|
Lotegorisch
Lotegorisch or ''Lottegorisch'' or ''Lekoudesch'' (older own description: ''lochne kodesch'', from the he, laschon = "tongue, language", and ''kodesch'' = "holy") is a trading language and Palatine variant of the secret language, Rotwelsch, spoken in the Leiningerland (especially in Carlsberg), where in the late 18th century many vagrants, including many Jews, were settled and where many of them worked as cattle traders, itinerant craftsmen, and peddler A peddler, in British English pedlar, also known as a chapman, packman, cheapjack, hawker, higler, huckster, (coster)monger, colporteur or solicitor, is a door-to-door and/or travelling vendor of goods. In England, the term was mostly used f ...s.Meißner (1999) References Literature *Anton Meißner: ''Die pfälzische Handelssprache Lotegorisch. Wörterbuch mit Leseproben''. Meißner Verlag, Wattenheim, 1999 (printed as a manuscript) External links www.lotegorisch.de (archived version at archive.org @ 2019-01-22 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotwelsch
Rotwelsch (, ''" beggar's foreign (language)"'') or Gaunersprache ( ''" crook's language"'') also Kochemer Loshn (from Yiddish "", "tongue of the wise") is a secret language, a cant or thieves' argot, spoken by groups (primarily marginalized groups) in Germany, Switzerland, Austria, and Bohemia. The language is based on a mix of Yiddish, Hebrew, Romani, Latin, and Czech with a German substrate. Name Rotwelsch was first named by Martin Luther in his preface of '' Liber Vagatorum'' in the 16th century. ''Rot'' means "beggar" while ''welsch'' means "incomprehensible": thus, ''rotwelsch'' signifies the incomprehensible cant of beggars. History was formerly common among travelling craftspeople and vagrants. The language is built on a strong substratum of German, but contains numerous words from other languages, notably from various German dialects, and other Germanic languages like Yiddish, as well as from Romany languages, notably Sintitikes. has also played a great role in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Dialects
Palatine German (endonym: ; Standard German: ), also known as Palatine Dutch, is a Rhenish Franconian language and is spoken in the Upper Rhine Valley, roughly in the area between Zweibrücken, Kaiserslautern, Alzey, Worms, Ludwigshafen am Rhein, Mannheim, Odenwald, Heidelberg, Speyer, Landau, Wörth am Rhein and the border to Alsace and Lorraine, in France, but also beyond. The Pennsylvania Dutch language, also called Pennsylvania German, is descended primarily from the Palatine German that was spoken by Palatine refugees who emigrated to North America from the 17th to the 19th centuries and maintained their native language. Danube Swabians in Croatia and Serbia also use many elements of Palatinate German. spoken in the western Palatinate () is normally distinguished from the spoken in the eastern Palatinate (). The English term ''Palatine'' refers to the Palatinate region, where the language is spoken. Pronunciation and grammar vary from region to region and even from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
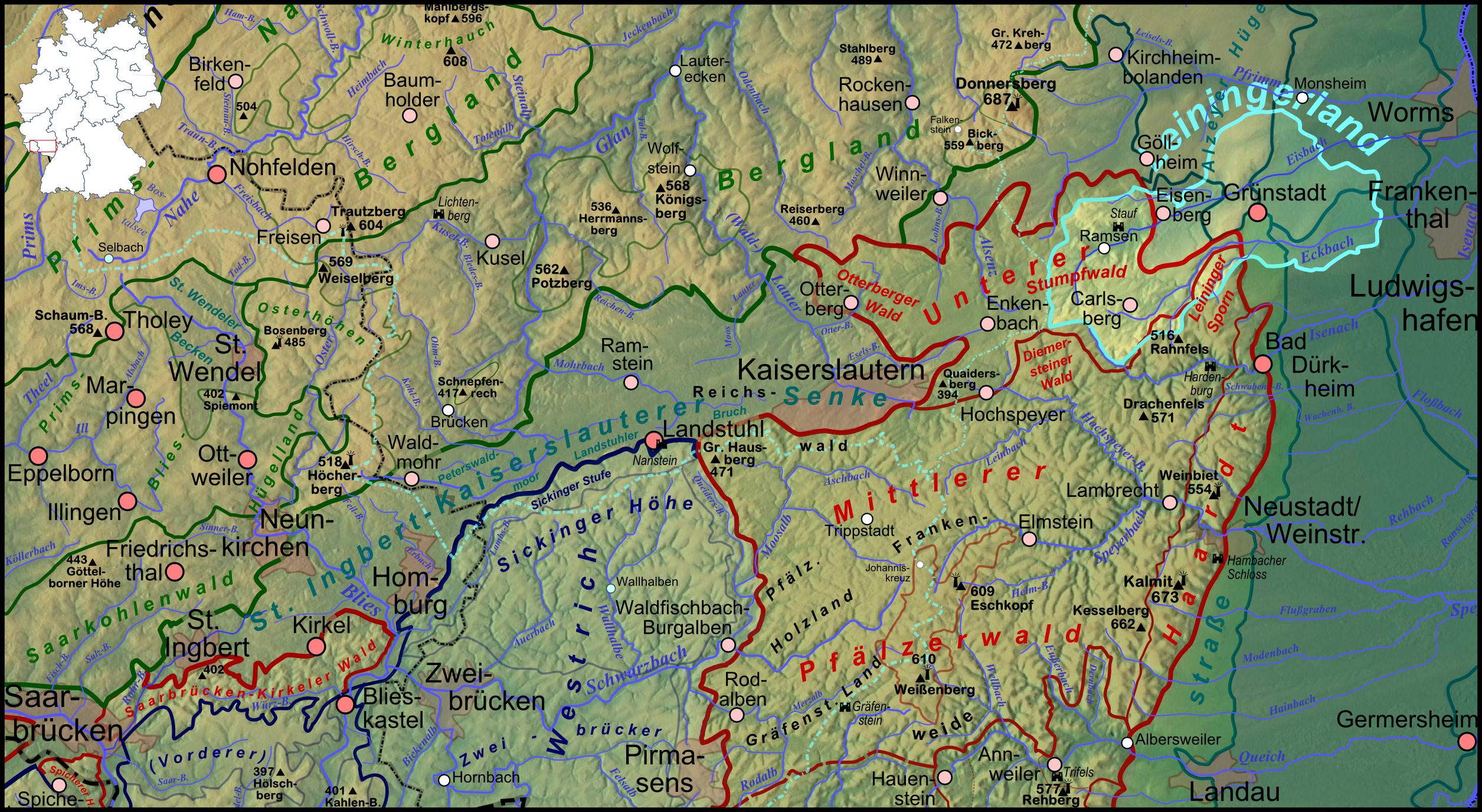
Leiningerland
The Leiningerland is an historic landscape in the Palatinate region in the German federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate. It is named after an aristocratic family that used to be the most important in the region, the House of Leiningen. Geography The Leiningerland lies in northeast Palatinate, mostly in the county of Bad Dürkheim. Its area coincides with large parts of the collective municipalities of Hettenleidelheim and Grünstadt-Land as well as the town of Grünstadt. Also a part of the historic Leiningerland is the region around the town of Eisenberg, which is in the county of Donnersbergkreis today. Its total area is just under 200 km2. The region does not have a uniform topography, but shares in three geological features: the Central Uplands, the Rhine Rift Valley and the Rhine Plain. the Leiningerland extends from the northeastern foothills of the Palatine Forest in the west across the northern part of the German Wine Road near Grünstadt to Dirmstein in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlsberg, Germany
Carlsberg () is an ''Ortsgemeinde'' – a municipality belonging to a ''Verbandsgemeinde'', a kind of collective municipality – in the Bad Dürkheim district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Geography Location The municipality lies at the north edge of the Palatinate Forest between the Haardt range in the south and the Autobahn A 6 in the north in the ''Leiningerland'' at an elevation of 285 m above sea level. Carlsberg belongs to the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' of Leiningerland, whose seat is in Grünstadt. The outlying centre of Hertlingshausen lies in the northern Palatinate Forest and is crossed by the river Eckbach, which rises in the part of the municipal area known as ''Kleinfrankreich'' (“Little France”). Since Carlsberg is a scattered settlement, it is not possible to say where Hertlingshausen ends and the main centre begins. Constituent communities Carlsberg's ''Ortsteile'' are Carlsberg and Hertlingshausen. History In 1754, Carlsberg, originall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagrancy (people)
Vagrancy is the condition of homelessness without regular employment or income. Vagrants (also known as bums, vagabonds, rogues, tramps or drifters) usually live in poverty and support themselves by begging, waste picker, scavenging, petty theft, temporary work, or welfare, social security (where available). Historically, vagrancy in Western societies was associated with petty crime, begging and lawlessness, and punishable by law with forced labor, military service, imprisonment, or confinement to dedicated labor houses. Both ''vagrant'' and ''vagabond'' ultimately derive from the Latin word ''Wikt:vagari, vagari'', meaning "to wander". The term ''vagabond'' is derived from Latin ''vagabundus''. In Middle English, ''vagabond'' originally denoted a person without a home or employment. Historical views Vagrants have been historically characterised as outsiders in settled, ordered communities: embodiments of Other (philosophy), otherness, objects of scorn or mistrust, or worthy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peddler
A peddler, in British English pedlar, also known as a chapman, packman, cheapjack, hawker, higler, huckster, (coster)monger, colporteur or solicitor, is a door-to-door and/or travelling vendor of goods. In England, the term was mostly used for travellers hawking goods in the countryside to small towns and villages. In London, more specific terms were used, such as costermonger. From antiquity, peddlers filled the gaps in the formal market economy by providing consumers with the convenience of door-to-door service. They operated alongside town markets and fairs where they often purchased surplus stocks which were subsequently resold to consumers. Peddlers were able to distribute goods to the more geographically-isolated communities such as those who lived in mountainous regions of Europe. They also called on consumers who, for whatever reason, found it difficult to attend town markets. Thus, peddlers played an important role in linking these consumers and regions to wider trade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Dialects
German dialects are the various traditional local varieties of the German language. Though varied by region, those of the southern half of Germany beneath the Benrath line are dominated by the geographical spread of the High German consonant shift, and the dialect continuum that connects German to the neighboring varieties of Low Franconian (Dutch) and Frisian. The varieties of German are conventionally grouped into Upper German, Central German and Low German; Upper and Central German form the High German subgroup. Standard German is a standardized form of High German, developed in the early modern period based on a combination of Central German and Upper German varieties. Etymology and nomenclature Traditionally, all of the major dialect groupings of German dialects are typically named after so-called " stem duchies" or "tribal duchies" (German: ''Stammesherzogtümer'') by early German linguists, among whom the Brothers Grimm were especially influential. These triba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Palatinate
The Palatinate (german: Pfalz; Palatine German: ''Palz'') is a region of Germany. In the Middle Ages it was known as the Rhenish Palatinate (''Rheinpfalz'') and Lower Palatinate (''Unterpfalz''), which strictly speaking designated only the western part of the Electorate of the Palatinate (''Kurfürstentum Pfalz''), as opposed to the Upper Palatinate (''Oberpfalz''). It occupies roughly the southernmost quarter of the German federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate (''Rheinland-Pfalz''), covering an area of with about 1.4 million inhabitants. Its residents are known as Palatines (''Pfälzer''). Geography The Palatinate borders Saarland in the west, historically also comprising the state's Saarpfalz District. In the northwest, the Hunsrück mountain range forms the border with the Rhineland region. The eastern border with Hesse and the Baden region runs along the Upper Rhine river, while the left bank, with Mainz and Worms as well as the Selz basin around Alzey, belong to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |