|
Loose Coupling
In computing and systems design, a loosely coupled system is one # in which components are weakly associated (have breakable relationships) with each other, and thus changes in one component least affect existence or performance of another component. # in which each of its components has, or makes use of, little or no knowledge of the definitions of other separate components. Subareas include the coupling of classes, interfaces, data, and services. Loose coupling is the opposite of tight coupling. Advantages and disadvantages Components in a loosely coupled system can be replaced with alternative implementations that provide the same services. Components in a loosely coupled system are less constrained to the same platform, language, operating system, or build environment. If systems are decoupled in time, it is difficult to also provide transactional integrity; additional coordination protocols are required. Data replication across different systems provides loose coupling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and software. Computing has scientific, engineering, mathematical, technological, and social aspects. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, computer science, cybersecurity, data science, information systems, information technology, and software engineering. The term ''computing'' is also synonymous with counting and calculation, calculating. In earlier times, it was used in reference to the action performed by Mechanical computer, mechanical computing machines, and before that, to Computer (occupation), human computers. History The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper (or for chalk and slate) with or without the aid of tables. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dynamic Binding (computing)
In computing, late binding or dynamic linkage—though not an identical process to dynamically linking imported code libraries—is a computer programming mechanism in which the method being called upon an object, or the function being called with arguments, is looked up by name at runtime. In other words, a name is associated with a particular operation or object at runtime, rather than during compilation. The name dynamic binding is sometimes used, but is more commonly used to refer to dynamic scope. With early binding, or static binding, in an object-oriented language, the compilation phase fixes all types of variables and expressions. This is usually stored in the compiled program as an offset in a virtual method table ("v-table"). In contrast, with late binding, the compiler does not read enough information to verify the method exists or bind its slot on the v-table. Instead, the method is looked up by name at runtime. The primary advantage of using late binding in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Clojure
Clojure (, like ''closure'') is a dynamic programming language, dynamic and functional programming, functional dialect (computing), dialect of the programming language Lisp (programming language), Lisp on the Java (software platform), Java platform. Like most other Lisps, Clojure's Syntax (programming languages), syntax is built on S-expressions that are first Parsing, parsed into data structures by a Lisp reader before being Compiler, compiled. Clojure's reader supports literal syntax for hash table, maps, sets, and Array (data structure), vectors along with lists, and these are compiled to the mentioned structures directly. Clojure treats Homoiconicity, code as data and has a Lisp macro system. Clojure is a Lisp-1 and is not intended to be code-compatible with other dialects of Lisp, since it uses its own set of data structures incompatible with other Lisps. Clojure advocates immutable object, immutability and persistent data structure, immutable data structures and encourages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Closure (computer Programming)
In programming languages, a closure, also lexical closure or function closure, is a technique for implementing lexically scoped name binding in a language with first-class functions. Operationally, a closure is a record storing a function together with an environment. The environment is a mapping associating each free variable of the function (variables that are used locally, but defined in an enclosing scope) with the value or reference to which the name was bound when the closure was created. Unlike a plain function, a closure allows the function to access those ''captured variables'' through the closure's copies of their values or references, even when the function is invoked outside their scope. History and etymology The concept of closures was developed in the 1960s for the mechanical evaluation of expressions in the λ-calculus and was first fully implemented in 1970 as a language feature in the PAL programming language to support lexically scoped first-class functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Continuation
In computer science, a continuation is an abstract representation of the control state of a computer program. A continuation implements ( reifies) the program control state, i.e. the continuation is a data structure that represents the computational process at a given point in the process's execution; the created data structure can be accessed by the programming language, instead of being hidden in the runtime environment. Continuations are useful for encoding other control mechanisms in programming languages such as exceptions, generators, coroutines, and so on. The "current continuation" or "continuation of the computation step" is the continuation that, from the perspective of running code, would be derived from the current point in a program's execution. The term ''continuations'' can also be used to refer to first-class continuations, which are constructs that give a programming language the ability to save the execution state at any point and return to that point at a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Functional Programming
In computer science, functional programming is a programming paradigm where programs are constructed by Function application, applying and Function composition (computer science), composing Function (computer science), functions. It is a declarative programming paradigm in which function definitions are Tree (data structure), trees of Expression (computer science), expressions that map Value (computer science), values to other values, rather than a sequence of Imperative programming, imperative Statement (computer science), statements which update the State (computer science), running state of the program. In functional programming, functions are treated as first-class citizens, meaning that they can be bound to names (including local Identifier (computer languages), identifiers), passed as Parameter (computer programming), arguments, and Return value, returned from other functions, just as any other data type can. This allows programs to be written in a Declarative programming, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Strong Coupling Example
Strong may refer to: Education * The Strong, an educational institution in Rochester, New York, United States * Strong Hall (Lawrence, Kansas), an administrative hall of the University of Kansas * Strong School, New Haven, Connecticut, United States, an overflow school for district kindergartners and first graders Music Albums * '' Strong (Tyler Hubbard album)'', 2024 * ''Strong'' (Anette Olzon album), 2021 * ''Strong'' (Arrested Development album), 2010 * ''Strong'' (Michelle Wright album), 2013 * ''Strong'' (Thomas Anders album), 2010 * ''Strong'' (Tracy Lawrence album), 2004 * ''Strong'', a 2000 album by Clare Quilty Songs * "Strong" (London Grammar song), 2013 * "Strong" (One Direction song), 2013 * "Strong" (Robbie Williams song), 1999 * "Strong" (Romy song), 2022 * "Strong", a song by After Forever from '' Remagine'' * "Strong", a song by Audio Adrenaline from '' Worldwide'' * "Strong", a song by LeAnn Rimes from ''Whatever We Wanna'' * "Strong", a song by London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Loose Coupling Example
Loose may refer to: Places *Loose, Germany *Loose, Kent, a parish and village in southeast England People * Loose (surname) Arts, entertainment, and media Music Albums * ''Loose'' (B'z album), a 1995 album by B'z * ''Loose'' (Crazy Horse album), a 1972 album by Crazy Horse * ''Loose'' (Nelly Furtado album), a 2006 album by Nelly Furtado **Loose Mini DVD, a 2007 DVD by Nelly Furtado ** Get Loose Tour, a concert tour by Nelly Furtado ** Loose: The Concert, a 2007 live DVD by Nelly Furtado * ''Loose'' (Victoria Williams album), a 1994 album by Victoria Williams *'' Loose...'', a 1963 album by jazz saxophonist Willis Jackson *''Loose'', a 2018 mixtape by Jack Harlow Songs * "Loose" (S1mba song), a 2020 song by S1mba featuring KSI * "Loose" (Stooges song), a 1970 song by the Stooges * "Loose" (Therapy? song), a 1996 Therapy? single Slang *Loose, slang for inebriated or high on drugs, as in "get loose" * Loose, slang antonym for anxious ("uptight"), as in "loosen up" * Loose woman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
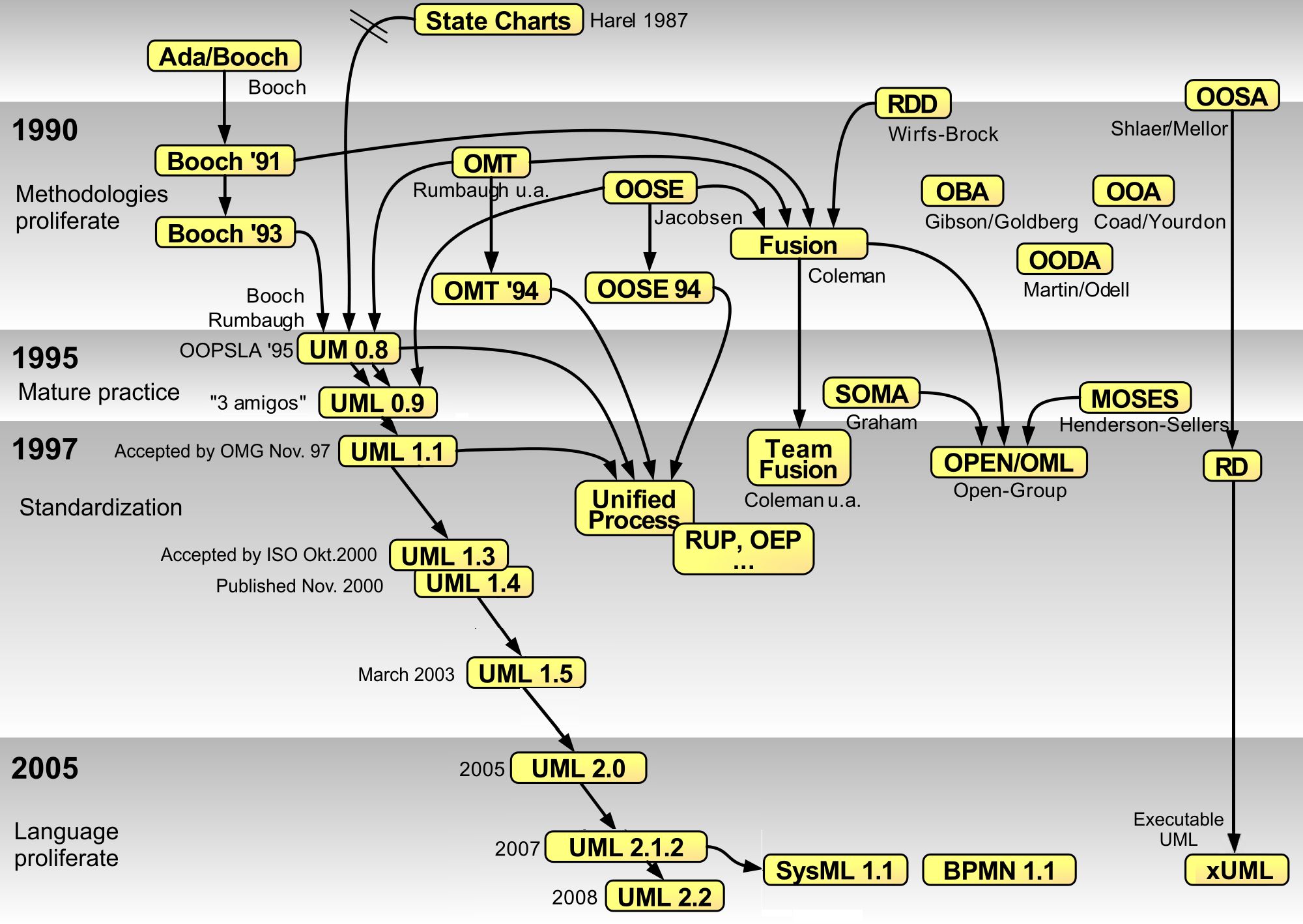
Unified Modeling Language
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system. UML provides a standard notation for many types of diagrams which can be roughly divided into three main groups: behavior diagrams, interaction diagrams, and structure diagrams. The creation of UML was originally motivated by the desire to standardize the disparate notational systems and approaches to software design. It was developed at Rational Software in 1994–1995, with further development led by them through 1996. In 1997, UML was adopted as a standard by the Object Management Group (OMG) and has been managed by this organization ever since. In 2005, UML was also published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as the ISO/IEC 19501 standard. Since then the standard has been periodically revised to cover the latest revision of UML. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dependency Inversion Principle
In object-oriented design, the dependency inversion principle is a specific methodology for Coupling (computer programming), loosely coupled software Modular programming, modules. When following this principle, the conventional dependency (computer science), dependency relationships established from high-level, policy-setting modules to low-level, dependency modules are reversed, thus rendering high-level modules independent of the low-level module implementation details. The principle states: By dictating that high-level and low-level objects must depend on the same abstraction, this design principle the way some people may think about object-oriented programming. The idea behind points A and B of this principle is that when designing the interaction between a high-level module and a low-level one, the interaction should be thought of as an abstract interaction between them. This has implications for the design of both the high-level and the low-level modules: the low-level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Encapsulation (object-oriented Programming)
In software systems, encapsulation refers to the bundling of data with the mechanisms or methods that operate on the data. It may also refer to the limiting of direct access to some of that data, such as an object's components. Essentially, encapsulation prevents external code from being concerned with the internal workings of an object. Encapsulation allows developers to present a consistent interface that is independent of its internal implementation. As one example, encapsulation can be used to hide the values or state of a structured data object inside a class. This prevents clients from directly accessing this information in a way that could expose hidden implementation details or violate state invariance maintained by the methods. Encapsulation also encourages programmers to put all the code that is concerned with a certain set of data in the same class, which organizes it for easy comprehension by other programmers. Encapsulation is a technique that encourages decoupling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
JSON
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation, pronounced or ) is an open standard file format and electronic data interchange, data interchange format that uses Human-readable medium and data, human-readable text to store and transmit data objects consisting of name–value pairs and array data type, arrays (or other serialization, serializable values). It is a commonly used data format with diverse uses in electronic data interchange, including that of web applications with server (computing), servers. JSON is a Language-independent specification, language-independent data format. It was derived from JavaScript, but many modern programming languages include code to generate and parse JSON-format data. JSON filenames use the extension .json. Douglas Crockford originally specified the JSON format in the early 2000s. Transcript: He and Chip Morningstar sent the first JSON message in April 2001. Naming and pronunciation The 2017 international standard (ECMA-404 and ISO/IEC 21778:2017) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |