|
Lomonosov (Martian Crater)
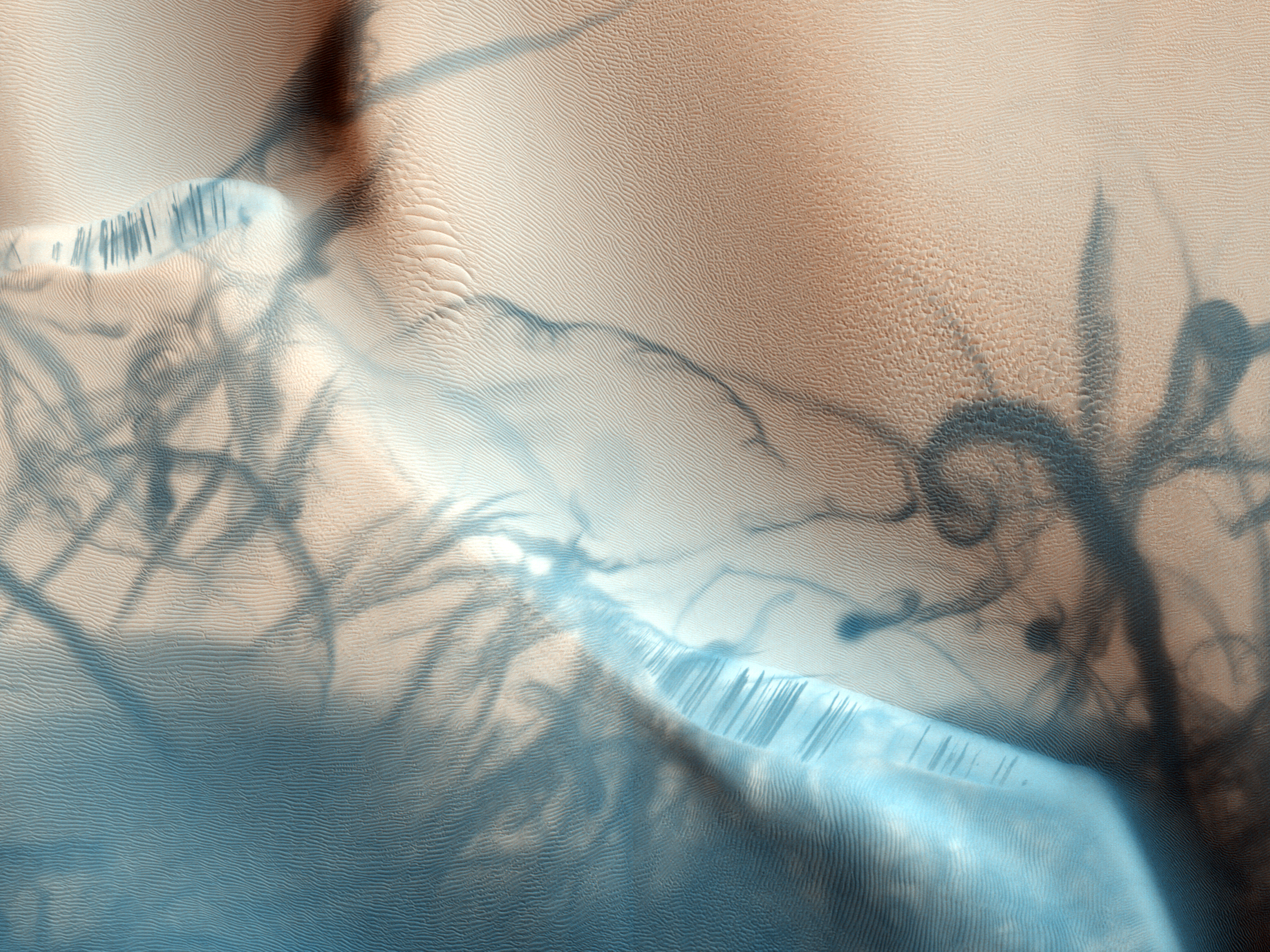
Lomonosov is a crater on Mars, with a diameter close to 150 km. It is located in the Martian northern plains. Since it is large and found close (64.9° north) to the boundary between the Mare Acidalium quadrangle and the Mare Boreum quadrangle, it is found on both maps. The topography is smooth and young in this area, hence Lomonosov is easy to spot on large maps of Mars. The crater was named in 1973 in honour of Mikhail V. Lomonosov. The impact that created the crater has been identified as a possible source of tsunami waves which washed the shores of an ancient ocean formerly present in the basin Vastitas Borealis.Costard, F., et al. 2018. Formation of the Northern Plains Lomonosov Crater During a Tsunami Generating Marine Impact Event. 49th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference 2018 (LPI Contrib. No. 2083). 1928.pdf In July 2019, further support was reported for an ancient ocean on Mars that may have been formed by a possible mega-tsunami source resulting from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere (less than 1% that of Earth's), and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons, Phobos (moon), Phobos and Deimos (moon), Deimos. Some of the most notable surface features on Mars include Olympus Mons, the largest volcano and List of tallest mountains in the Solar System, highest known mountain in the Solar System and Valles Marineris, one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. The North Polar Basin (Mars), Borealis basin in the Northern Hemisphere covers approximately 40% of the planet and may be a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteorite Impact
An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or meteoroids and have minimal effect. When large objects impact terrestrial planets such as the Earth, there can be significant physical and biospheric consequences, though atmospheres mitigate many surface impacts through atmospheric entry. Impact craters and structures are dominant landforms on many of the Solar System's solid objects and present the strongest empirical evidence for their frequency and scale. Impact events appear to have played a significant role in the evolution of the Solar System since its formation. Major impact events have significantly shaped Earth's history, and have been implicated in the formation of the Earth–Moon system. Impact events also appear to have played a significant role in the evolutionary history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1379 Lomonosowa
1379 Lomonosowa ( ''prov. designation'': ) is a stony background asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately in diameter. Discovered by Grigory Neujmin at the Simeiz Observatory in 1936, the asteroid was later named after Russian physicist and astronomer Mikhail Lomonosov. Discovery ''Lomonosowa'' was discovered on 19 March 1936, by Soviet astronomer Grigory Neujmin at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. On the same night, it was independently discovered by Serbian astronomer Petar Đurković at Uccle Observatory in Belgium. The Minor Planet Center only recognizes the first discoverer. A first precovery of ''Lomonosowa'' was taken at the Lowell Observatory in October 1905. The asteroid was first identified as at Heidelberg Observatory in September 1933. Orbit and classification ''Lomonosowa'' is a non-family asteroid of the main belt's background population. It orbits the Sun in the central asteroid belt at a distance of 2.3–2.8&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction of the University of Arizona's Lunar and Planetary Laboratory by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. It consists of a 0.5m (19.7 in) aperture reflecting telescope, the largest so far of any deep space mission, which allows it to take pictures of Mars with resolutions of 0.3m/pixel (1ft/pixel), resolving objects below a meter across. HiRISE has imaged Mars exploration rovers on the surface, including the ''Opportunity'' rover and the ongoing ''Curiosity'' mission. History In the late 1980s, of Ball Aerospace & Technologies began planning the kind of high-resolution imaging needed to support sample return and surface exploration of Mars. In early 2001 he teamed up with Alfred McEwen of the University of Arizona to propose such a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Global Surveyor
''Mars Global Surveyor'' (MGS) was an American robotic space probe developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched November 1996. MGS was a global mapping mission that examined the entire planet, from the ionosphere down through the atmosphere to the surface. As part of the larger Mars Exploration Program, Mars Global Surveyor performed atmospheric monitoring for sister orbiters during aerobraking, and helped Mars rovers and lander missions by identifying potential landing sites and relaying surface telemetry. It completed its primary mission in January 2001 and was in its third extended mission phase when, on 2 November 2006, the spacecraft failed to respond to messages and commands. A faint signal was detected three days later which indicated that it had gone into safe mode. Attempts to recontact the spacecraft and resolve the problem failed, and NASA officially ended the mission in January 2007. MGS remains in a stable near-polar circular orbit at about 450 km ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking Program
The ''Viking'' program consisted of a pair of identical American space probes, ''Viking 1'' and ''Viking 2'', which landed on Mars in 1976. Each spacecraft was composed of two main parts: an orbiter designed to photograph the surface of Mars from orbit, and a lander designed to study the planet from the surface. The orbiters also served as communication relays for the landers once they touched down. The Viking program grew from NASA's earlier, even more ambitious, Voyager Mars program, which was not related to the successful Voyager deep space probes of the late 1970s. ''Viking 1'' was launched on August 20, 1975, and the second craft, ''Viking 2'', was launched on September 9, 1975, both riding atop Titan IIIE rockets with Centaur upper stages. ''Viking 1'' entered Mars orbit on June 19, 1976, with ''Viking 2'' following on August 7. After orbiting Mars for more than a month and returning images used for landing site selection, the orbiters and landers detached; the lander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planets
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a young protostar orbited by a protoplanetary disk. Planets grow in this disk by the gradual accumulation of material driven by gravity, a process called accretion. The Solar System has at least eight planets: the terrestrial planets Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, and the giant planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. These planets each rotate around an axis tilted with respect to its orbital pole. All of them possess an atmosphere, although that of Mercury is tenuous, and some share such features as ice caps, seasons, volcanism, hurricanes, tectonics, and even hydrology. Apart from Venus and Mars, the Solar System planets generate magnetic fields, and all except Venus and Mercury have natural satellites. The giant planets bear planetary ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |