|
London Society Of West India Planters And Merchants
The London Society of West India Planters and Merchants was an organization established to represent the views of the British West Indian plantocracy, i.e. the ruling class who owned and ran the slave-based plantations in what is now the Caribbean. The organization played a major role in resisting the abolition of the slave trade and that of slavery itself. The Society was formed in 1780, and brought together three different groups: British sugar merchants, absentee planters and colonial agents. Background Estimates of the size of the West India Lobby vary between 20 and 60 members of parliament, the wide variance arising from whether tight or loose criteria are used to define what was an informal lobby. This informal way of organizing was effective prior to 1763 while their interest was aligned with the mercantilist approach which dominated British thinking: by supplying tropical staples, they did not compete with produce grown in Britain, and they provided a market for the produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British West Indian
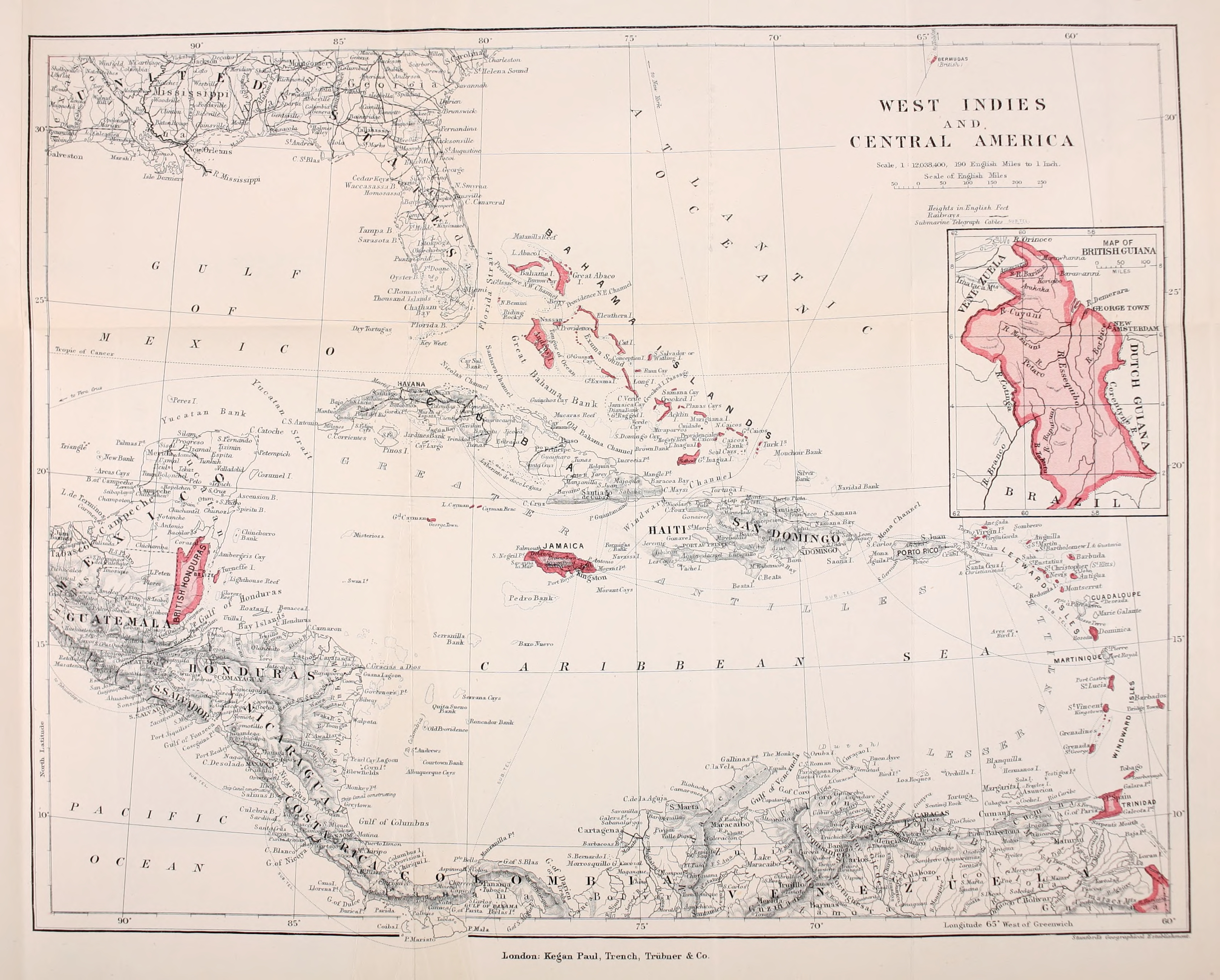
The British West Indies (BWI) were colonized British territories in the West Indies: Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, British Guiana (now Guyana) and Trinidad and Tobago. Other territories include Bermuda, and the former British Honduras (now Belize). The colonies were also at the center of the transatlantic slave trade, around 2.3 million slaves were brought to the British Caribbean. Before the decolonisation period in the later 1950s and 1960s the term was used to include all British colonies in the region as part of the British Empire. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British West Indies
The British West Indies (BWI) were colonized British territories in the West Indies: Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, British Guiana (now Guyana) and Trinidad and Tobago. Other territories include Bermuda, and the former British Honduras (now Belize). The colonies were also at the center of the transatlantic slave trade, around 2.3 million slaves were brought to the British Caribbean. Before the decolonisation period in the later 1950s and 1960s the term was used to include all British colonies in the region as part of the British Empire. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West India Dock
The West India Docks are a series of three docks, quaysides and warehouses built to import goods from and export goods and occasionally passengers to the British West Indies on the Isle of Dogs in London the first of which opened in 1802. Following their commercial closure in 1980, the Canary Wharf development was built around the wet docks by narrowing some of their broadest tracts. History Early history Robert Milligan, of a Scottish family, (–1809) was largely responsible for the construction of the West India Docks. He was a wealthy West Indies merchant, slave trader and ship owner, who returned to London having managed his family's Jamaica sugar plantations. Outraged at losses due to theft and delay at London's riverside wharves, Milligan headed a group of powerful businessmen, including the chairman of the London Society of West India Planters and Merchants, George Hibbert, a merchant, politician, and ship-owner, who promoted the creation of a wet dock circled by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
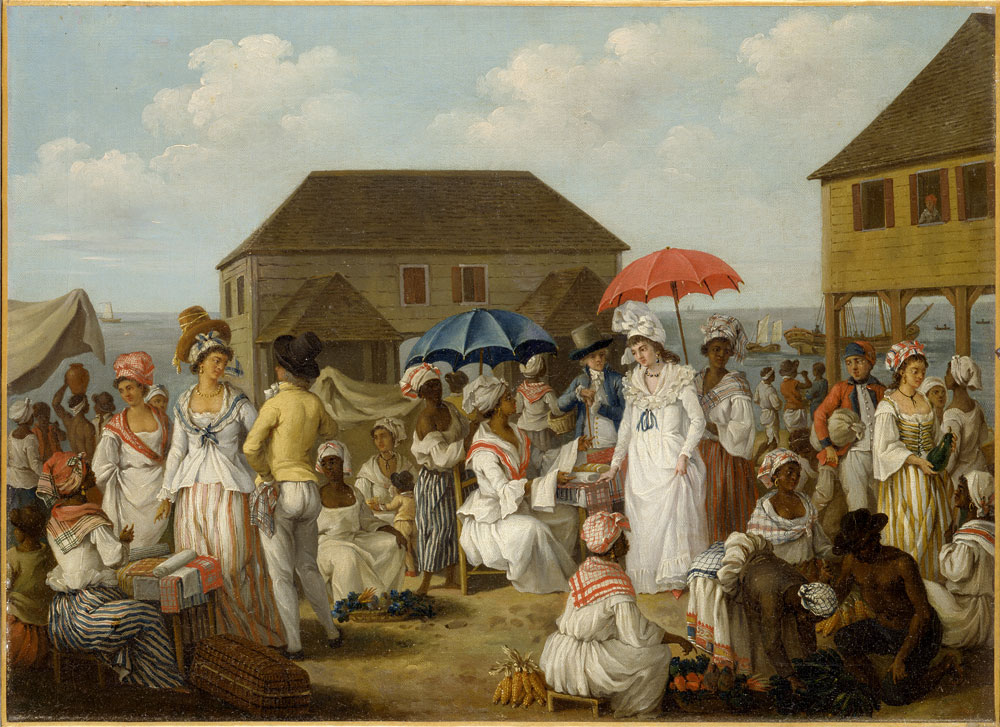
Plantocracy
A slavocracy, also known as a plantocracy, is a ruling class, political order or government composed of (or dominated by) slave owners and plantation owners. A number of early European colonies in the New World were largely plantocracies, usually consisting of a small European settler population relying on a predominantly West African chattel slave population (as well as smaller numbers of indentured servants, both European and non-European in origin), and later, freed Black and poor white sharecroppers for labor. These plantocracies proved to be a decisive force in the anti-abolitionist movement. One prominent organization largely representing (and collectively funded by) a number of plantocracies was the " West India Interest", which lobbied in Parliament against the abolition of slavery. It is credited with delaying the abolition of the slave trade from the 1790s until 1806–1808, and likewise with respect to emancipation in the 1820s (instead, a policy known as "Ameliorati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Plantations In The Caribbean
Sugar plantations in the Caribbean were a major part of the economy of the islands in the 18th, 19th, and 20th centuries. Most Caribbean, Caribbean islands were covered with Sugarcane, sugar cane fields and mills for refining the crop. The main source of labor, until Abolitionism, the abolition of chattel slavery, was Atlantic slave trade, enslaved Africans. After the abolition of slavery, Indentured servitude, indentured laborers from India, China, Portugal and other places were brought to the Caribbean to work in the sugar industry. These plantations produced 80 to 90 percent of the sugar consumed in Western Europe, later supplanted by European-grown sugar beet. The sugar trade Sugar cane development in the Americas The Portuguese introduced sugar plantations in the 1550s off the coast of their Brazilian settlement colony, located on the island Sao Vincente. As the Portuguese and Spanish maintained a strong colonial presence in the Caribbean, the Iberian Peninsula amassed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West India Interest
The West India Interest lobbied on behalf of the Caribbean sugar trade in Britain during the late eighteenth century. Beginning in the 17th century, Caribbean colonies appointed paid lobbyists, who were called colonial agents, to act on behalf of the legislatures in the colonies. These local legislatures represented the interests of the plantation owning class in the colonies. The agents, who lobbied to protect the interests of plantation owners, were often members of the British Parliament. Lillian Penson identified three distinct interest groups in London, who decided to work together: agents from the West Indian colonies, merchants who traded with the colonies and plantation owners who lived in London. This group supported the Molasses Act of 1733, which sought to tax molasses that was shipped to New England from the Caribbean. This tax was supposed to be collected from the American people. When tensions between the American colonies and the British Crown increased in the yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Augustine, Trinidad And Tobago
Saint Augustine is a town in the northwest of Trinidad, Trinidad and Tobago. Town It is the site of the University of the West Indies at St. Augustine (UWI-STA). In the 2019-2020 school year, there were 16,571 students enrolled in the university, making college students a vital part of the town's economy. Many houses in the general university area have been converted to students' accommodation, but due to the lack of fee regulation, they are generally more than double the cost of university housing. Four of the five halls of residence provided by the University are located here, namely St. John's Hall, Freedom Hall (previously named Milner Hall), Canada Hall, and Trinity Hall. The town comprises many different communities like St John, St Michael Village, Mt St Benedict(all of these to the north of eastern main road), as well as the surrounding area of UWI, Monte Grande east of the campus and Morang village, south of the campus on the highway. St. John's Road in St. Augustine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of The West Indies
The University of the West Indies (UWI), originally University College of the West Indies, is a public university system established to serve the higher education needs of the residents of 17 English-speaking countries and territories in the Caribbean: Anguilla, Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Bermuda, British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Jamaica, Montserrat, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago, and Turks and Caicos Islands. Each country is either a member of the Commonwealth of Nations or a British Overseas Territory. The aim of the university is to help "unlock the potential for economic and cultural growth" in the West Indies, thus allowing improved regional autonomy. The university was originally instituted as an independent external college of the University of London. The university has produced students who have excelled in a number of disciplines such as the arts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alma Jordan Library
The Alma Jordan Library at the University of the West Indies (UWI), Trinidad and Tobago, was named after UWI librarian Dr. Alma Jordan in 2012. The four-storied library is located on the St. Augustine Campus of the UWI. It is the largest of the libraries in the St Augustine Campus libraries network, with approximately 600,000 monographs, 31,000 e-books, 4,000 serial titles, 57,000 e-journal subscriptions and access to over 200 databases. The Alma Jordan Library houses the Eric Williams Memorial Collection, which has been named to the UNESCO Memory of the World Register. The library houses the minute books of the London Society of West India Planters and Merchants, a major anti-abolitionist organisation of the British West Indian plantocracy.Ryden D. (2015) The Society of West India Planters and Merchants in the Age of Emancipation, c.1816-35Economic History Society Annual Conference, University of Wolverhampton accessed 5 January 2016 Other libraries in the St Augustine Campu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad And Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of Grenada and off the coast of northeastern Venezuela. It shares maritime boundaries with Barbados to the northeast, Grenada to the northwest and Venezuela to the south and west. Trinidad and Tobago is generally considered to be part of the West Indies. The island country's capital is Port of Spain, while its largest and most populous city is San Fernando. The island of Trinidad was inhabited for centuries by Indigenous peoples before becoming a colony in the Spanish Empire, following the arrival of Christopher Columbus, in 1498. Spanish governor José María Chacón surrendered the island to a British fleet under the command of Sir Ralph Abercromby in 1797. Trinidad and Tobago were ceded to Britain in 1802 under the Treaty of Amiens as se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West India Committee
The West India Committee is a British-based organisation promoting ties and trade with the British Caribbean. It operates as a charity and NGO (non-governmental organisation). It evolved out of a lobbying group formed in 1780 to represent the interests of the plantocracy. Historically, the principal commodities of the region were cane sugar, rum, mahogany, other softwood, spices and tropical produce, early on largely confined to types that would last a long transatlantic voyage such as coffee, nuts and desiccated coconut but later expanded to include tropical fruits in general. London Society of West India Planters and Merchants The London Society of West India Planters and Merchants was established to represent the views of the British West Indian plantocracy. The organisation played a major role in resisting the abolition of the slave trade and that of slavery itself. The Society was formed in 1780, and brought together three different groups: British sugar merchants, absentee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of the United States, fighting began on April 19, 1775, followed by the Lee Resolution on July 2, 1776, and the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The American Patriots were supported by the Kingdom of France and, to a lesser extent, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Empire, in a conflict taking place in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. Established by royal charter in the 17th and 18th centuries, the American colonies were largely autonomous in domestic affairs and commercially prosperous, trading with Britain and its Caribbean colonies, as well as other European powers via their Caribbean entrepôts. After British victory over the French in the Seven Years' War in 1763, tensions between the motherland and he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

