|
Liu Hui
Liu Hui () was a Chinese mathematician who published a commentary in 263 CE on ''Jiu Zhang Suan Shu (The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art).'' He was a descendant of the Marquis of Zixiang of the Eastern Han dynasty and lived in the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period (220-280 CE) of China. His major contributions as recorded in his commentary on ''The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art'' include a proof of the Pythagorean theorem, theorems in solid geometry, an improvement on Archimedes's approximation of , and a systematic method of solving linear equations in several unknowns. In his other work, '' Haidao Suanjing (The Sea Island Mathematical Manual)'', he wrote about geometrical problems and their application to surveying. He probably visited Luoyang, where he measured the sun's shadow. Mathematical work Liu Hui expressed mathematical results in the form of decimal fractions that utilized metrological units (i.e., related units of length with base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Nine Chapters On The Mathematical Art
''The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art'' () is a Chinese mathematics book, composed by several generations of scholars from the 10th–2nd century BCE, its latest stage being from the 2nd century CE. This book is one of the earliest surviving mathematical texts from China, the first being ''Suan shu shu'' (202 BCE – 186 BCE) and '' Zhoubi Suanjing'' (compiled throughout the Han until the late 2nd century CE). It lays out an approach to mathematics that centres on finding the most general methods of solving problems, which may be contrasted with the approach common to ancient Greek mathematicians, who tended to deduce propositions from an initial set of axioms. Entries in the book usually take the form of a statement of a problem, followed by the statement of the solution and an explanation of the procedure that led to the solution. These were commented on by Liu Hui in the 3rd century. History Original book The full title of ''The Nine Chapters on the Mathemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zibo
Zibo (, ) is a prefecture-level city in central Shandong province, China. It borders the provincial capital Jinan to the west, Tai'an to the southwest, Linyi to the south, Weifang to the east, Dongying to the northeast, and Binzhou to the north. Zibo spans . As of the 2010 cenus, Zibo's population was 4.53 million, of which 4.41 million lived in the metro area comprising five urban districts— Zhangdian, Zichuan, Boshan, Zhoucun and Linzi–and parts of neighboring counties Huantai, Gaoqing, and Yiyuan. The Zibo area was the centre of the ancient State of Qi, whose capital Linzi was the most populous city in China at its peak. Pu Songling, a well-known writer of the Qing dynasty, is one of the most famous people from Zibo. As the birthplace of Qi culture, Zibo is a notable tourist city. Manufacturing holds an important place of the city's economy, particularly ceramics manufacturing. Other key industries include the petrochemical industry, pharmaceuticals, metal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
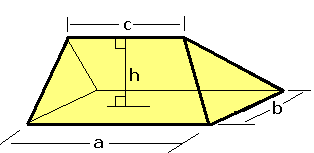
Wedge (geometry)
In solid geometry, a wedge is a polyhedron defined by two triangles and three trapezoid faces. A wedge has five faces, nine edges, and six vertices. A wedge is a subclass of the prismatoids with the base and opposite ridge in two parallel planes. A wedge can also be classified as a digonal cupola. Comparisons: * A wedge is a parallelepiped where a face has collapsed into a line. * A quadrilaterally-based pyramid is a wedge in which one of the edges between two trapezoid faces has collapsed into a point. Volume For a rectangle based wedge, the volume is :V = bh\left(\frac+\frac\right), where the base rectangle is ''a'' by ''b'', ''c'' is the apex edge length parallel to ''a'', and ''h'' the height from the base rectangle to the apex edge. Examples Wedges can be created from decomposition of other polyhedra. For instance, the dodecahedron can be divided into a central cube with 6 wedges covering the cube faces. The orientations of the wedges are such that the triangle and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised geodetic datumthat is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead the midpoint between a mean low and mean high tide at a particular location. Sea levels can be affected by many factors and are known to have varied greatly over geological time scales. Current sea level rise is mainly caused by human-induced climate change. When temperatures rise, mountain glaciers and the polar ice caps melt, increasing the amount of water in water bodies. Because most of human settlement and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Pagoda
A pagoda is an Asian tiered tower with multiple eaves common to Nepal, India, China, Japan, Korea, Myanmar, Vietnam, and other parts of Asia. Most pagodas were built to have a religious function, most often Buddhist but sometimes Taoist, and were often located in or near viharas. The pagoda traces its origins to the stupa of ancient India. Chinese pagodas () are a traditional part of Chinese architecture. In addition to religious use, since ancient times Chinese pagodas have been praised for the spectacular views they offer, and many classical poems attest to the joy of scaling pagodas. Chinese sources credit the Nepalese architect Araniko with introducing the pagoda to China. The oldest and tallest pagodas were built of wood, but most that survived were built of brick or stone. Some pagodas are solid with no interior. Hollow pagodas have no higher floors or rooms, but the interior often contains an altar or a smaller pagoda, as well as a series of staircases for the vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. A land surveying professional is called a land surveyor. These points are usually on the surface of the Earth, and they are often used to establish maps and boundaries for ownership, locations, such as the designed positions of structural components for construction or the surface location of subsurface features, or other purposes required by government or civil law, such as property sales. Surveyors work with elements of geodesy, geometry, trigonometry, regression analysis, physics, engineering, metrology, programming languages, and the law. They use equipment, such as total stations, robotic total stations, theodolites, GNSS receivers, retroreflectors, 3D scanners, LiDAR sensors, radios, inclinometer, handheld tablets, optical and digital levels, subsurface locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Island Survey
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, as well as certain large, entirely landlocked, saltwater lakes, such as the Caspian Sea. The sea moderates Earth's climate and has important roles in the water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles. Humans harnessing and studying the sea have been recorded since ancient times, and evidenced well into prehistory, while its modern scientific study is called oceanography. The most abundant solid dissolved in seawater is sodium chloride. The water also contains salts of magnesium, calcium, potassium, and mercury, amongst many other elements, some in minute concentrations. Salinity varies widely, being lower near the surface and the mouths of large rivers and higher in the depths of the ocean; however, the relative proportions of dissolved salts va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmagupta
Brahmagupta ( – ) was an Indian mathematician and astronomer. He is the author of two early works on mathematics and astronomy: the '' Brāhmasphuṭasiddhānta'' (BSS, "correctly established doctrine of Brahma", dated 628), a theoretical treatise, and the '' Khaṇḍakhādyaka'' ("edible bite", dated 665), a more practical text. Brahmagupta was the first to give rules for computing with '' zero''. The texts composed by Brahmagupta were in elliptic verse in Sanskrit, as was common practice in Indian mathematics. As no proofs are given, it is not known how Brahmagupta's results were derived. In 628 CE, Brahmagupta first described gravity as an attractive force, and used the term "gurutvākarṣaṇam (गुरुत्वाकर्षणम्)" in Sanskrit to describe it. Life and career Brahmagupta was born in 598 CE according to his own statement. He lived in ''Bhillamāla'' in Gurjaradesa (modern Bhinmal in Rajasthan, India) during the reign of the Chavda dynasty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Chunfeng
Li Chunfeng (; 602–670) was a Chinese mathematician, astronomer, historian, and politician who was born in today's Baoji, Shaanxi, during the Sui and Tang dynasties. He was first appointed to the Imperial Astronomy Bureau to help institute a calendar reform. He eventually ascended to deputy of the Imperial Astronomy Bureau and designed the Linde calendar. His father was an educated state official and also a Taoist. Li died in Chang'an in 670. Background and career The Sui dynasty was integral for uniting China, so it was a good time for learning. But when Li was sixteen the Sui fell, and the Tang rose. Nevertheless, the Tang did not harm the conditions for education. Indeed, it rather strengthened it. The Imperial Academy's math teaching was formalized. He was appointed into the Imperial Astronomy Bureau as an advanced court astronomer and historian, in 627. Once several years had passed, he then was promoted to deputy director of the Imperial Astronomy Bureau in 641, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devastating An Lushan Rebellion (755–763) shook the nation and led to the decline of central authority in the dynasty' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zu Gengzhi
Zu Geng or Zu Gengzhi (; ca. 480 – ca. 525) was a Chinese mathematician, politician, and writer. His courtesy name was Jingshuo (). He was the son of the famous mathematician Zu Chongzhi. He is known principally for deriving and proving the formula for the volume of a sphere. He additionally measured the angular distance between Polaris and the celestial north pole The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where Earth's rotation around a fixed axis, axis of rotation, indefinitely extended, intersects the celestial sphere. The north and south celestial poles appear permanently dire .... See also * List of Chinese mathematicians References External links * 480 births 525 deaths 5th-century Chinese mathematicians 6th-century Chinese writers 6th-century Chinese mathematicians Ancient Chinese mathematicians Liang dynasty politicians Southern Qi politicians {{Asia-mathematician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zu Chongzhi
Zu Chongzhi (; 429–500 AD), courtesy name Wenyuan (), was a Chinese astronomer, mathematician, politician, inventor, and writer during the Liu Song and Southern Qi dynasties. He was most notable for calculating pi as between 3.1415926 and 3.1415927, a record in accuracy which would not be surpassed for over 800 years. Life and works Chongzhi's ancestry was from modern Baoding, Hebei. To flee from the ravages of war, Zu's grandfather Zu Chang moved to the Yangtze, as part of the massive population movement during the Eastern Jin. Zu Chang () at one point held the position of Chief Minister for the Palace Buildings () within the Liu Song and was in charge of government construction projects. Zu's father, Zu Shuozhi (), also served the court and was greatly respected for his erudition. Zu was born in Jiankang. His family had historically been involved in astronomical research, and from childhood Zu was exposed to both astronomy and mathematics. When he was only a youth his t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_crop.jpg)


