|
Lomer–Cottrell Junction
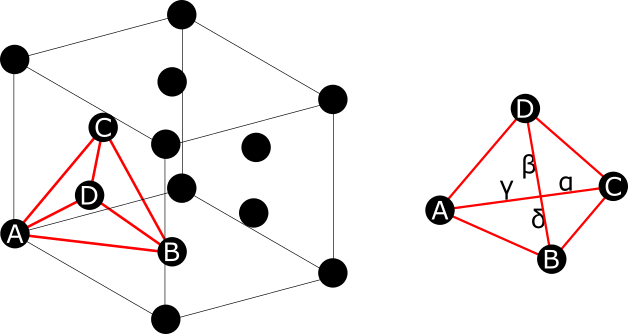
In materials science, a Lomer–Cottrell junction is a particular configuration of dislocations. When two perfect dislocations encounter along a slip plane, each perfect dislocation can split into two Shockley partial dislocations: a leading dislocation and a trailing dislocation. When the two leading Shockley partials combine, they form a separate dislocation with a burgers vector that is not in the slip plane. This is the Lomer–Cottrell dislocation. It is sessile and immobile in the slip plane, acting as a barrier against other dislocations in the plane. The trailing dislocations pile up behind the Lomer–Cottrell dislocation, and an ever greater force is required to push additional dislocations into the pile-up. ex. FCC lattice along slip planes , leading, , trailing, :\fractext\rightarrow \fractext+ \fractext/math> :\fractext\rightarrow \fractext+ \fractext/math> Combination of leading dislocations: :\fractext+ \fractext\rightarrow \fractext Text may r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to slide over each other at low stress levels and is known as ''glide'' or slip. The crystalline order is restored on either side of a ''glide dislocation'' but the atoms on one side have moved by one position. The crystalline order is not fully restored with a ''partial dislocation''. A dislocation defines the boundary between ''slipped'' and ''unslipped'' regions of material and as a result, must either form a complete loop, intersect other dislocations or defects, or extend to the edges of the crystal. A dislocation can be characterised by the distance and direction of movement it causes to atoms which is defined by the Burgers vector. Plastic deformation of a material occurs by the creation and movement of many dislocations. The number and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Dislocations
In materials science, a partial dislocation is a decomposed form of dislocation that occurs within a crystalline material. An ''extended dislocation'' is a dislocation that has dissociated into a pair of partial dislocations. The vector sum of the Burgers vectors of the partial dislocations is the Burgers vector of the extended dislocation. Reaction favorability A dislocation will decompose into partial dislocations if the energy state of the sum of the partials is less than the energy state of the original dislocation. This is summarized by ''Frank's Energy Criterion'': : \begin , \boldsymbol, ^2>&, \boldsymbol, ^2+, \boldsymbol, ^2 \text\\ , \boldsymbol, ^2& , \frac \sqrt, ^2+, \frac \sqrt, ^2\\ \frac >& \frac+\frac \end The components of the ''Shockley Partials'' must add up to the original vector that is being decomposed: : \begin \frac (1) =& \frac(2)+\frac(1)\\ \frac (0) =& \frac(-1)+\frac(1)\\ \frac (-1) =& \frac(-1)+\frac(-2) \end Frank partial dislocations ''Frank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |