. The Lower Rivington reservoir has two dams - the Millstone Embankment, which is long and high, and the Horwich Embankment, which is long and high. Filter beds were constructed at the foot of the Horwich Embankment, The original sand filters were replaced by a new treatment plant from where a pipeline runs to the service reservoirs at Eccleston, St Helens. The River Douglas was diverted through a paved channel in a deep cutting into Lower Rivington. On the Rivington bank of the reservoir is a folly which is a repli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation. Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of water, interrupting a watercourse to form an embayment within it, through excavation, or building any number of retaining walls or levees. In other contexts, "reservoirs" may refer to storage spaces for various fluids; they may hold liquids or gasses, including hydrocarbons. ''Tank reservoirs'' store these in ground-level, elevated, or buried tanks. Tank reservoirs for water are also called cisterns. Most underground reservoirs are used to store liquids, principally either water or petroleum. Types Dammed valleys Dammed reservoirs are artificial lakes created and controlled by a dam A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivington
Rivington is a village and civil parish of the Borough of Chorley, Lancashire, England, occupying . It is about southeast of Chorley and about northwest of Bolton. Rivington is a rural area consisting primarily of agricultural grazing land, moorland, with hill summits including Rivington Pike and Winter Hill within the West Pennine Moors. The area has a thriving tourist industry centred around reservoirs created to serve Liverpool in the Victorian era and Lever Park created as a public park by William Lever at the turn of the 20th century, with two converted barns, a replica of Liverpool Castle and open countryside. Rivington and Blackrod High School is located here. Rivington and its village had a population of 109 at the 2011 Census. History Toponymy The name Rivington is made up of three elements: ''riv'' is from the Old English ''hrēof'' meaning rough or rugged; ''ing'' is a place name forming suffix that seems to have crept in over the years; the last is the Old En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reservoirs
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation. Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of water, interrupting a watercourse to form an embayment within it, through excavation, or building any number of retaining walls or levees. In other contexts, "reservoirs" may refer to storage spaces for various fluids; they may hold liquids or gasses, including hydrocarbons. ''Tank reservoirs'' store these in ground-level, elevated, or buried tanks. Tank reservoirs for water are also called cisterns. Most underground reservoirs are used to store liquids, principally either water or petroleum. Types Dammed valleys Dammed reservoirs are artificial lakes created and controlled by a dam constructed across a valley, and rely on the natural topography to provide most of the basin of the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly. The non-metropolitan county of Lancashire was created by the Local Government Act 1972. It is administered by Lancashire County Council, based in Preston, and twelve district councils. Although Lancaster is still considered the county town, Preston is the administrative centre of the non-metropolitan county. The ceremonial county has the same boundaries except that it also includes Blackpool and Blackburn with Darwen, which are unitary authorities. The historic county of Lancashire is larger and includes the cities of Manchester and Liverpool as well as the Furness and Cartmel peninsulas, but excludes Bowland area of the West Riding of Yorkshire transferred to the non-metropolitan county in 1974 History Before the county During Roman times the area was part of the Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Rivington Reservoir
Upper Rivington Reservoir is situated centrally in the Rivington chain of reservoirs, on the West Pennine Moors in Lancashire, England, between Rivington and Anglezarke. The engineer for the Rivington reservoirs was Thomas Hawksley and construction for Liverpool Corporation Waterworks took place between 1852 and 1857. The two dams of the Upper Rivington reservoir are the Horrobin Embankment that separates it from the lower reservoir and carries a road into the village from the west, and the long, high Yarrow Embankment. There is an island. A bridleway and residence, The Street are on the side of the reservoir. It is a popular walking destination, between Anglezarke Reservoir to the north, Lower Rivington Reservoir Lower Rivington Reservoir is at the end of the Rivington chain of reservoirs in Lancashire, England, with Upper Rivington Reservoir to the north, and Rivington Water Treatment Works to the south. The Rivington chain primarily supplies 70,000 hou ... to the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivington Water Treatment Works
Rivington Water Treatment Works is a water treatment plant in Rivington, Lancashire, England. It is located below the Lower Rivington Reservoir, the last in the Rivington chain of reservoirs. The first treatment works, a slow-sand filter plant on the site opened in 1860, supplying water to Liverpool. The present works was built in 1994, and in 2007 was the largest automated three-stage plant operated by United Utilities, the water is now disinfected by adding small amounts of chlorine. Most of its output supplies customers in the Wigan area. Raw water from the Rivington chain of reservoirs can be supplied to the Thirlmere Aqueduct The Thirlmere Aqueduct is a 95.9-mile-long (154.3-kilometre-long) pioneering section of water supply system in England, built by the Manchester Corporation Water Works between 1890 and 1925. Often incorrectly thought of as one of the longest tun ... via a pipeline downstream of the Lower Rivington Reservoir embankment and treated water via a pumping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool Corporation Waterworks
Liverpool Corporation Waterworks and its successors have provided a public water supply and sewerage and sewage treatment services to the city of Liverpool, England. In 1625 water was obtained from a single well and delivered by cart, but as the town grew, companies supplied water to homes through pipes. There were two main companies by the 1840s, but the water supply was intermittent, and there was general dissatisfaction with the service. Liverpool Corporation decided that such an important service should be provided by a public body, and sought to take over the water supply companies. A series of Acts of Parliament were obtained, the first being the Liverpool Sanatory Act 1846, which created three key posts, the Medical Officer of Health, the Inspector of Nuisances, and the Borough Engineer. The latter post was filled by James Newlands, a visionary man who defined the role of the Borough Engineer, to be copied by many other towns and cities. He set about creating large scale ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eccleston, St Helens
Eccleston is a civil parish in the Metropolitan Borough of St Helens, Merseyside, England. At the 2011 census, it had a population of 10,433. Within the boundaries of the historic county of Lancashire, the early history of Eccleston is marked by its status as a township, an area much larger than the modern civil parish, extending into what is now St. Helens. Part of the township was united with Parr, Sutton and part of Windle to form the Municipal Borough of St Helens in 1868. Eccleston is one of seven civil parishes in the Borough of St Helens and one of the largest, covering the neighbourhoods of Eccleston Park, Gillars Green, Eccleston Mere, Eccleston village and an area around the A580 East Lancashire Road. Origins of the name Eccleston appears to derive its name from either the Latin ''ecclesia'' or the Welsh ''eglwys'', both meaning "church", suggesting a common link to a place of worship (although none is known in that township until the 19th century) and a possible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Borough Of St Helens
The Metropolitan Borough of St Helens is a local government district with borough status in Merseyside, North West England. The borough is named after its largest settlement, St Helens but also includes neighbouring towns and villages such as Earlestown, Rainhill, Eccleston, Clock Face, Haydock, Billinge, Rainford and Newton-le-Willows. The Metropolitan Borough Council is made up of 48 councillors, three representing each of the 16 wards. History The Metropolitan Borough was formed on 1 April 1974 as a merger of the former County Borough of St Helens, along with the urban districts of Haydock, Newton-le-Willows and Rainford, and parts of Billinge-and-Winstanley and Ashton-in-Makerfield urban districts, along with part of Whiston Rural District, all from the administrative county of Lancashire. Between 1974 and 1986 (when it was abolished), the borough council shared functions with Merseyside County Council. After abolition, the functions of this body were in part devolved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Douglas, Lancashire
The River Douglas, also known as the River Asland or Astland, flows through parts of Lancashire and Greater Manchester in North West England. It is a tributary of the River Ribble and has several tributaries, the major ones being the River Tawd and the River Yarrow. In 1720 an act of Parliament was passed allowing Thomas Steers and William Squire to make the Douglas navigable to small ships between Wigan and its mouth. Amid financial irregularities, the Douglas Navigation was not completed until 1742, and by 1783, it had been superseded by the Leeds and Liverpool Canal. It reverted to being a river, although the remains of several locks can still be seen between Parbold and Gathurst. The Rufford Branch of the canal joins the river at Tarleton. The river rises on Winter Hill on the West Pennine Moors, and flows for through several towns and onto the Ribble estuary past Tarleton, the last or so being tidal. In 1892 the Douglas was diverted in Wigan to allow the construction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folly
In architecture, a folly is a building constructed primarily for decoration, but suggesting through its appearance some other purpose, or of such extravagant appearance that it transcends the range of usual garden buildings. Eighteenth-century English landscape gardening and French landscape gardening often featured mock Roman temples, symbolising classical virtues. Other 18th-century garden follies represented Chinese temples, Egyptian pyramids, ruined medieval castles or abbeys, or Tatar tents, to represent different continents or historical eras. Sometimes they represented rustic villages, mills, and cottages to symbolise rural virtues. Many follies, particularly during times of famine, such as the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine in Ireland, were built as a form of poor relief, to provide employment for peasants and unemployed artisans. In English, the term began as "a popular name for any costly structure considered to have shown wikt:folly#Noun, folly in the builde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
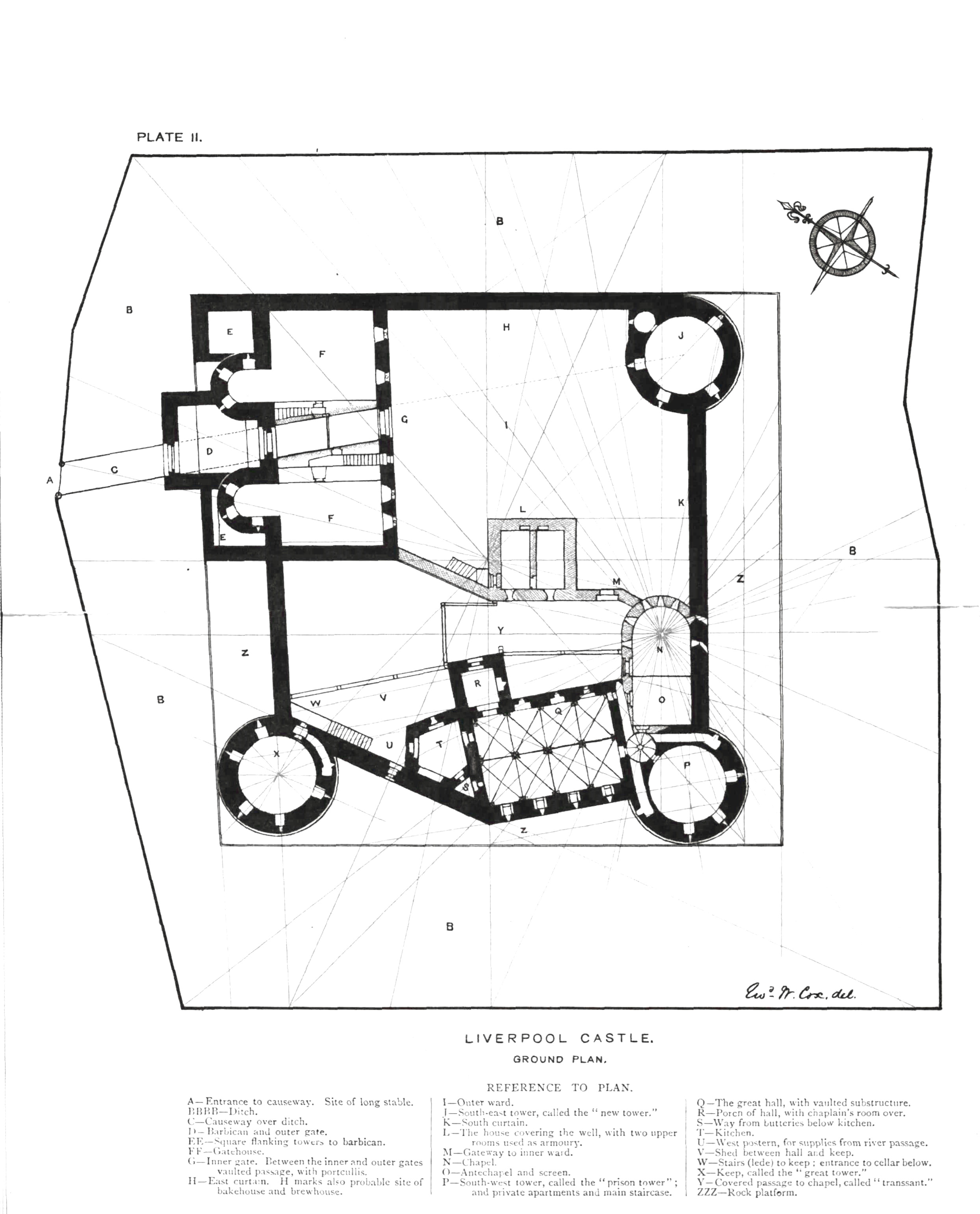
Liverpool Castle
Liverpool Castle was a castle in Liverpool, England, that stood from the early 13th century to the early 18th century (1237–1726). Construction The castle was probably erected in the 1230s, between 1232 and 1235, under the orders of William de Ferrers, 4th Earl of Derby. No records of the castle construction survive, except the licence to fortify de Ferrers received in 1235. Nearby in West Derby, there had long been a castle, which was taken by the Ferrerses in 1232, but by 1296 it lay in ruins. The castle in Liverpool was built to protect King John's new port, and was sited at the top of modern-day Lord Street, the highest point in the city which overlooks the Pool. This corresponds to present day Derby Square ( Queen Victoria Monument), near the city centre. Description The castle was built on top of a plateau, which had been specially constructed, and a moat measuring 20 yards (18 m) was cut out of solid rock. The main building of the castle consisted of the gatehouse flank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |