|
Loricosaurus
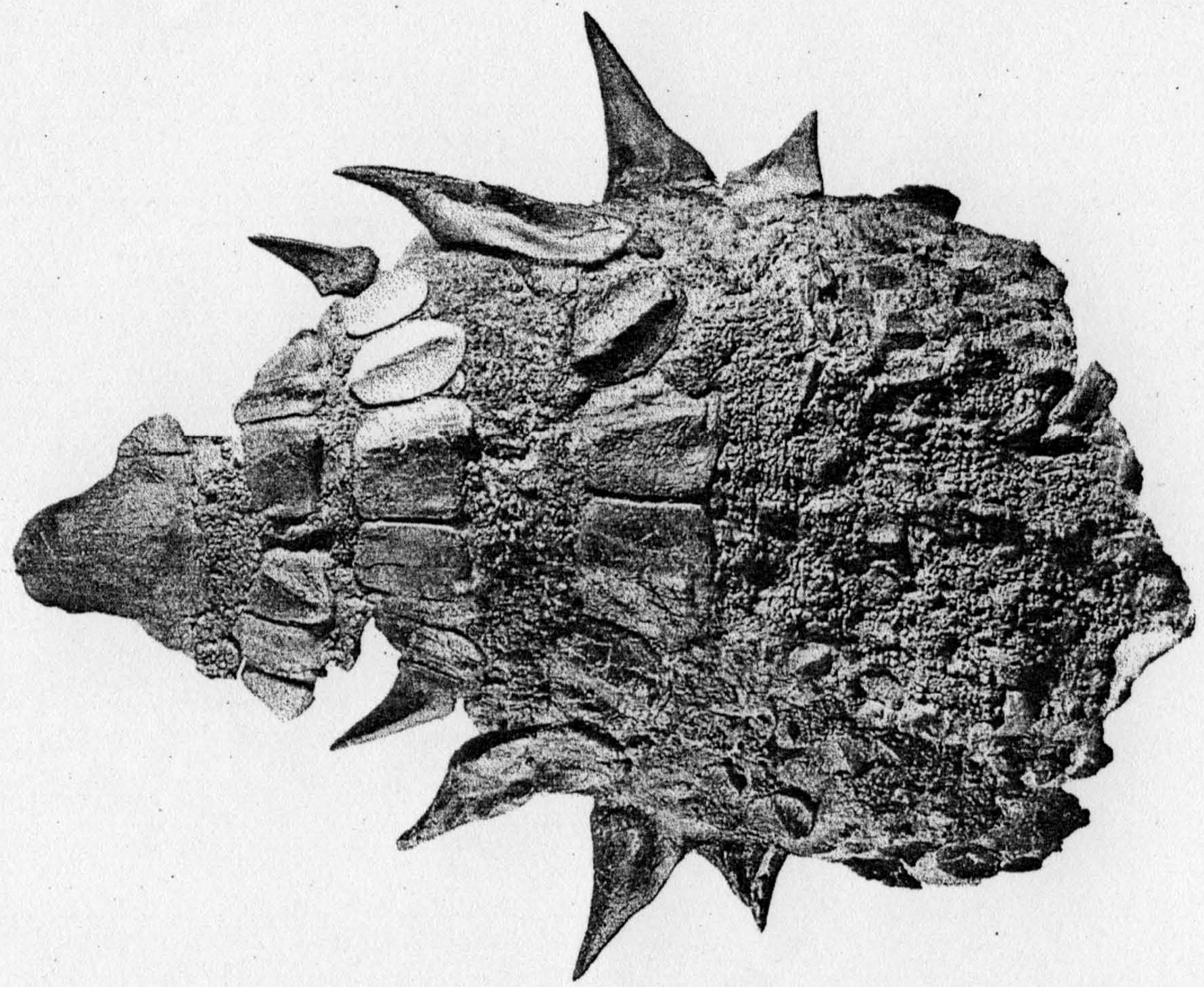
''Loricosaurus'' (meaning " armour lizard") is a genus of sauropod represented by a single species. It is a titanosaurian that lived near the end of the Late Cretaceous period, approximately 71 million years ago in the early Maastrichtian. Found in the province of Neuquen, Argentina in the Allen Formation. Due to the presence of armour, at first it was thought that it was an ankylosaur, but today it is considered to be the armour of a titanosaur. Armour The armour of ''Loricosaurus'' has caused some controversy. When Huene first described it, he considered it to be from an ankylosaur. Later, it was discovered to not belong to ankylosaurs, but to belong to titanosaurs.Holtz, Thomas R Jr. (2011) ''Dinosaurs: The Most Complete,Up-to-date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers Of All Ages, Winter 2010 Appendix./ref> Now it is considered to possibly belong to ''Neuquensaurus'' or ''Saltasaurus''. Species In 1929 von Huene described ''Loricosaurus'' based on some armour osteoderms found i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saltasaurus
''Saltasaurus'' (which means "lizard from Salta") is a genus of saltasaurid dinosaur of the Late Cretaceous period of Argentina. Small among sauropods, though still heavy by the standards of modern creatures, ''Saltasaurus'' was characterized by a short neck and stubby limbs. It was the first genus of sauropod known to possess armour of bony plates embedded in its skin. Such small bony plates, called osteoderms, have since been found on other titanosaurians. Discovery The fossils of ''Saltasaurus'' were excavated by José Bonaparte, Martín Vince and Juan C. Leal between 1975 and 1977 at the Estancia "El Brete". The find was in 1977 reported in the scientific literature. ''Saltasaurus'' was named and described by Bonaparte and Jaime E. Powell in 1980. The type species is ''Saltasaurus loricatus''. Its generic name is derived from Salta Province, the region of north-west Argentina where the first fossils were recovered. The specific name means "protected by small armoured plat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuquensaurus
''Neuquensaurus'' (meaning "Neuquén lizard") is a genus of saltasaurid sauropod dinosaur that lived in the Late Cretaceous, about 80 million years ago in Argentina and Uruguay in South America. Its fossils were recovered from outcrops of the Anacleto Formation around Cinco Saltos, near the Neuquén river from which its name is derived. History In 1893, Richard Lydekker named ''Titanosaurus australis'', based on a series of caudal vertebrae and limb elements. The remains had been found by Santiago Roth and F. Romero in the Neuquén Province of Argentina at the Neuquén River, and were by Lydekker assigned to a single individual. Six caudal vertebrae, with the inventory numbers MLP Ly 1-6-V-28-1, were the holotype of the species. They had probably been found in a layer of the Anacleto Formation. Some elements that had been referred to ''Titanosaurus australis'' were reassigned to '' Laplatasaurus araukanicus'' by Friedrich von Huene in 1929. The same year, von Huene named a ''Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1929 In Paleontology
Plants Ferns and fern allies Conifers Flowering plants Arthropods Crustaceans Insects Archosauromorphs * ''Barosaurus'' gastroliths documented.Janensch, W. (1929). Sanders, Manley, and Carpenter (2001), "Table 12.1" page 167. Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Synapsids Non-mammalian References {{portal, Paleontology * Janensch, W. (1929). Magensteine bei Sauropoden der Tendaguru-Schichten. Palaeontographica (Suppl. 7) 2:135-144. * Sanders F, Manley K, Carpenter K. Gastroliths from the Lower Cretaceous sauropod Cedarosaurus weiskopfae. In: Tanke D.H, Carpenter K, editors. Mesozoic vertebrate life: new research inspired by the paleontology of Philip J. Currie. Indiana University Press; Bloomington, IN: 2001. pp. 166–180. 1920s in paleontology Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosaur
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the order Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs. They are known to have first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, and persisted until the end of the Cretaceous Period. The two main families of Ankylosaurs, Nodosauridae and Ankylosauridae are primarily known from the Northern Hemisphere, but the more basal Parankylosauria are known from southern Gondwana during the Cretaceous. Ankylosauria was first named by Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1923.Osborn, H. F. (1923). "Two Lower Cretaceous dinosaurs of Mongolia." ''American Museum Novitates'', 95: 1–1/ref> In the Linnaean classification system, the group is usually considered either a suborder or an infraorder. It is contained within the group Thyreophora, which also includes the stegosaurs, armored dinosaurs known for their combination of plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of Argentina
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous Argentina
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous Dinosaurs Of South America
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) * Tardiness * Tardiness (scheduling) In scheduling, tardiness is a measure of a delay in exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saltasaurids
Saltasauridae (named after the Salta region of Argentina where they were first found) is a family of armored herbivorous sauropods from the Upper Cretaceous. They are known from fossils found in South America, Asia, North America, and Europe. They are characterized by their vertebrae and feet, which are similar to those of ''Saltasaurus'', the first of the group to be discovered and the source of the name. The last and largest of the group and only one found in North America, ''Alamosaurus'', was in length and one of the last sauropods to go extinct. Most of the saltasaurids were smaller, around in length, and one, ''Rocasaurus'', was only long. Like all sauropods, the saltasaurids were quadrupeds, their necks and tails were held almost parallel to the ground, and their small heads had only tiny, peg-like teeth. They were herbivorous, stripping leaves off of plants and digesting them in their enormous guts. Although large animals, they were smaller than other sauropods of their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (taxonomy)
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoderms
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct amphibians), various groups of dinosaurs (most notably ankylosaurs and stegosaurians), phytosaurs, aetosaurs, placodonts, and hupehsuchians (marine reptiles with possible ichthyosaur affinities). Osteoderms are uncommon in mammals, although they have occurred in many xenarthrans ( armadillos and the extinct glyptodonts and mylodontid and scelidotheriid ground sloths). The heavy, bony osteoderms have evolved independently in many different lineages. The armadillo osteoderm is believed to develop in subcutaneous dermal tissues. These varied structures should be thought of as anatomical analogues, not homologues, and do not necessarily indicate monophyly. The structures are however derived from scutes, common to all classes of amnio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_(2).jpg)
