|
Louise Elisabeth Of Württemberg-Oels
Louise Elisabeth of Württemberg-Oels (4 March 1673 – 28 April 1736), was a Duchess of Württemberg-Oels by birth and by marriage Duchess of Saxe-Merseburg-Lauchstädt. In 1709, she revived the Ducal Württemberg-Oels Order of the Skull as a chivalric order for ladies. Early life and family Born in Bernstadt (now called Bierutów), the capital of the Duchy of Bernstadt in Silesia, she was the eldest of the seven children of Duke Christian Ulrich I of Württemberg-Oels and his first wife, Anna Elisabeth, a daughter of Prince Christian II of Anhalt-Bernburg and Eleonore Sophie of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg. Her mother died after complications in her last childbirth on 3 September 1680 and her father remarried three more times: in Doberlug on 27 October 1683 to Sibylle Maria, a daughter of Duke Christian I of Saxe-Merseburg; in Hamburg on 4 February 1695 to Sophie Wilhelmine, a daughter of Prince Enno Louis ''Cirksena'' of East Frisia and in Güstrow on 6 December 1700 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Saxon Consorts
This is a list of the Duchesses, Electresses and Queens of Saxony; the consorts of the Duke of Saxony and its successor states; including the Electorate of Saxony, the Kingdom of Saxony, the House of Ascania, Albertine, and the Ernestine duchies, Ernestine Saxony. Ducal Saxony Duchess of Duchy of Saxony, Saxony * ? – 800: Geva of Westfold, wife of Widukind, daughter of the Danish king Goimo I and sister of the Danish kings Ragnar Lodbrok, Ragnar and Siegfried, d. a. 800 Ascanian Ducal Saxony Duchess of Saxe-Lauenburg Duchess of Saxe-Wittenberg Saxe-Meißen, incorporating Saxe-Wittenberg in 1547 Saxe-Thuringia, including Saxe-Wittenberg until 1547 Electorate of Saxony Electress of Saxony :''See: Electress#Electresses of Saxony, Electresses of Saxony.'' Albertine Ducal Saxony Duchess of Saxe-Weissenfels Duchess of Saxe-Merseburg Duchess of Saxe-Zeitz Ernestine Saxony Duchess of Saxe-Weimar Duchess of Saxe-Coburg-Eisenach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustav Adolph, Duke Of Mecklenburg-Güstrow
Gustav Adolph, Duke of Mecklenburg Güstrow(26 February 1633 – 6 October 1695) was the last ruler of Mecklenburg-Güstrow from 1636 until his death and last Lutheran Administrator of the Prince-Bishopric of Ratzeburg from 1636 to 1648.Jonathan Strom: ''Orthodoxy and reform: the clergy in seventeenth century in Rostoc '', Mohr Siebeck, Tübingen 1999, Life Gustav Adolph was born at the ducal residence in Güstrow, the son of Duke John Albert II and his third wife Eleonore Marie (1600–1657), daughter of Prince Christian I of Anhalt-Bernburg. As Gustav Adolph was a minor when his father died in 1636, his uncle Duke Adolph Frederick I of Mecklenburg-Schwerin at first became regent at Güstrow. This was fiercely opposed by Gustav Adolph's mother. In 1654 he came of age and married Magdalene Sibylle, a daughter of Duke Frederick III of Holstein-Gottorp. Their marriage produced eleven children: * Johann, Hereditary Prince of Mecklenburg-Güstrow (2 December 1655 – 6 Feb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including the Iberian Peninsula it continued, together with new styles, until the first decade of the 19th century. It followed Renaissance art and Mannerism and preceded the Rococo (in the past often referred to as "late Baroque") and Neoclassical styles. It was encouraged by the Catholic Church as a means to counter the simplicity and austerity of Protestant architecture, art, and music, though Lutheran Baroque art developed in parts of Europe as well. The Baroque style used contrast, movement, exuberant detail, deep colour, grandeur, and surprise to achieve a sense of awe. The style began at the start of the 17th century in Rome, then spread rapidly to France, northern Italy, Spain, and Portugal, then to Austria, southern Germany, and Russia. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christmas Cantata
A Christmas cantata or Nativity cantata is a cantata, music for voice or voices in several movements, for Christmas. The importance of the feast inspired many composers to write cantatas for the occasion, some designed to be performed in church services, others for concert or secular celebration. The Christmas story, telling of music of the angels and suggesting music of the shepherds and cradle song, invited musical treatment. The term is called in German, and in French. Christmas cantatas have been written on texts in several other languages, such as Czech, Italian, Romanian, and Spanish. Christmas cantata can also mean the performance of the music. Many choirs have a tradition of an annual Christmas cantata. Theme Different from Christmas oratorios, which present the Christmas story, Christmas cantatas deal with aspects of it. Bach's ''Christmas Oratorio'', written for performance in Leipzig in 1734/1735 touches many of these themes. It consists of six parts, each part is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian August Jacobi
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χριστός), a translation of the Biblical Hebrew term ''mashiach'' (מָשִׁיחַ) (usually rendered as ''messiah'' in English). While there are diverse interpretations of Christianity which sometimes conflict, they are united in believing that Jesus has a unique significance. The term ''Christian'' used as an adjective is descriptive of anything associated with Christianity or Christian churches, or in a proverbial sense "all that is noble, and good, and Christ-like." It does not have a meaning of 'of Christ' or 'related or pertaining to Christ'. According to a 2011 Pew Research Center survey, there were 2.2 billion Christians around the world in 2010, up from about 600 million in 1910. Today, about 37% of all Christians live in the Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hofmeister (office)
In medieval Europe, within the Holy Roman Empire, a Hofmeister (literally "court-master" or "house-master" in German; la, Magister, Praefectus curiae; da, hofmester, hovmester, sv, hovmästare, cs, hofmistr, pl, ochmistrz; french: précepteur; it, precettore / istitutore) was an official who acted as an aide to royalty or to a senior nobleman or cleric. Later it became a term for a schoolmaster who looked after the welfare of students in addition to their education. Roles In the service of royalty and other magnates A ''Hofmeister'' was one of the highest offices in the courts of German emperors and kings, and also existed in other princely courts and the courts of smaller dynasties. His official role was initially in the direction of the royal household and serving privately on the monarch's person. In the 15th century it became a government office and in the German princely courts finally became equivalent to a privy counsellor or cabinet minister, and sometimes as someth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bad Lauchstädt
(until 1925 ''Lauchstädt''), officially Goethestadt Bad Lauchstädt, is a town in the district Saalekreis, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany, 13 km southwest of Halle. Population 8,781 (2020). Lauchstädt was a popular watering-place in the 18th century, the dukes of Saxe-Merseburg often making it their summer residence. From 1789 to 1811 the Weimar court theatrical company gave performances here of the plays of Friedrich Schiller and Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, an attraction which greatly contributed to the well-being of the town. Further reading noted there: * Maak, ''Das Goethetheater in Lauchstädt'' (Lauchstädt, 1905); * Nasemann, ''Bad Lauchstädt'' (Halle, 1885). During the 19th century, its industries included malting, vinegar-making and brewing. In January 2008, Bad Lauchstädt incorporated the former municipalities Schafstädt, Delitz am Berge and Klobikau. On 1 January 2010 Milzau was also incorporated, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
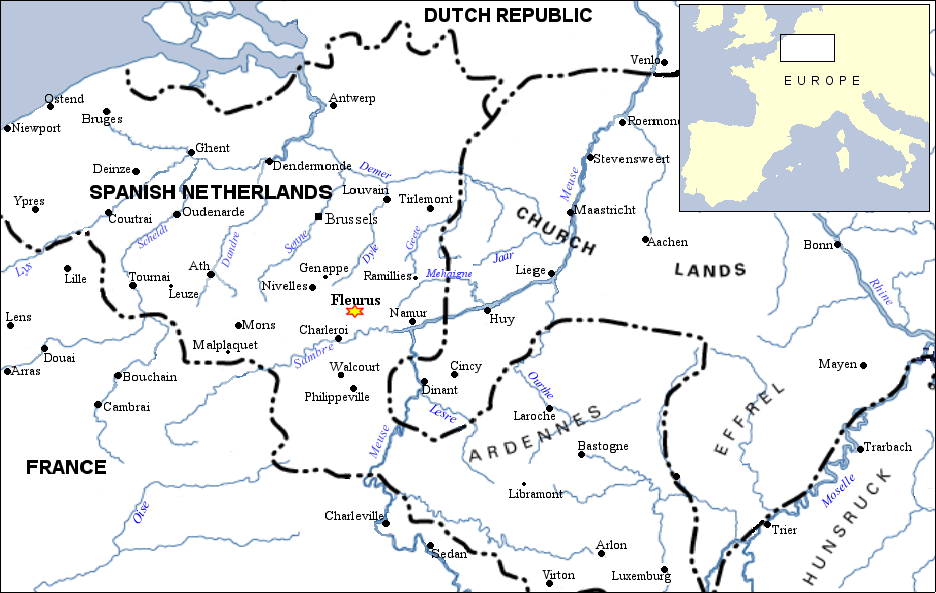
Fleurus
Fleurus (; wa, Fleuru) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It has been the site of four major battles. The municipality consists of the following districts: Brye, Heppignies, Fleurus, Lambusart, Saint-Amand, Wagnelée, Wanfercée-Baulet (wa: ''Wanfercêye-Bålet''), and Wangenies. History Traces of agriculture dating back to the Neolithic Age were found in area known as Fleurjoux and Neuve Baraque. Later the site saw the construction of the Chaussée Brunehaut, a road network of uncertain origin, perhaps attributable to the Roman Empire. In October 1155, Henry IV of Luxembourg, also Count of Namur enfranchised the municipality which became the city of Fleurus. Henry IV had a castle in Heppignies. The town has given its name to three battles fought in the area : *The Battle of Fleurus (1622) in the Thirty Years' War. *The Battle of Fleurus (1690) in the Nine Years' War. *The Battle of Fleurus (1794) in the French Revolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Fleurus (1690)
The Battle of Fleurus, fought on 1 July 1690, was a major engagement of the Nine Years' War. In a bold and masterful envelopment, Marshal Luxembourg, commanding a French army of some 35,000 men, inflicted a severe defeat on Prince Waldeck’s Allied force of approximately 38,000 men. Waldeck lost 50% of his army and Luxembourg moved ahead to control Flanders. Although the battle was a brilliant tactical feat and the French War Minister, Louvois, wished to press ahead and secure further success, King Louis overruled him and ordered Luxembourg to reinforce the Dauphin’s army on the Rhine and forgo any major siege. The Allies, meanwhile, withdrew to Brussels to recover and rebuild their forces. Background In 1690 the main theatre of the Nine Years' War moved to the Spanish Netherlands. Command of French forces now passed to the talented Marshal Luxembourg (a position he would keep until his death in 1695), superseding Marshal Humières who had suffered defeat at the Battle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merseburg
Merseburg () is a town in central Germany in southern Saxony-Anhalt, situated on the river Saale, and approximately 14 km south of Halle (Saale) and 30 km west of Leipzig. It is the capital of the Saalekreis district. It had a diocese founded by Archbishop Adalbert of Magdeburg. The University of Merseburg is located within the town. Merseburg has around 33,000 inhabitants. Names * cs, Merseburk, Meziboř * french: Mersebourg * german: Merseburg * la, Merseburga * pl, Międzybórz * wen, Mjezybor Geography The town Merseburg consists of Merseburg proper and the following four ''Ortschaften'' or municipal divisions:Hauptsatzung der Stadt Merseburg § 15, April 2019. * |
Schloss Bernstadt Sammlung Duncker
''Schloss'' (; pl. ''Schlösser''), formerly written ''Schloß'', is the German term for a building similar to a château, palace, or manor house. Related terms appear in several Germanic languages. In the Scandinavian languages, the cognate word ''slot''/''slott'' is normally used for what in English could be either a palace or a castle (instead of words in rarer use such as ''palats''/''palæ'', ''kastell'', or ''borg''). In Dutch, the word ''slot'' is considered to be more archaic. Nowadays, one commonly uses ''paleis'' or ''kasteel''. But in English, the term does not appear, for instance, in the United Kingdom, this type of structure would be known as a stately home or country house. Most ''Schlösser'' were built after the Middle Ages as residences for the nobility, not as true fortresses, although originally, they often were fortified. The usual German term for a true castle is ''burg'', that for a fortress is ''festung'', and — the slightly more archaic term — ''v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auguste Louise Of Württemberg-Oels
Auguste Louise of Württemberg-Oels (21 January 1698 - 4 January 1739), was a Duchess of Württemberg-Oels by birth and by marriage Duchess of Saxe-Weissenfels-Barby. Born in Bernstadt (now called Bierutów), the capital of the Duchy of Bernstadt in Silesia, she was the only child of Duke Christian Ulrich I of Württemberg-Oels and his third wife, Sophie Wilhelmine, a daughter of Enno Louis, Prince of East Frisia. Her mother died fourteen days after her birth (4 February 1698), probably from childbirth complications. From her father's two previous marriages, Auguste Louise had fourteen older half-siblings, of whom only four survive adulthood: Louise Elisabeth (by marriage Duchess of Saxe-Merseburg-Lauchstädt), Sophie Angelika (by marriage Duchess of Saxe-Zeitz-Pegau-Neustadt) -both born from Christian Ulrich I's first marriage with Anna Elisabeth of Anhalt-Bernburg-, Charles Frederick II, Duke of Württemberg-Oels and Christian Ulrich II, Duke of Württemberg-Wilhelminenort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |