|
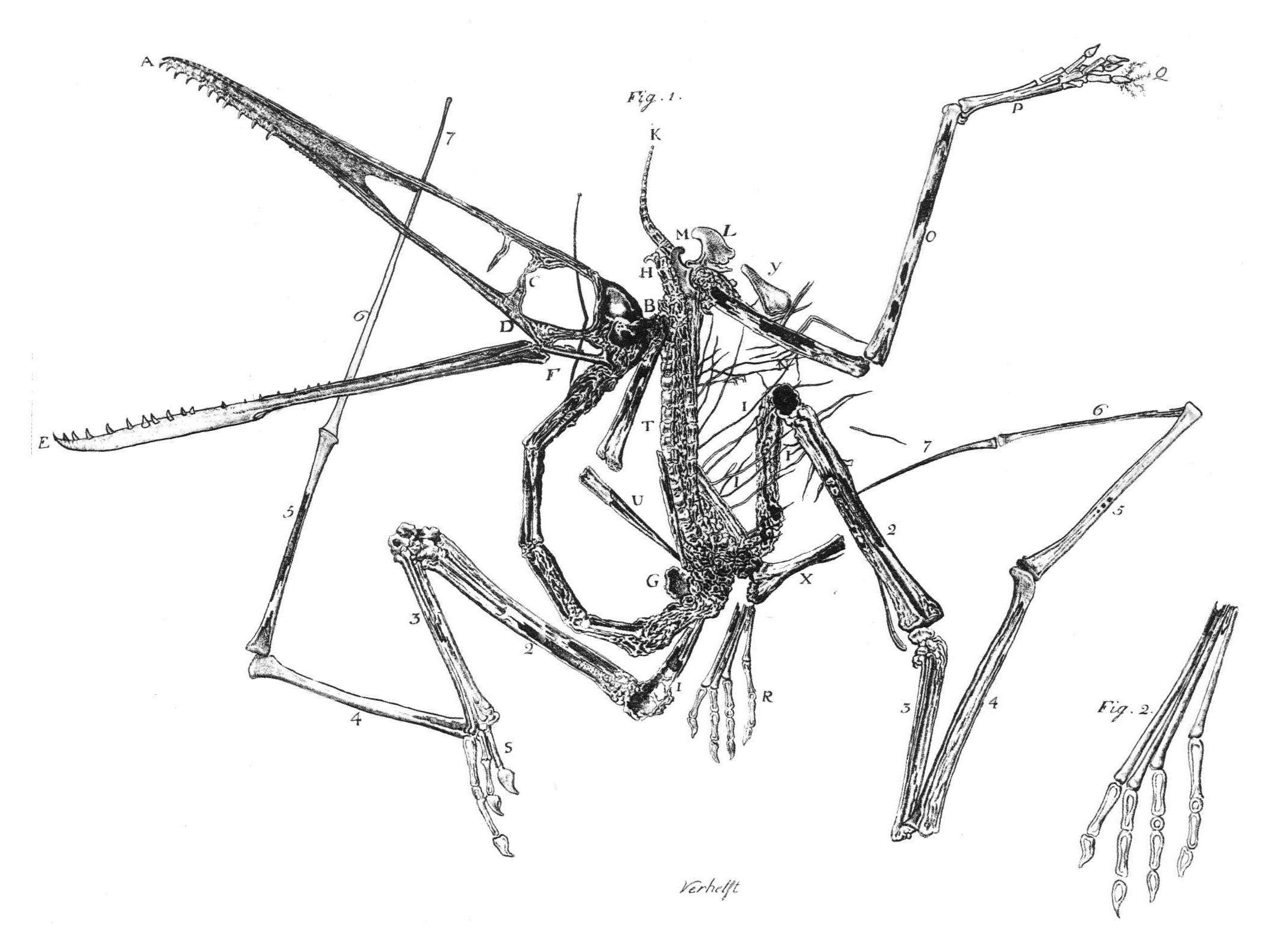
Lonchodraco
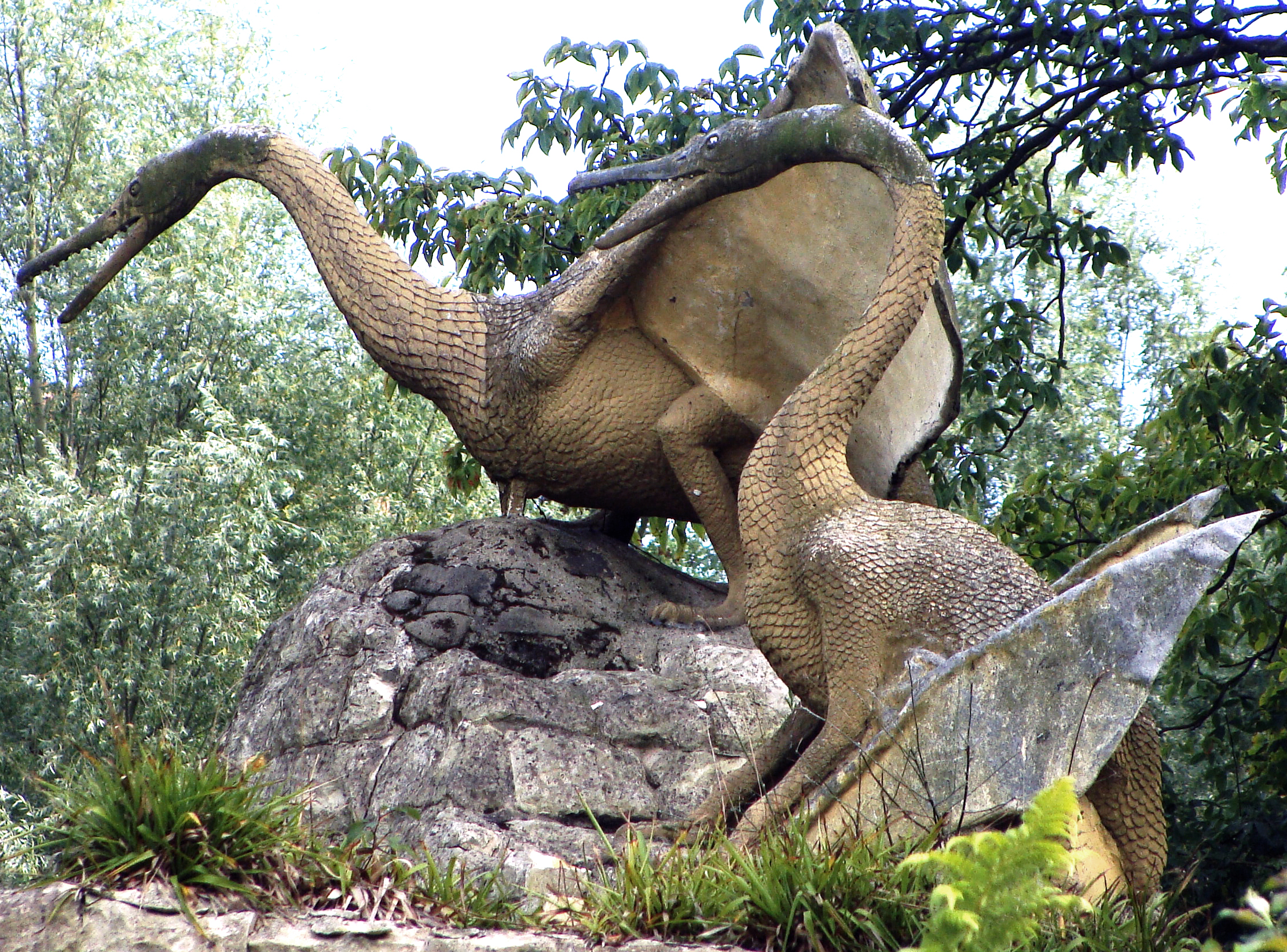
''Lonchodraco'' is a genus of lonchodraconid Pterodactyloidea, pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Late Cretaceous of southern England. The genus includes species that were previously assigned to other genera. Discovery and naming In 1846, James Scott Bowerbank named and described some remains found in a chalk pit at Burham near Maidstone in Kent, as a new species of ''Pterodactylus'': ''Pterodactylus giganteus''. The specific name (zoology), specific name means "the gigantic one" in Latin. The same pit generated remains of ''Cimoliopterus, Pterodactylus cuvieri''. In 1848, Bowerbank published a histological study of the bone structure of ''P. giganteus''. At the time, the British Association Code of 1843 allowed to change names if they were inappropriate. In 1850, Richard Owen, considering the species not to have been particularly large, and renamed it into ''Pterodactylus conirostris''; the specific name meaning "cone-snouted", which was based on the conical snout of specimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lonchodraconid
Lonchodectidae or LonchodraconidaePêgas, R.V., Holgado, B., Leal, M.E.C., 2019. "''Targaryendraco wiedenrothi'' gen. nov. (Pterodactyloidea, Pteranodontoidea, Lanceodontia) and recognition of a new cosmopolitan lineage of Cretaceous toothed pterodactyloids", ''Historical Biology'', 1–15. doi:10.1080/08912963.2019.1690482 is a group of pterosaurs within the clade Pterodactyloidea. It has variously been considered to be within Ctenochasmatoidea, Azhdarchoidea and Pteranodontia.Witton, M.P., Martill, D.M., and Green, M. (2009). "On pterodactyloid diversity in the British Wealden (Lower Cretaceous) and a reappraisal of “Palaeornis” ''cliftii'' Mantell, 1844." ''Cretaceous Research'', 30: 676–686. They are notable for their high, conical tooth sockets and raised alveolar margins. Taxonomic history Lonchodectidae was first named by paleontologist Reginald Walter Hooley in 1914, and was first considered to only contain species of ''Lonchodectes''.Unwin, David M. 2001. "An overv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lonchodectes
''Lonchodectes'' (meaning "lance biter") was a genus of lonchodectid pterosaur from several formations dating to the Turonian (Late Cretaceous) of England, mostly in the area around Kent. The species belonging to it had been assigned to ''Ornithocheirus'' until David Unwin's work of the 1990s and 2000s.Kellner, A.W.A. (2003). Pterosaur phylogeny and comments on the evolutionary history of the group: In: Buffetaut, E., and Mazin, J.-M. (Eds.). ''Evolution and Palaeobiology of Pterosaurs''. Geological Society Special Publication 217:105-137. 1-86239-143-2. Several potential species are known; most are based on scrappy remains, and have gone through several other generic assignments. The genus is part of the complex taxonomy issues surrounding Early Cretaceous pterosaurs from Brazil and England, such as ''Amblydectes'', ''Anhanguera'', ''Coloborhynchus'', and ''Ornithocheirus''. History and species Numerous species have been referred to this genus over time, and only those more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 to 66 million years ago). Pterosaurs are the earliest vertebrates known to have evolved powered flight. Their wings were formed by a membrane of skin, muscle, and other tissues stretching from the ankles to a dramatically lengthened fourth finger. There were two major types of pterosaurs. Basal pterosaurs (also called 'non-pterodactyloid pterosaurs' or 'rhamphorhynchoids') were smaller animals with fully toothed jaws and, typically, long tails. Their wide wing membranes probably included and connected the hind legs. On the ground, they would have had an awkward sprawling posture, but the anatomy of their joints and strong claws would have made them effective climbers, and some may have even lived in trees. Basal pterosaurs were insectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterodactylus
''Pterodactylus'' (from Greek () meaning 'winged finger') is an extinct genus of pterosaurs. It is thought to contain only a single species, ''Pterodactylus antiquus'', which was the first pterosaur to be named and identified as a flying reptile. Fossil remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have primarily been found in the Solnhofen limestone of Bavaria, Germany, which dates from the Late Jurassic period (early Tithonian stage), about 150.8 to 148.5 million years ago. More fragmentary remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have tentatively been identified from elsewhere in Europe and in Africa. ''Pterodactylus'' was a generalist carnivore that probably fed on a variety of invertebrates and vertebrates. Like all pterosaurs, ''Pterodactylus'' had wings formed by a skin and muscle membrane stretching from its elongated fourth finger to its hind limbs. It was supported internally by collagen fibres and externally by keratinous ridges. ''Pterodactylus'' was a small pterosaur compared to other famo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cimoliopterus
''Cimoliopterus'' is a genus of pterosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what is now England and the United States. The first known specimen, consisting of the front part of a snout including part of a crest, was discovered in the Grey Chalk Subgroup of Kent, England, and described as the new species ''Pterodactylus cuvieri'' in 1851. The specific name ''cuvieri'' honours the palaeontologist George Cuvier, whereas the genus ''Pterodactylus'' was then used for many pterosaur species that are not thought to be closely related today. It was one of the first pterosaurs to be depicted as models in Crystal Palace Park in the 1850s. The species was subsequently assigned to various other genera, including ''Ornithocheirus'' and ''Anhanguera''. In 2013, the species was moved to a new genus, as ''Cimoliopterus cuvieri''; the generic name ''Cimoliopterus'' is derived from the Greek words for "chalk" and "wing". Other specimens and species have also been assigned to or synonymi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterodactylus Giganteus
''Pterodactylus giganteus'' is a scientific name which has been used for at least three distinct species of pterosaurs previously classified in the genus ''Pterodactylus''. It may refer to: * "''Pterodactylus''" ''giganteus'' ( Oken, 1819): Originally '' Ornithocephalus giganteus'', currently considered a synonym of ''Rhamphorhynchus muensteri'' * "''Pterodactylus''" ''giganteus'' (Morris, 1854): A synonym of ''Cimoliornis diomedeus ''Cimoliornis'' is a pterosaur genus containing the single species ''Cimoliornis diomedeus'', meaning "long-winged bird of the chalk". It is known from a partial metacarpal (lower wing bone) found in late Cretaceous period English Chalk Formation ...'' * "''Pterodactylus''" ''giganteus'' ( Bowerbank, 1846): Now '' Lonchodraco giganteus'' {{Species Latin name disambiguation Pterodactyloids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterodactyloidea
Pterodactyloidea (derived from the Greek words ''πτερόν'' (''pterón'', for usual ''ptéryx'') "wing", and ''δάκτυλος'' (''dáktylos'') "finger" meaning "winged finger", "wing-finger" or "finger-wing") is one of the two traditional suborders of pterosaurs ("wing lizards"), and contains the most derived members of this group of flying reptiles. They appeared during the middle Jurassic Period, and differ from the basal (though paraphyletic) rhamphorhynchoids by their short tails and long wing metacarpals (hand bones). The most advanced forms also lack teeth, and by the late Cretaceous, all known pterodactyloids were toothless. Many species had well-developed crests on the skull, a form of display taken to extremes in giant-crested forms like ''Nyctosaurus'' and ''Tupandactylus''. Pterodactyloids were the last surviving pterosaurs when the order became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous Period, together with the non-avian dinosaurs and most marine reptiles. "Pteroda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Association Code
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *''Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen (20 July 1804 – 18 December 1892) was an English biologist, comparative anatomist and paleontologist. Owen is generally considered to have been an outstanding naturalist with a remarkable gift for interpreting fossils. Owen produced a vast array of scientific work, but is probably best remembered today for coining the word '' Dinosauria'' (meaning "Terrible Reptile" or "Fearfully Great Reptile"). An outspoken critic of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection, Owen agreed with Darwin that evolution occurred, but thought it was more complex than outlined in Darwin's ''On the Origin of Species''. Owen's approach to evolution can be considered to have anticipated the issues that have gained greater attention with the recent emergence of evolutionary developmental biology. Owen was the first president of the Microscopical Society of London in 1839 and edited many issues of its journal – then known as ''The Microscopic Journal''. Owen also c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reginald Walter Hooley
Reginald Walter Hooley (5 September 1865 – 5 May 1923) was a businessman and amateur paleontologist, collecting on the Isle of Wight. He is probably best remembered for describing the dinosaur ''Iguanodon atherfieldensis'', now ''Mantellisaurus.'' Biography Reginald Hooley was born on 5 September 1865 in Southampton, the son of William Hooley, a wealthy gentleman. In 1889 R.W. Hooley began to work for ''Godrich & Petman'', wine merchants, and later in life became managing director of that firm. Living in Portswood, in 1912 he married E.E. Holden and moved to Winchester. In 1913 he was elected a member of the Winchester city council. Hooley was a member of the Hampshire Field Club & Archaeological Society at Winchester from 1890. He was one of the founders of the Isle of Wight Natural History and Archaeological Society. He was an honorary curator of the Winchester Museum between 1918 and 1923. Isle of Wight Hooley made regular visits to the Isle of Wight and found hundreds of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Kellner
Alexander Wilhelm Armin Kellner (born September 26, 1961) is a Brazilian geologist and paleontologist who is a leading expert in the field of studying pterosaurs. His research has focused mainly on fossil reptiles from the Cretaceous Period, including extinct dinosaurs and crocodylomorphs. Kellner has over 500 publications to his name, has published more than 160 primary studies and two science books. He has participated in paleontological expeditions to many locations including Brazil, Chile, Iran, the United States, Argentina, China, and Antarctica. His scientific achievements include the description of more than thirty species. For his work he has received several honors and prizes, including the TWAS Prize for Earth Sciences from The World Academy of Sciences and admission to the National Order of Scientific Merit (class Comendador), one Brazil's most prestigious awards. Biography Kellner was born in Vaduz, Liechtenstein, son of a German father and Austrian mother. In hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |